We will talk about one of the most confusing values in JavaScript:
NaN. You will learn what it means, why it happens, and how we can deal with it.
Handling NaN in JavaScript – What is NaN?
N stands for
Not a Number. It is a special value that JavaScript returns when a mathematical operation fails. It is basically a value used to denote a failure.
Even though it reads as Not a Number, its type is actually a number in JavaScript.
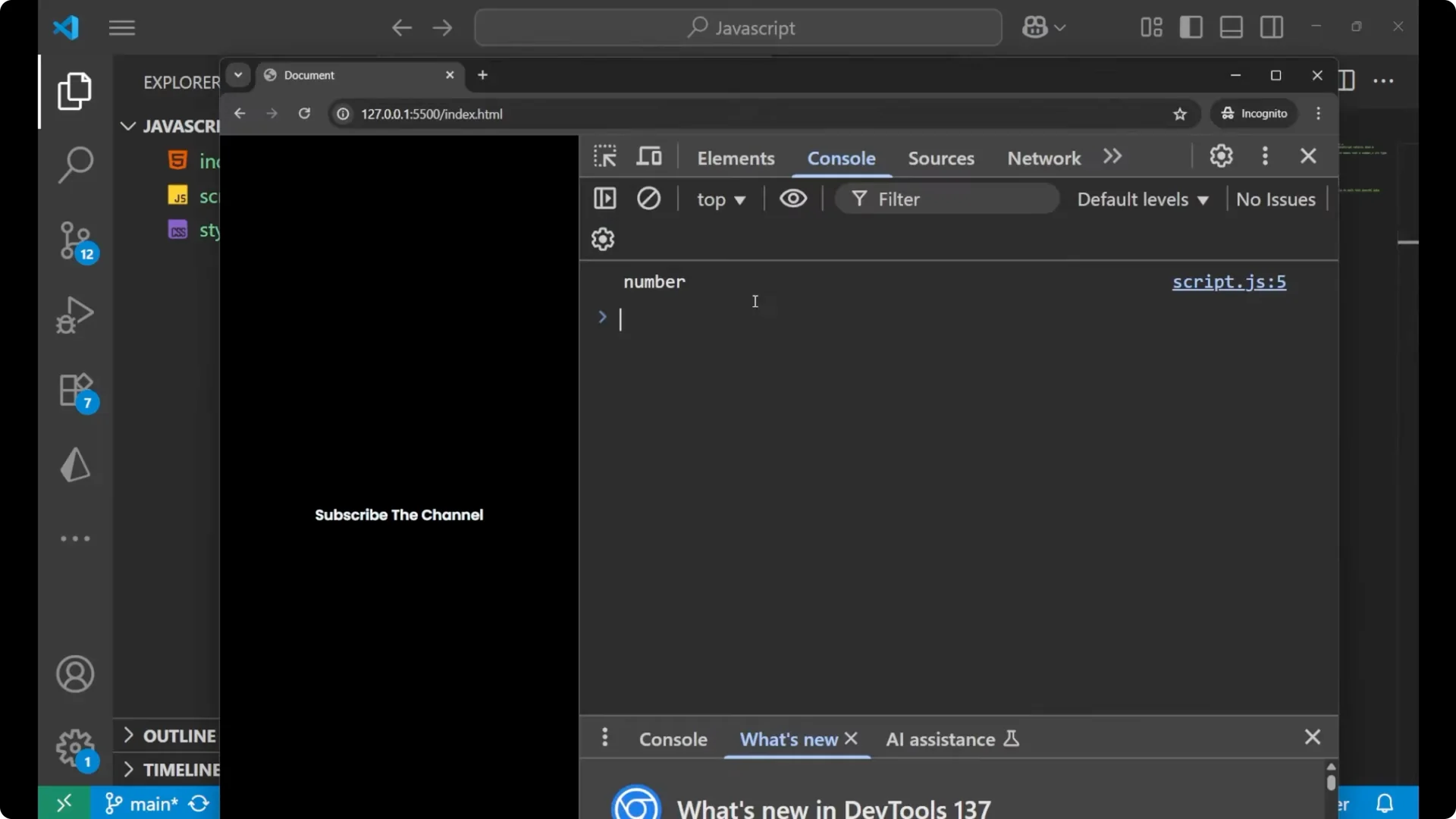
console.log(typeof NaN); // 'number'
Handling NaN in JavaScript – When you get it
You get
NaN whenever a mathematical operation fails.
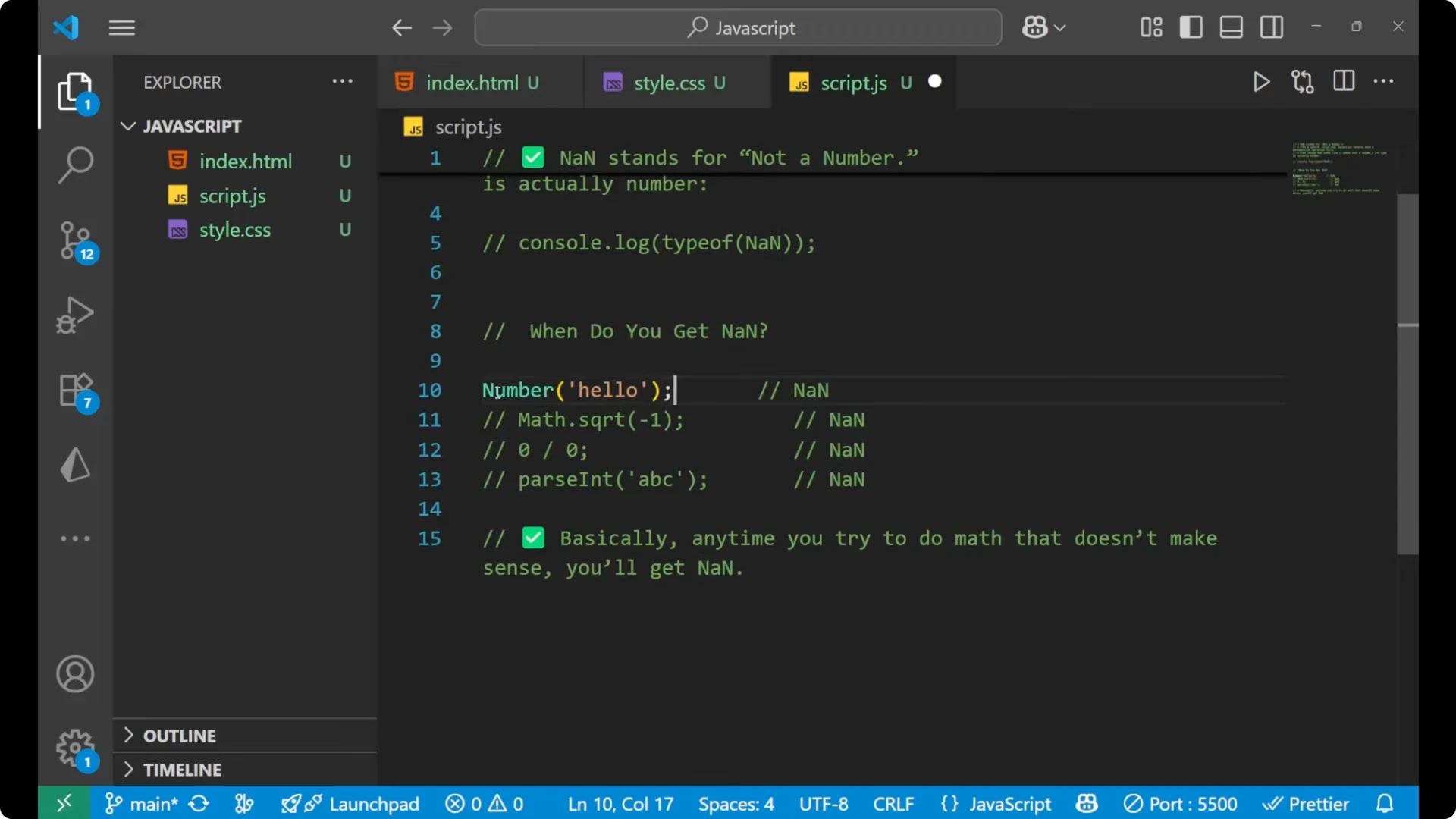
Converting a non-numeric string to a number results in
NaN.
console.log(Number('hello')); // NaN
Square root of a negative number results in
NaN.
console.log(Math.sqrt(-1)); // NaN
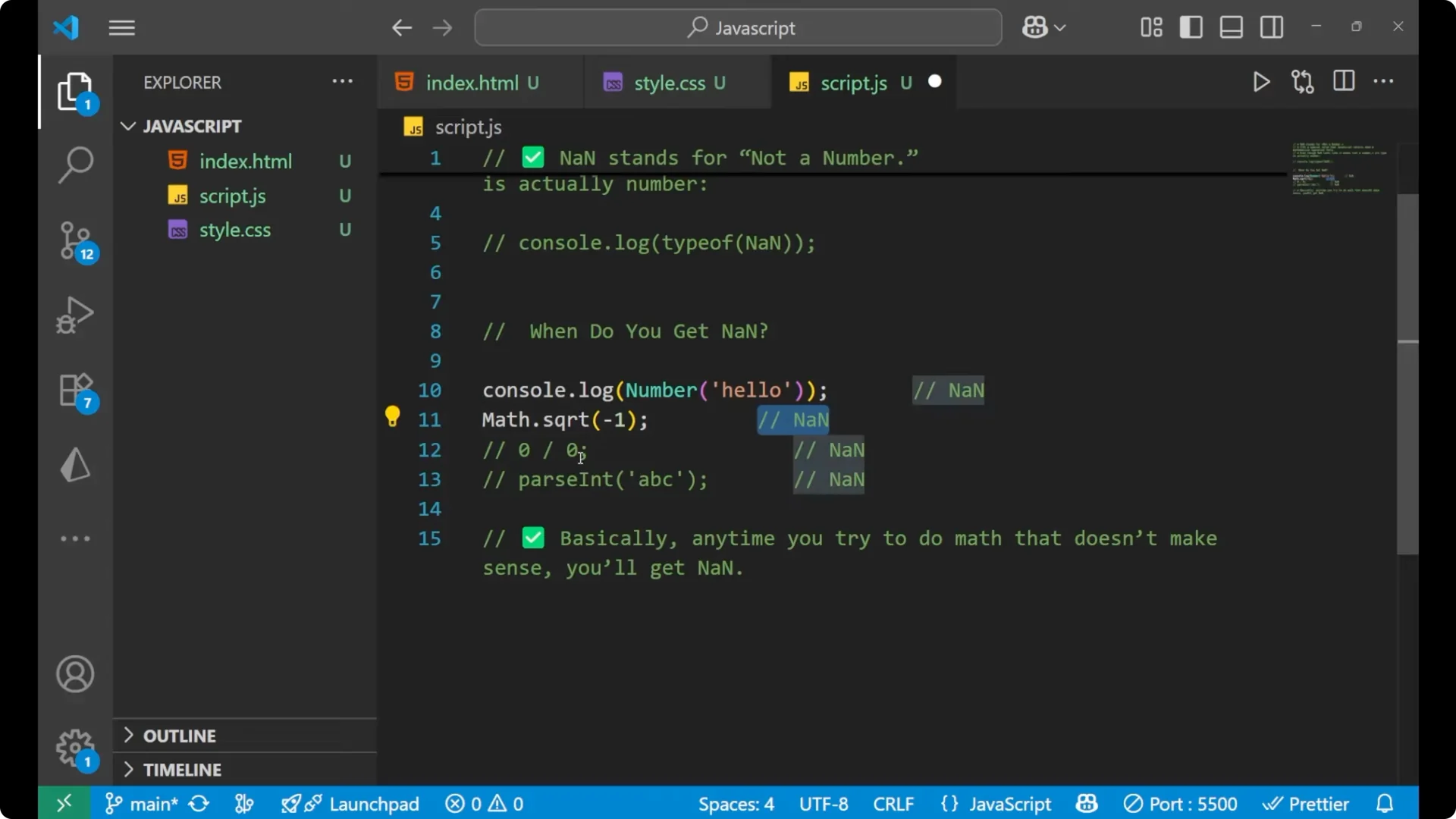
Division of 0 by 0 results in
NaN.
console.log(0 / 0); // NaN
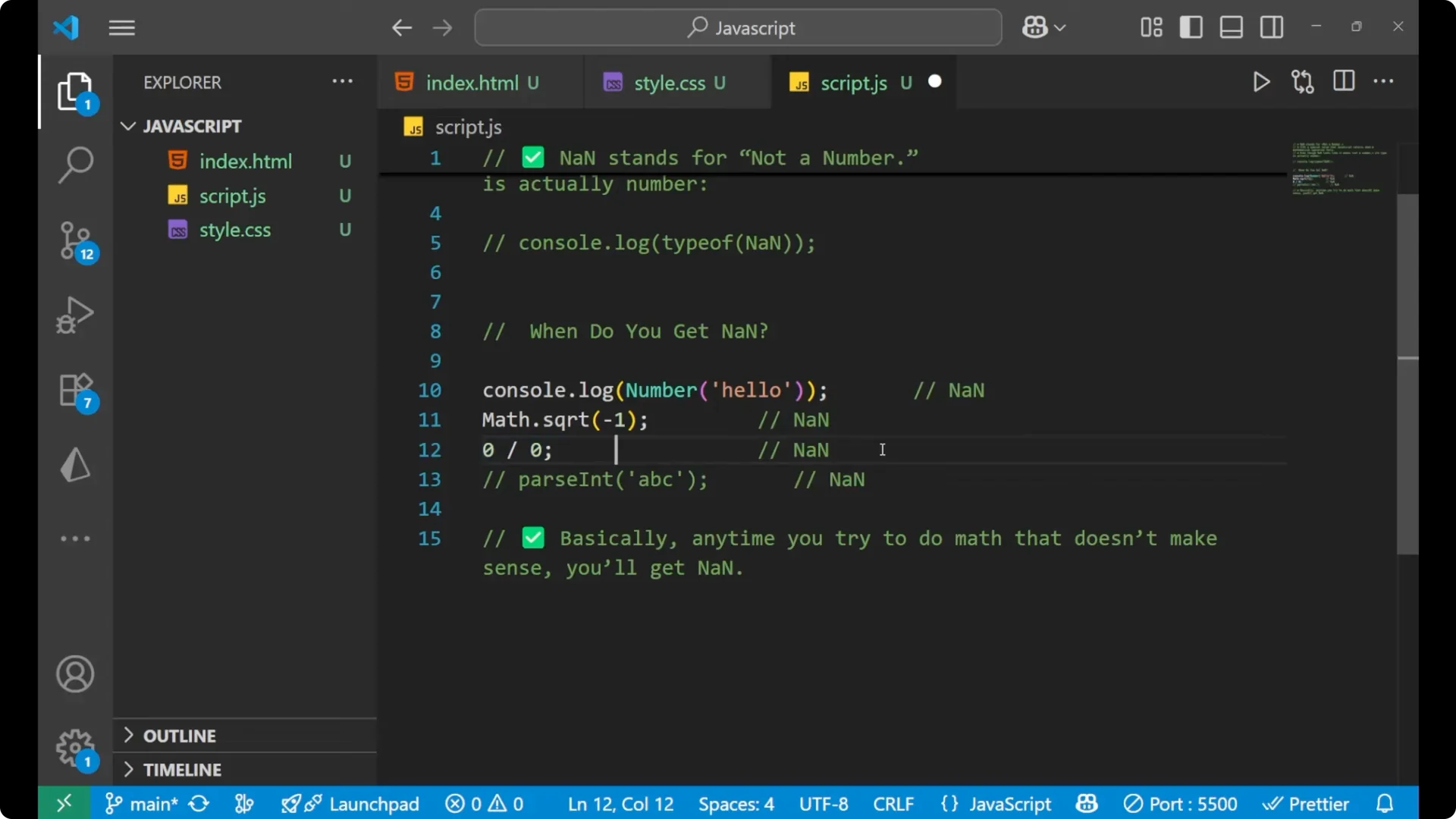
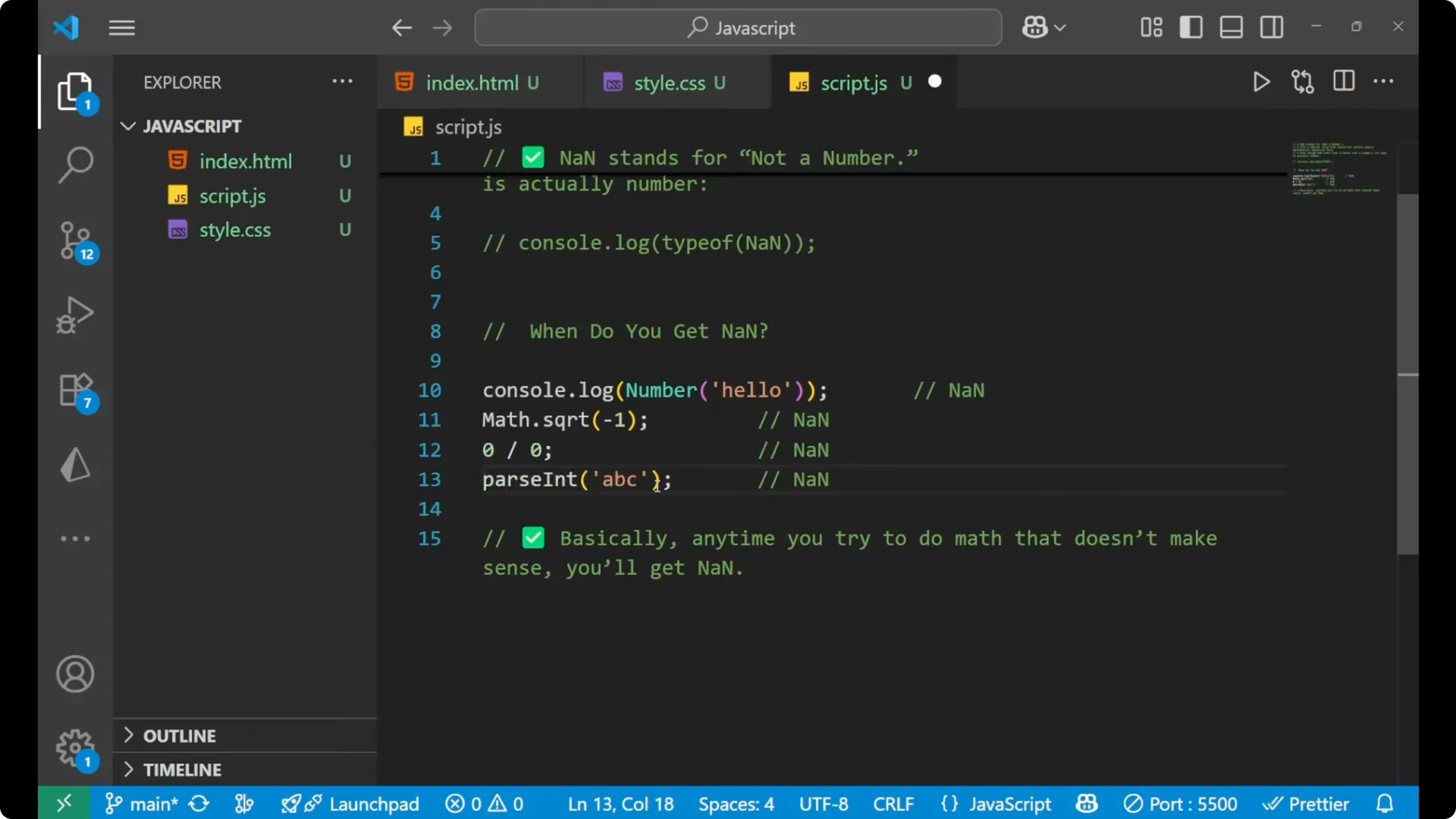
Parsing an integer from a non-numeric string results in
NaN.
console.log(parseInt('hello')); // NaN
Any time you try to do math that does not make sense, you will get
NaN.
Handling NaN in JavaScript – The surprise
 NaN is not equal to NaN
NaN is not equal to NaN.
console.log(NaN === NaN); // false
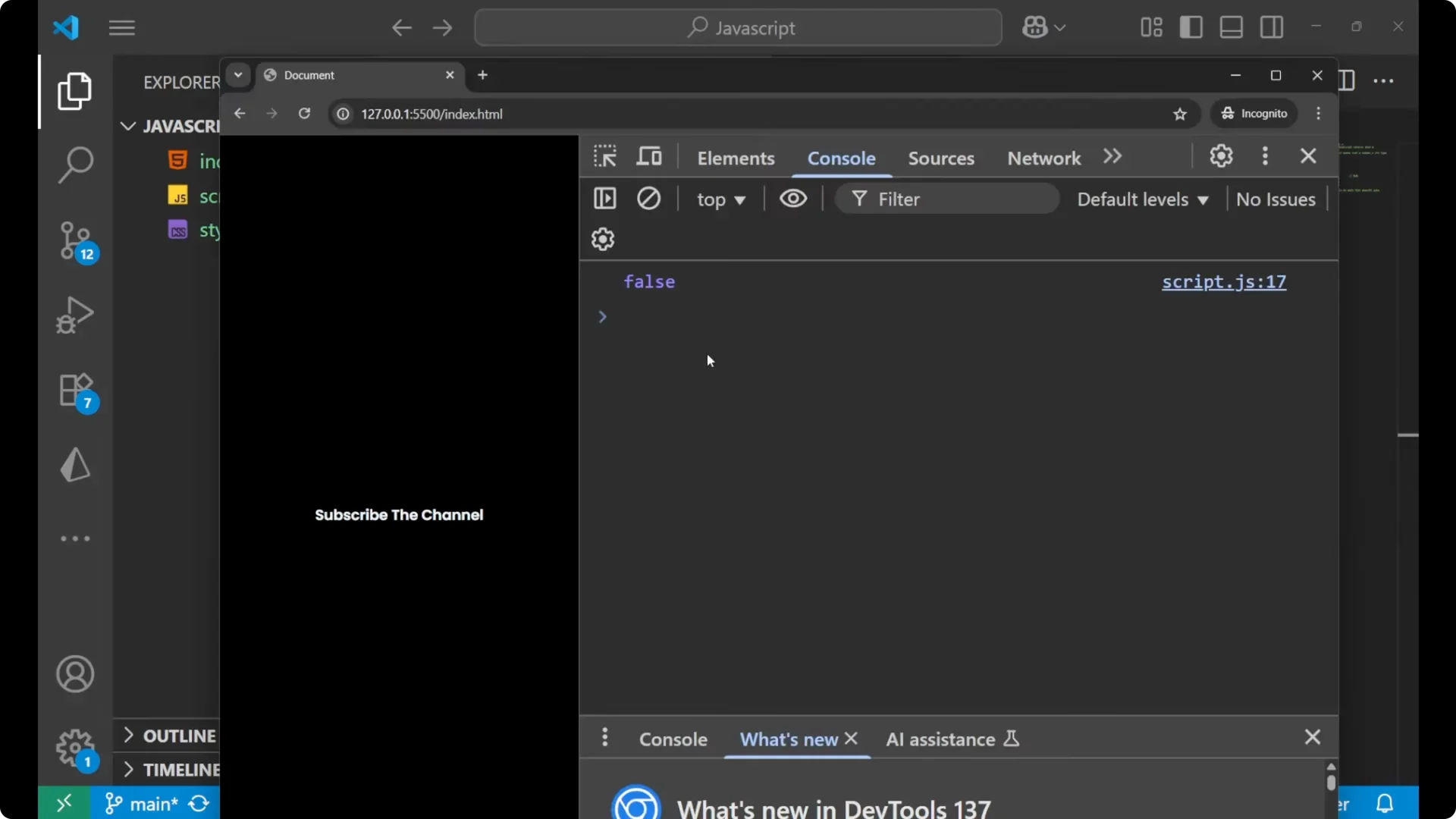
This is one of the most important things asked in interviews. Since
NaN !== NaN, you need special ways to check for
NaN.
Handling NaN in JavaScript – How to check for it
isNaN
`isNaN` is used to check if a value is
NaN. If it is, it returns `true`, otherwise it returns `false`.
console.log(isNaN('hello')); // true
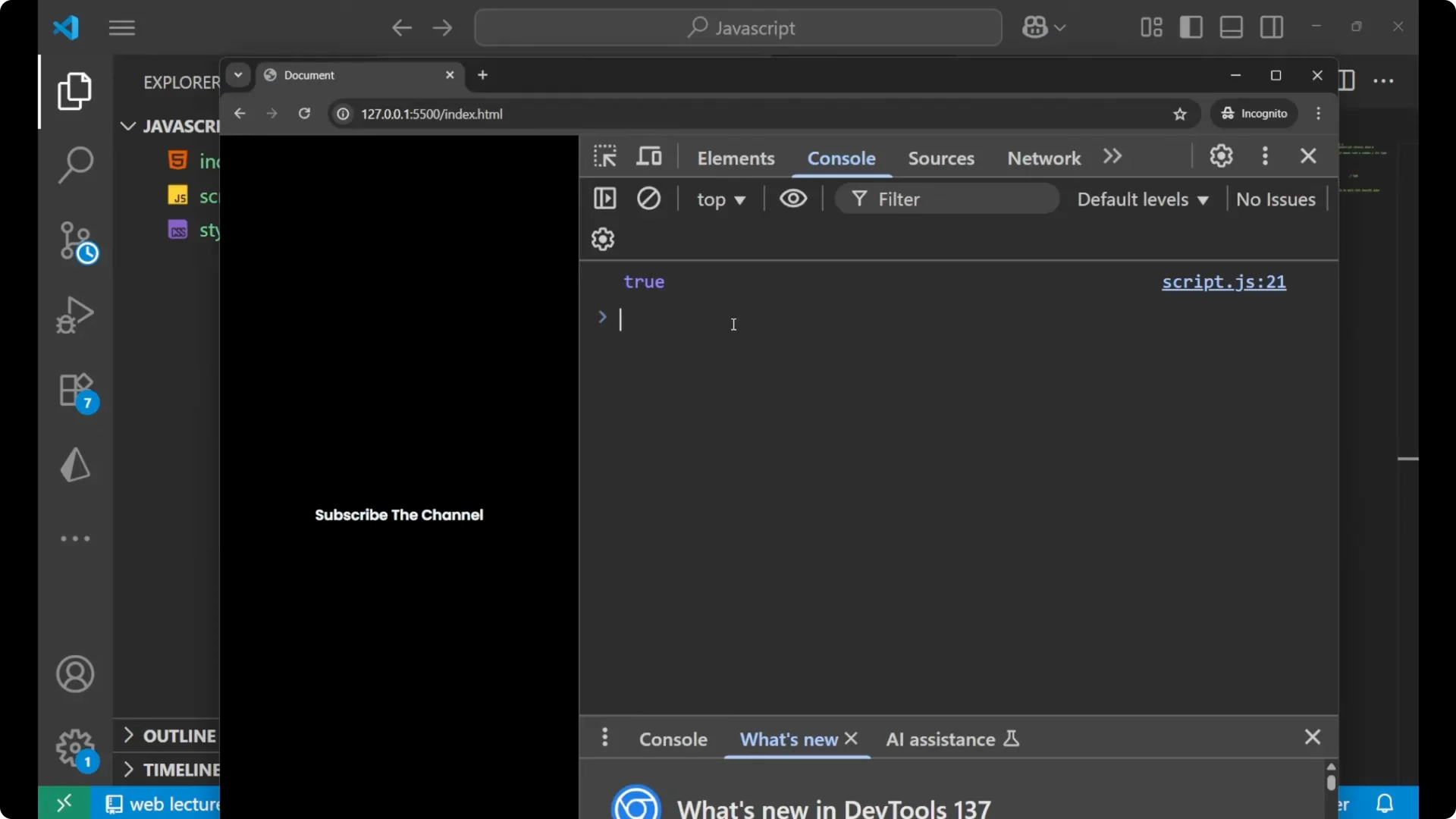
This returns `true` because the string gets coerced to a number and that failed.
Number.isNaN
`Number.isNaN` is a stricter method that we normally use for checking.
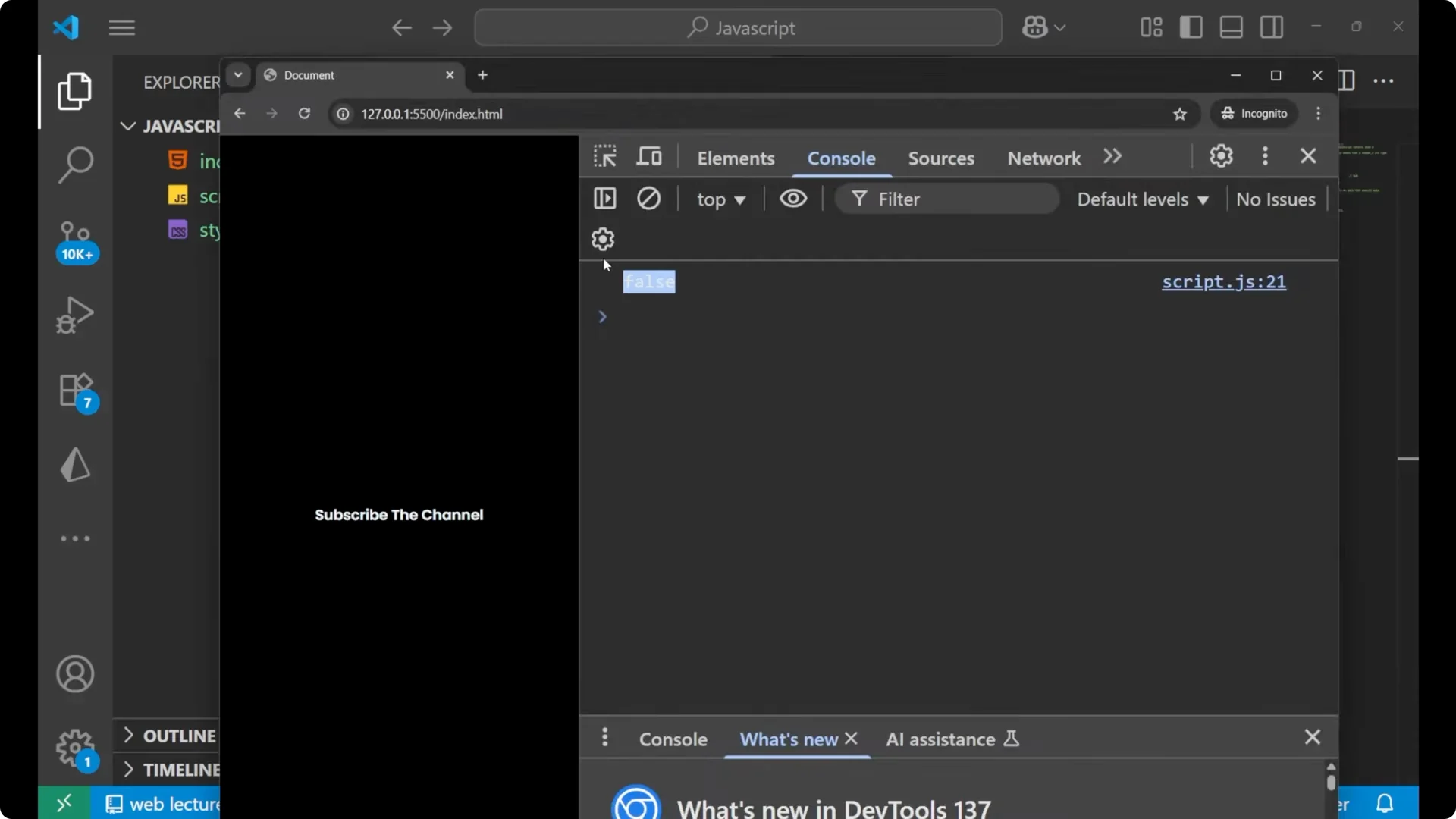
console.log(Number.isNaN('hello')); // false
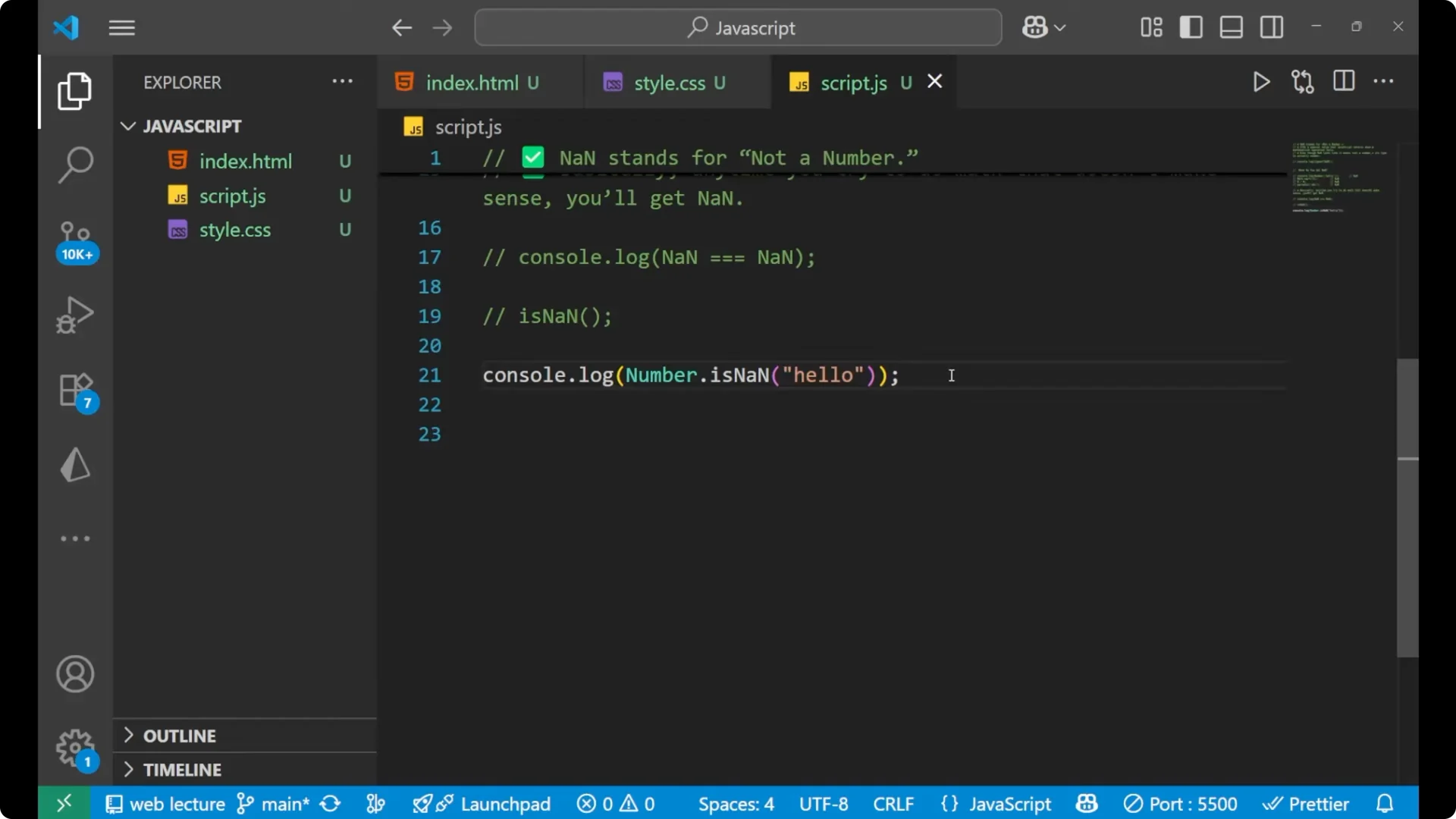
`Number.isNaN` does not coerce the value, so plain strings like `’hello’` return `false`.
Handling NaN in JavaScript – Simple handling pattern
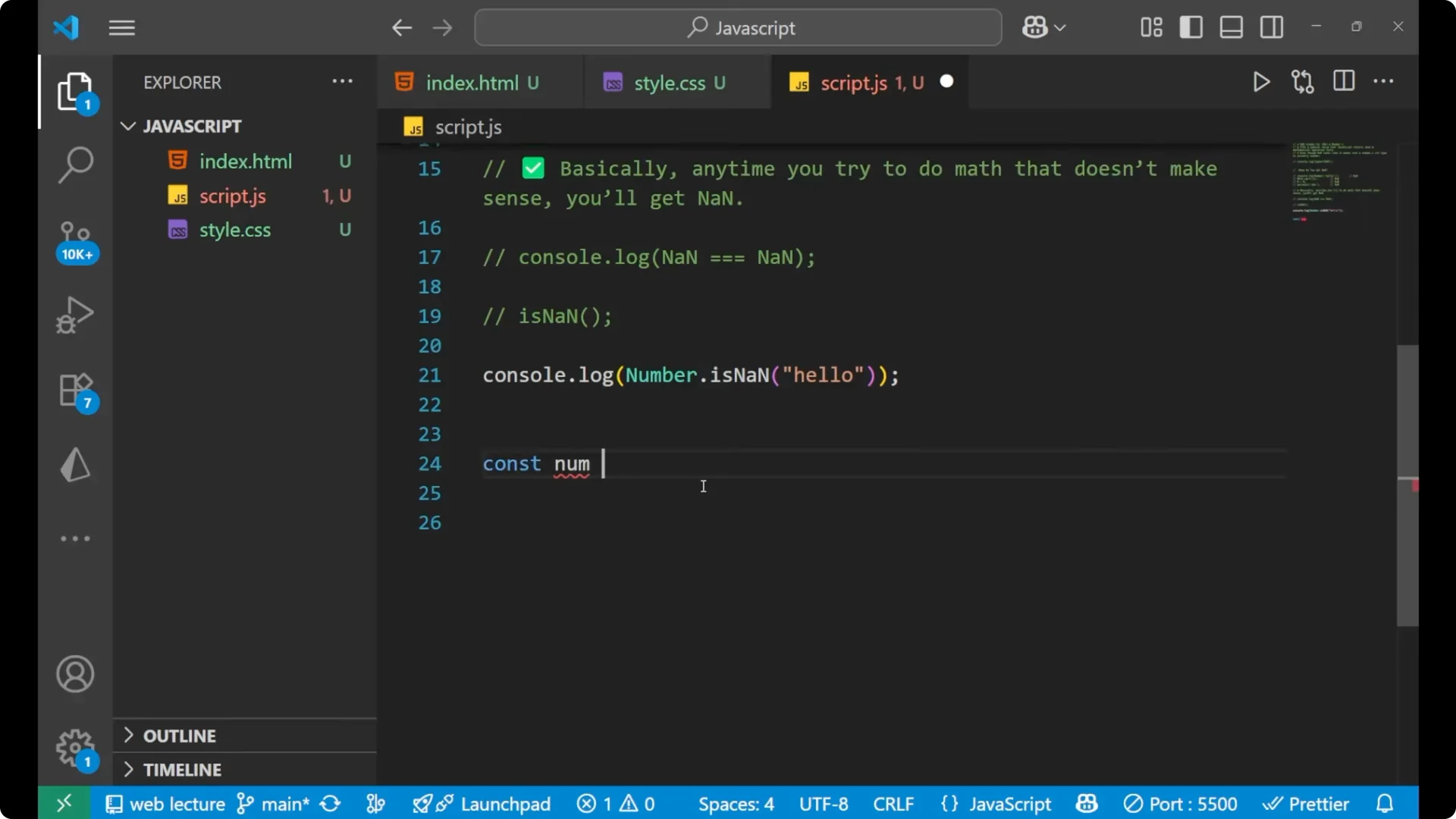
Create a number from input.
const num = parseInt('hello');
Check using `Number.isNaN` and handle the case.
if (Number.isNaN(num)) {
console.log('Oops. Invalid number.');
}
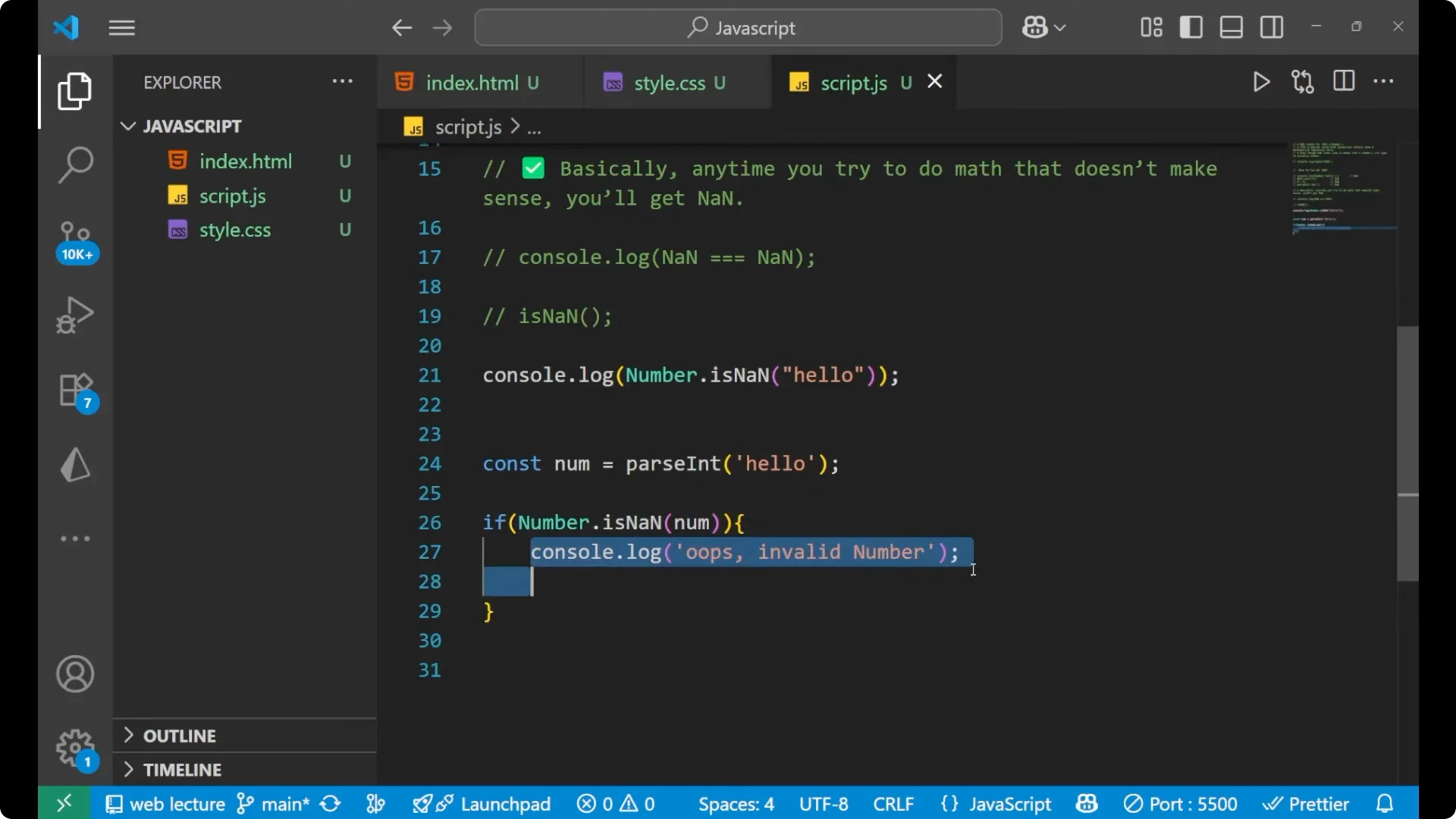
This prints
Oops. Invalid number. because parsing the given string resulted in
NaN, the condition evaluated to `true`, and the message was printed.
You can also use a ternary operator or other defaulting logic while dealing with
NaN values.
Final Thoughts
NaN stands for
Not a Number, but its type is still a number. You see it when math fails, like converting non-numeric strings, `Math.sqrt(-1)`, `0 / 0`, or `parseInt(‘hello’)`. Remember that
NaN !== NaN, so use `isNaN` for loose checks and prefer `Number.isNaN` for strict checks. When parsing or computing, guard with `Number.isNaN` and handle invalid cases clearly.
 N stands for Not a Number. It is a special value that JavaScript returns when a mathematical operation fails. It is basically a value used to denote a failure.
Even though it reads as Not a Number, its type is actually a number in JavaScript.
N stands for Not a Number. It is a special value that JavaScript returns when a mathematical operation fails. It is basically a value used to denote a failure.
Even though it reads as Not a Number, its type is actually a number in JavaScript.

 You get NaN whenever a mathematical operation fails.
Converting a non-numeric string to a number results in NaN.
You get NaN whenever a mathematical operation fails.
Converting a non-numeric string to a number results in NaN.
 Square root of a negative number results in NaN.
Square root of a negative number results in NaN.
 Division of 0 by 0 results in NaN.
Division of 0 by 0 results in NaN.
 Parsing an integer from a non-numeric string results in NaN.
Parsing an integer from a non-numeric string results in NaN.
 Any time you try to do math that does not make sense, you will get NaN.
Any time you try to do math that does not make sense, you will get NaN.
 NaN is not equal to NaN.
NaN is not equal to NaN.
 This is one of the most important things asked in interviews. Since NaN !== NaN, you need special ways to check for NaN.
This is one of the most important things asked in interviews. Since NaN !== NaN, you need special ways to check for NaN.

 This returns `true` because the string gets coerced to a number and that failed.
This returns `true` because the string gets coerced to a number and that failed.
 `Number.isNaN` does not coerce the value, so plain strings like `’hello’` return `false`.
`Number.isNaN` does not coerce the value, so plain strings like `’hello’` return `false`.
 Create a number from input.
Create a number from input.
 Check using `Number.isNaN` and handle the case.
Check using `Number.isNaN` and handle the case.
 This prints Oops. Invalid number. because parsing the given string resulted in NaN, the condition evaluated to `true`, and the message was printed.
You can also use a ternary operator or other defaulting logic while dealing with NaN values.
This prints Oops. Invalid number. because parsing the given string resulted in NaN, the condition evaluated to `true`, and the message was printed.
You can also use a ternary operator or other defaulting logic while dealing with NaN values.
