We will learn how to create a shallow copy of an object in JavaScript. A basic but powerful technique every developer should know.
A
JavaScript shallow copy copies only the first level of properties in an object.
Nested objects or arrays are not cloned – they are still referenced from the original. This is useful when you are okay about sharing nested data but want to duplicate top level properties.
Understanding JavaScript Shallow Copy
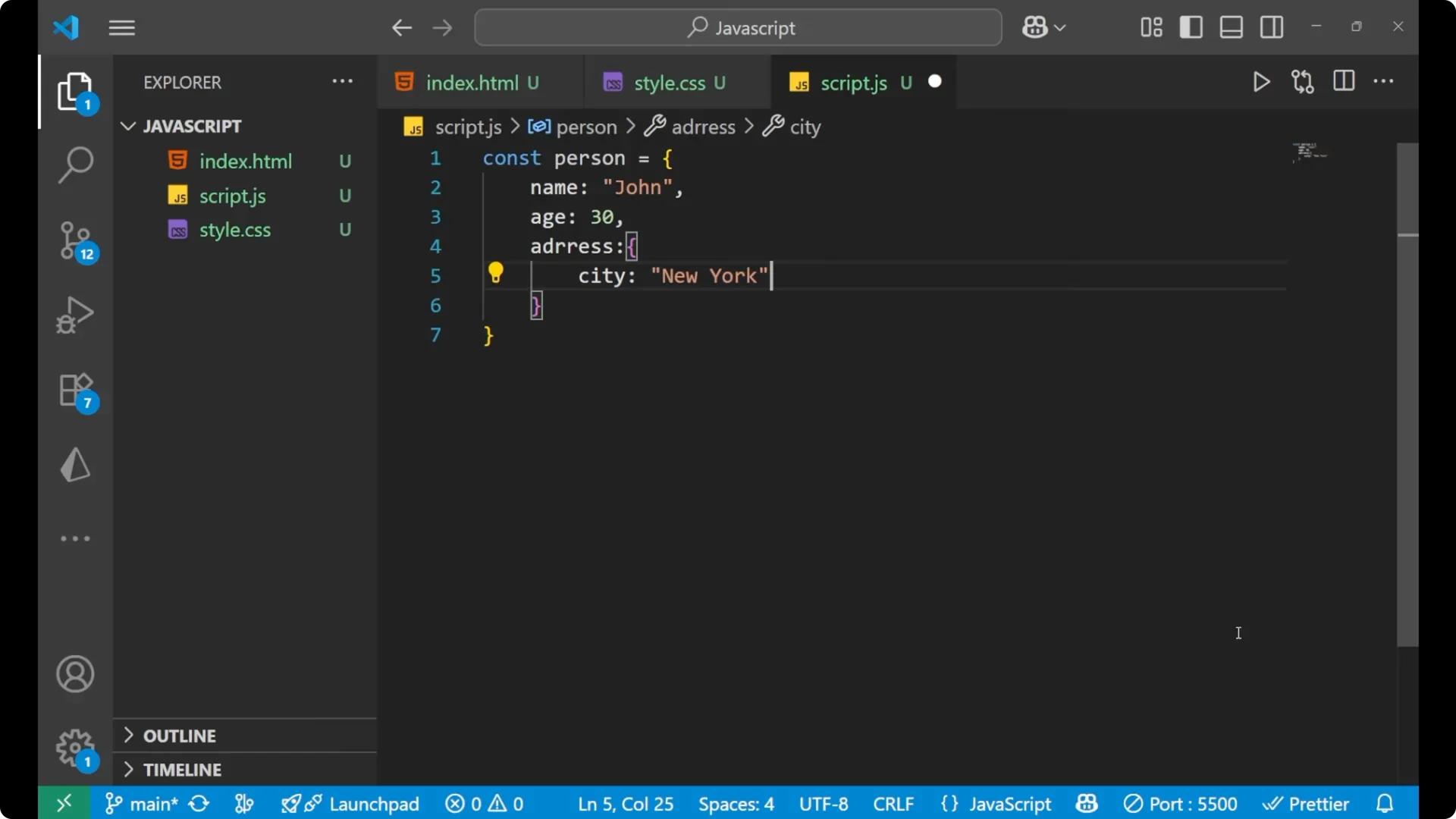
I will start with an example object that contains a nested object so we can see the effect of a shallow copy clearly.
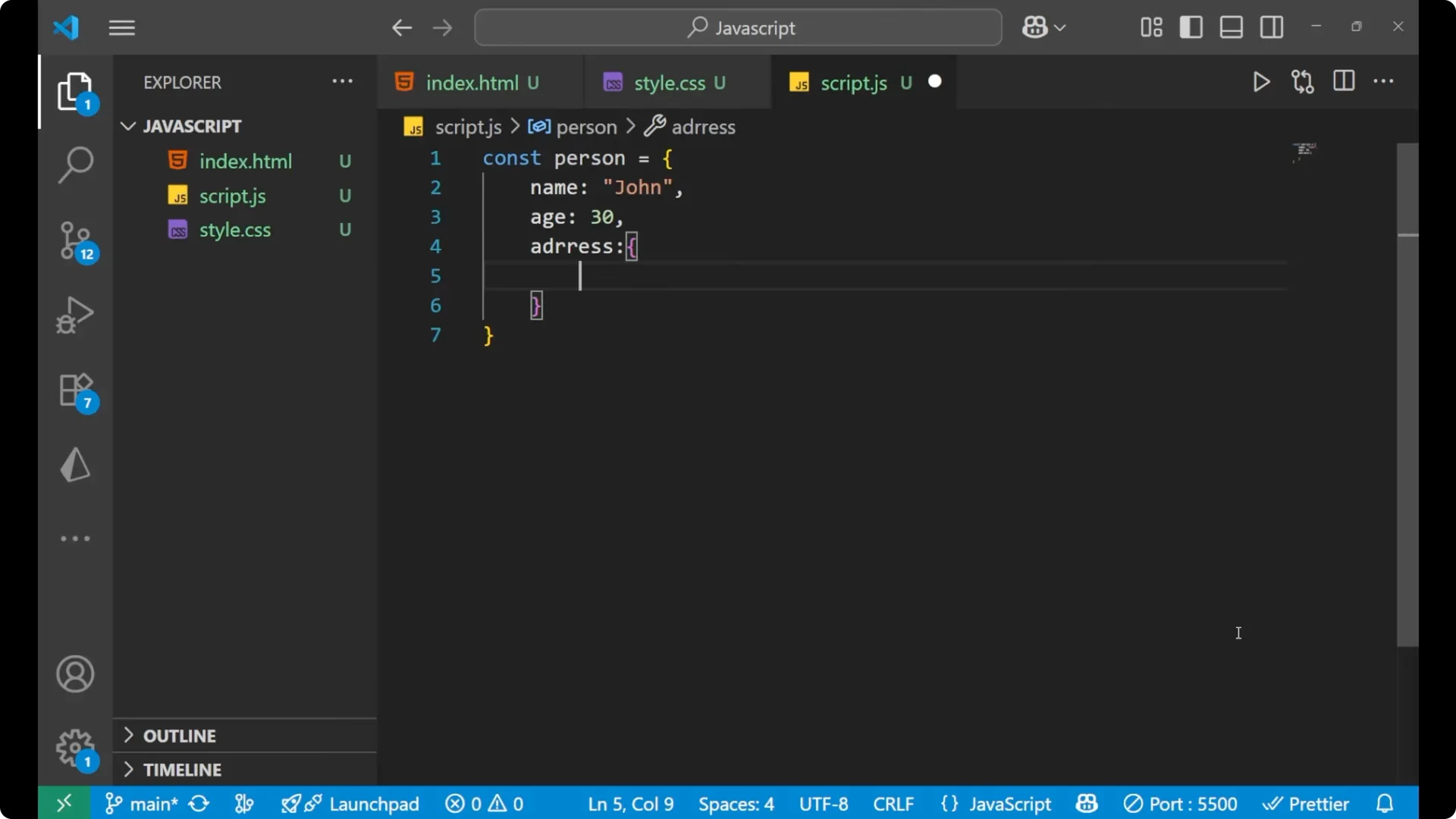
const person = {
name: 'John',
age: 30,
address: {
city: 'New York'
}
};
Create a JavaScript Shallow Copy with the Spread Operator
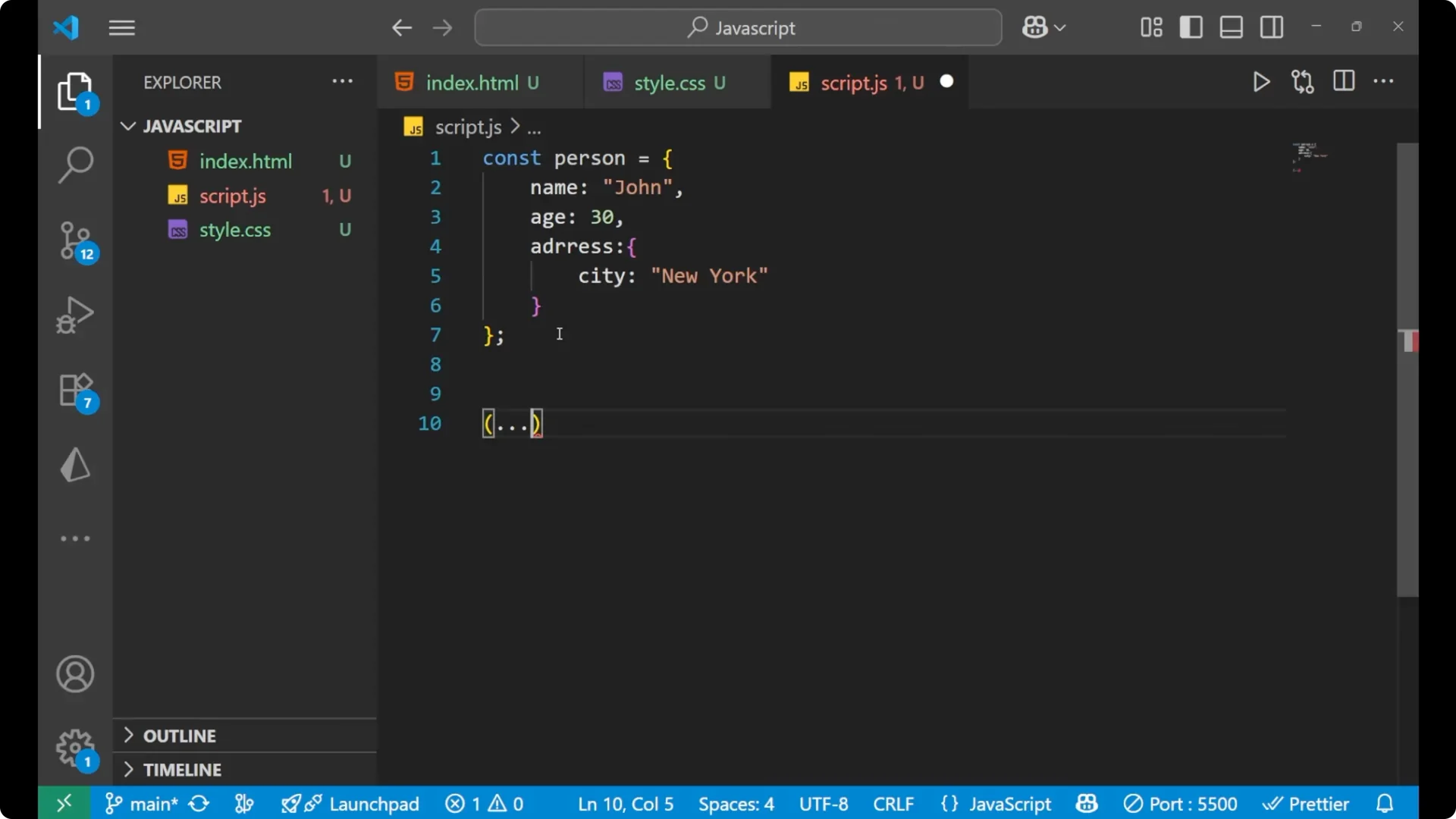
To perform a shallow clone, use the
spread operator. The spread operator is denoted by three dots.
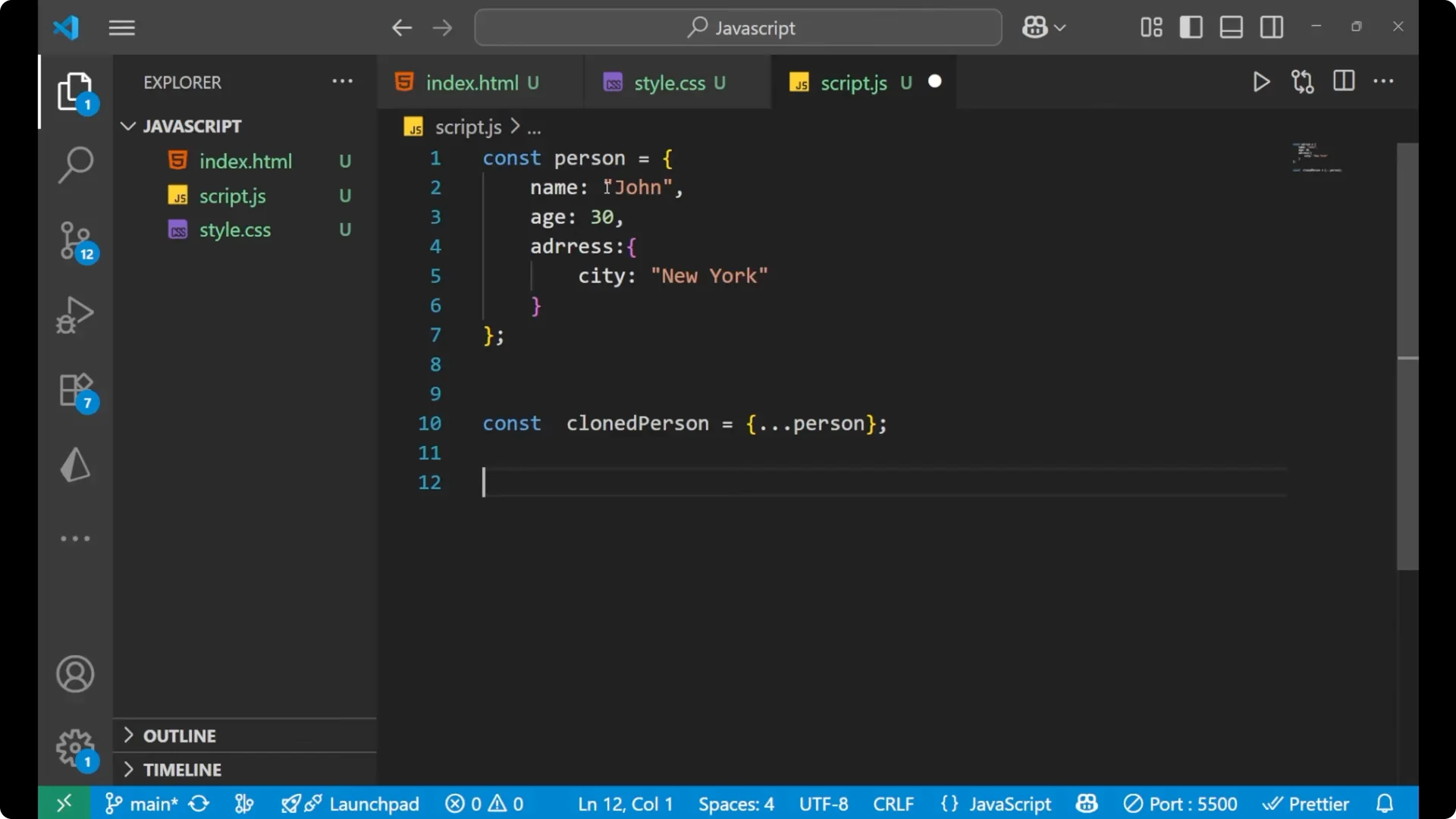
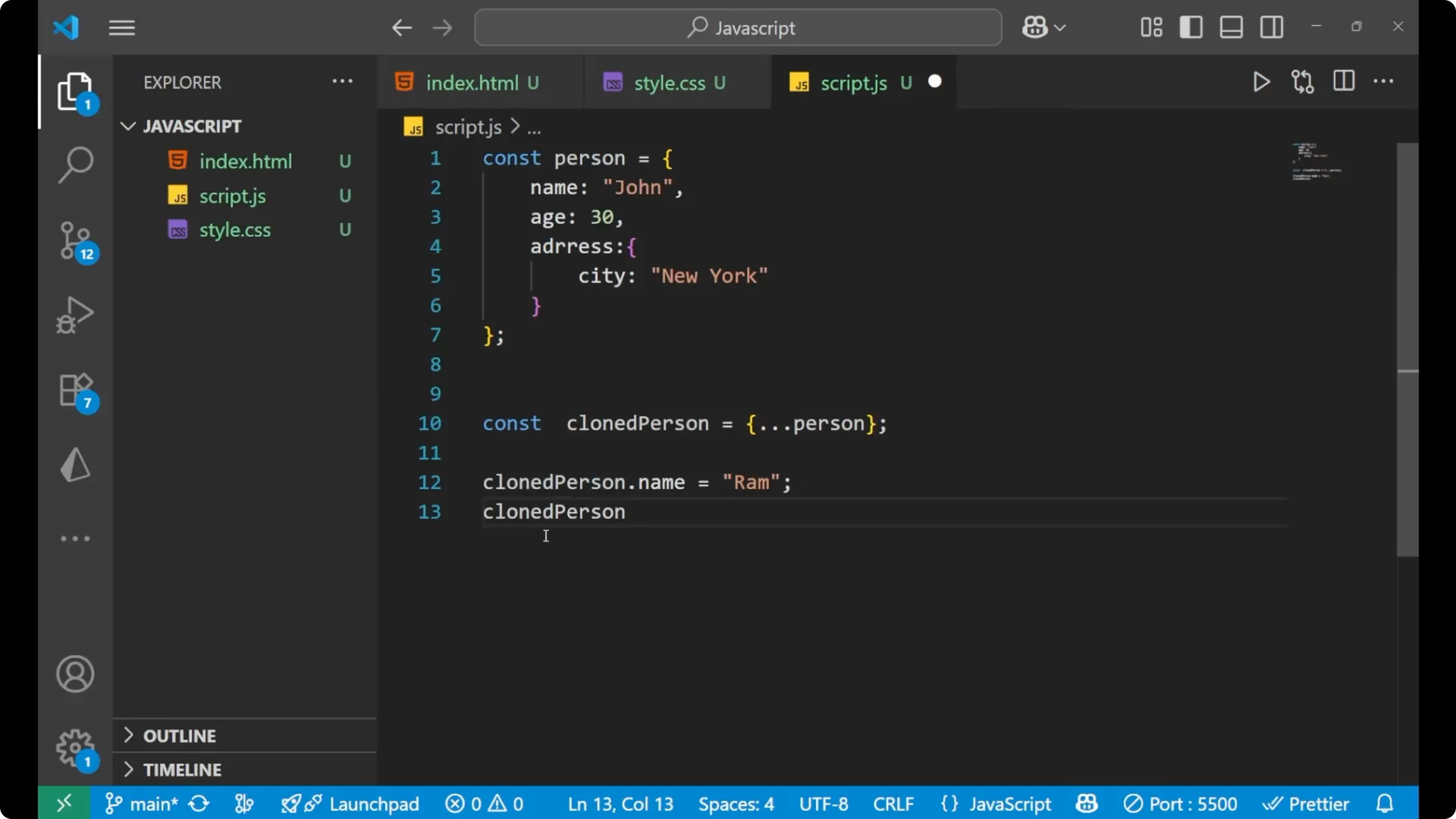
const clonedPerson = { ...person };
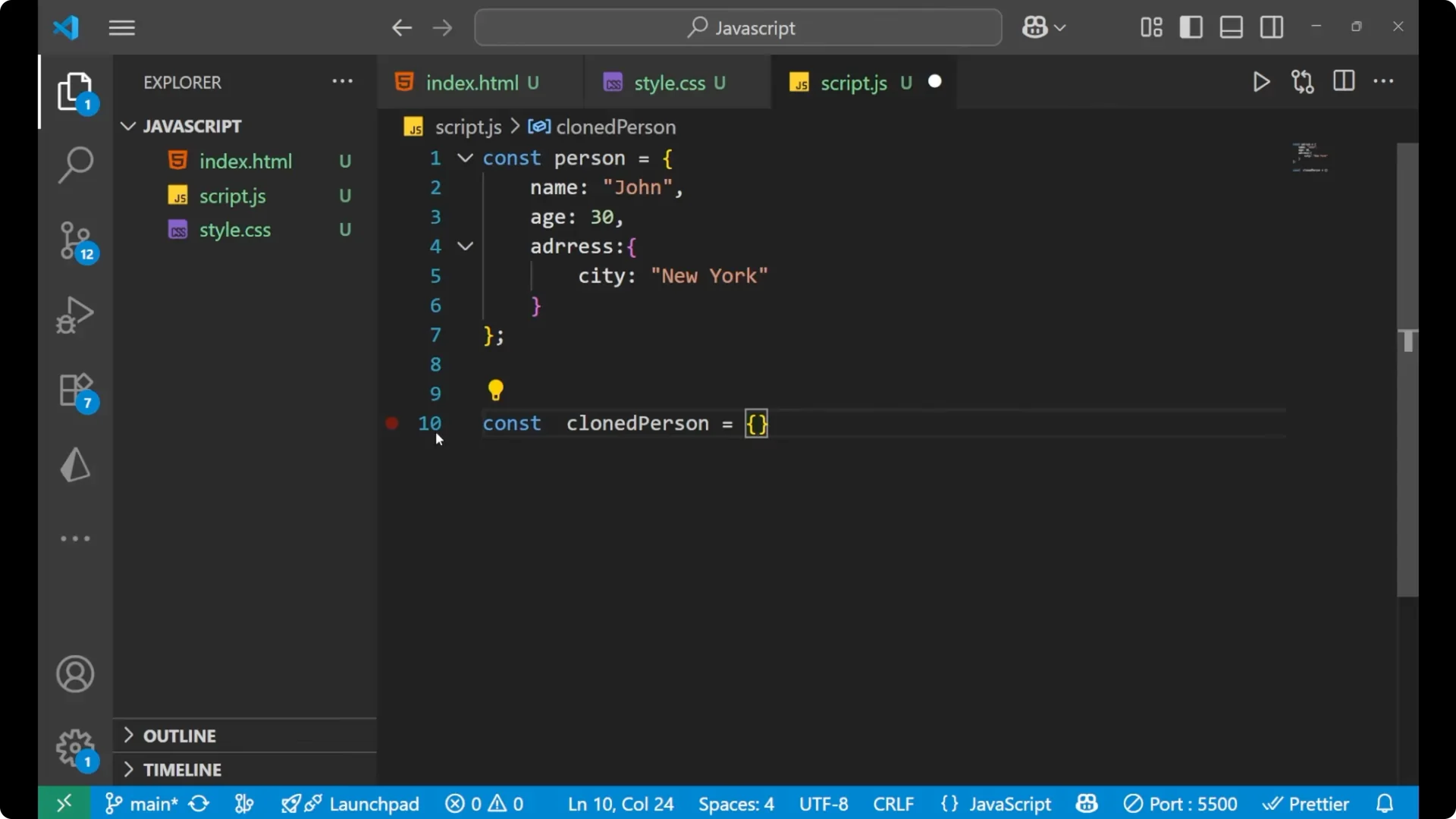
This creates a new object with the same top level properties as `person`. The nested `address` object is still the same reference in memory for both `person` and `clonedPerson`.
Step by step
Create the original object with a nested `address` so we can observe reference behavior.
Create a new object using `{ …person }` to make a shallow clone.
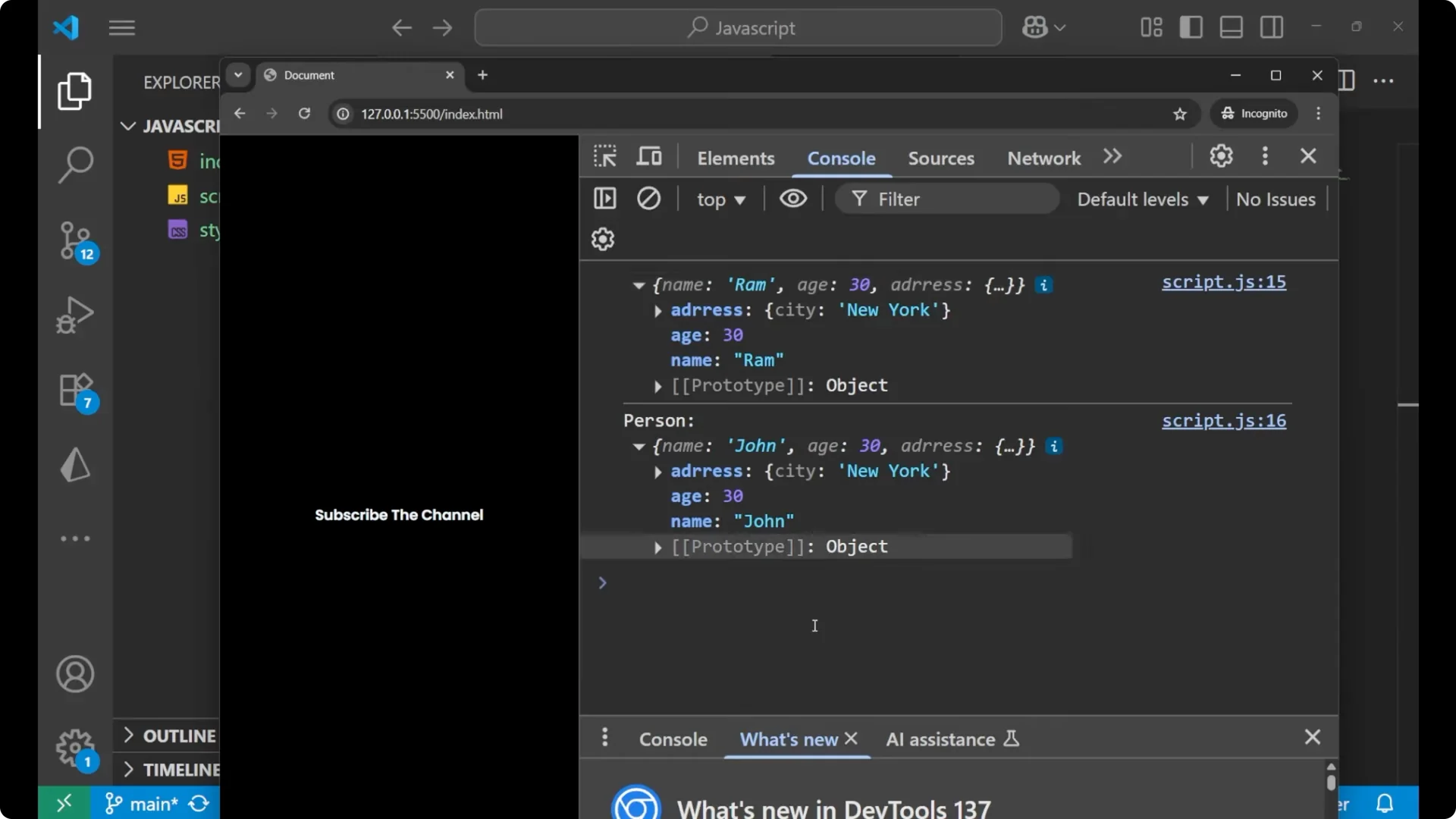
Change a top level property on the clone and verify it does not affect the original.
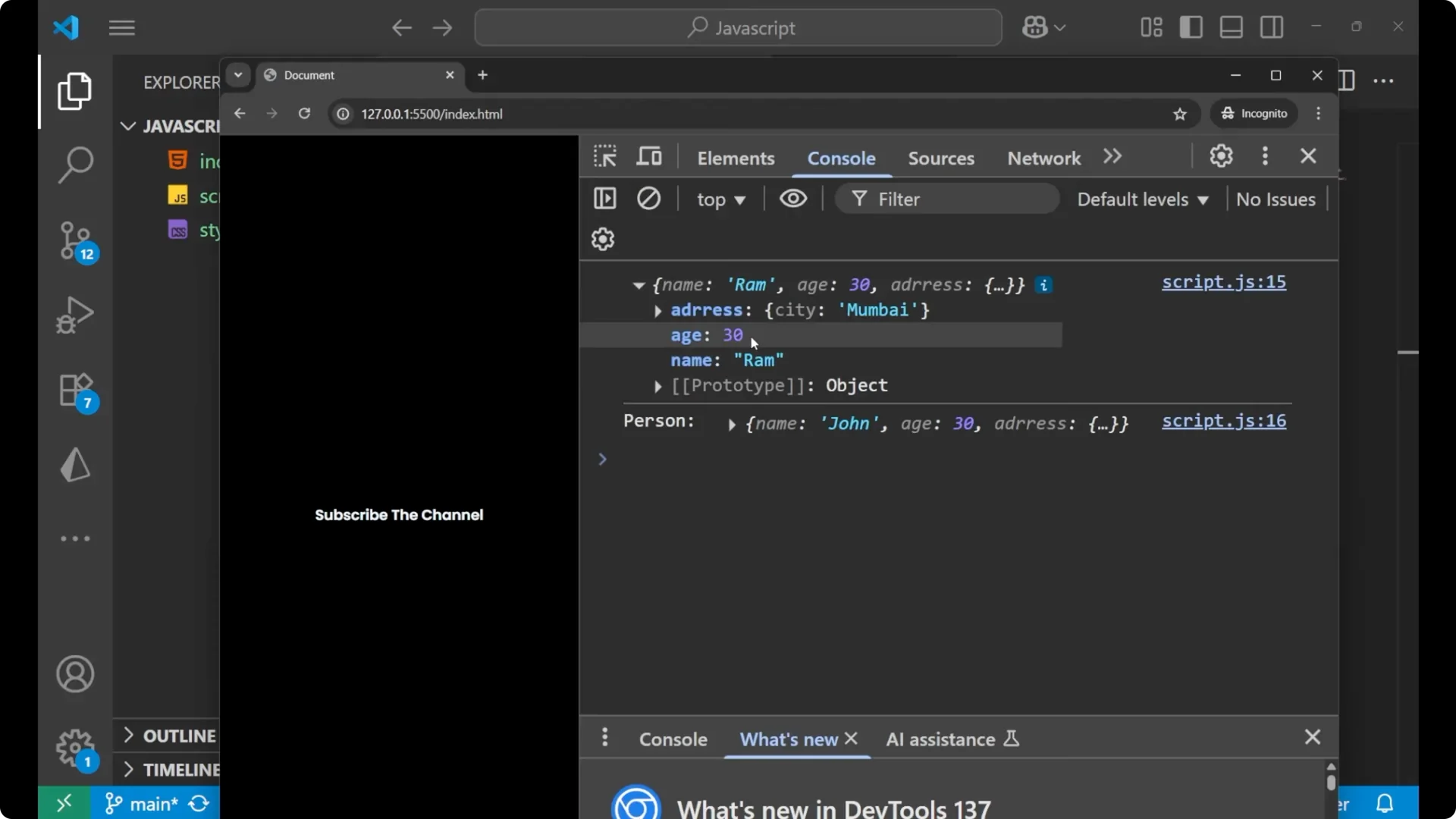
Change a nested property on the clone and observe that it also changes in the original.
Editing Top Level vs Nested Properties
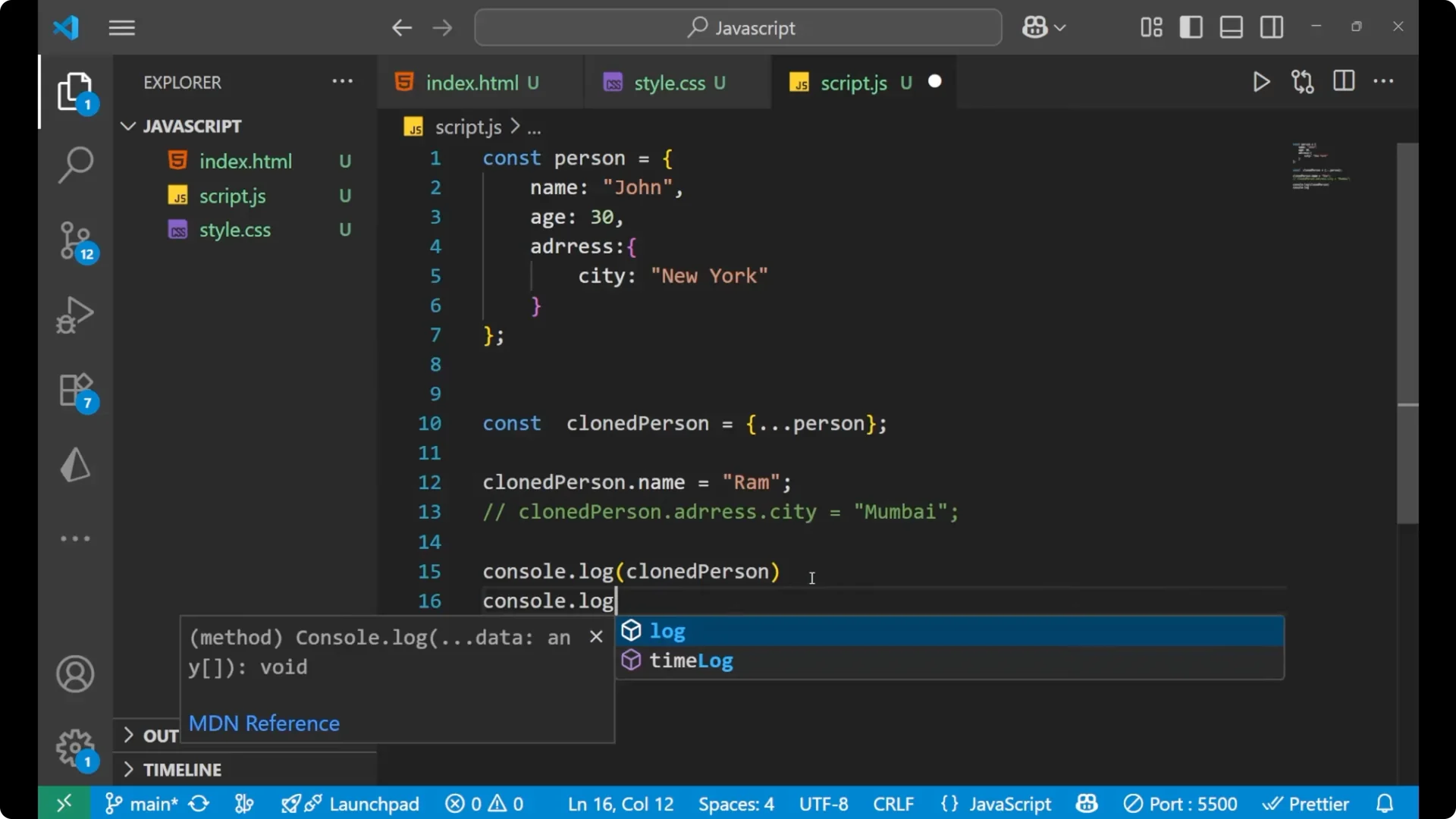
Top level change stays isolated
Changing a top level property like `name` on the cloned object does not affect the original object, because those primitive values are copied.
const person = {
name: 'John',
age: 30,
address: { city: 'New York' }
};
const clonedPerson = { ...person };
// Change top level property on the clone
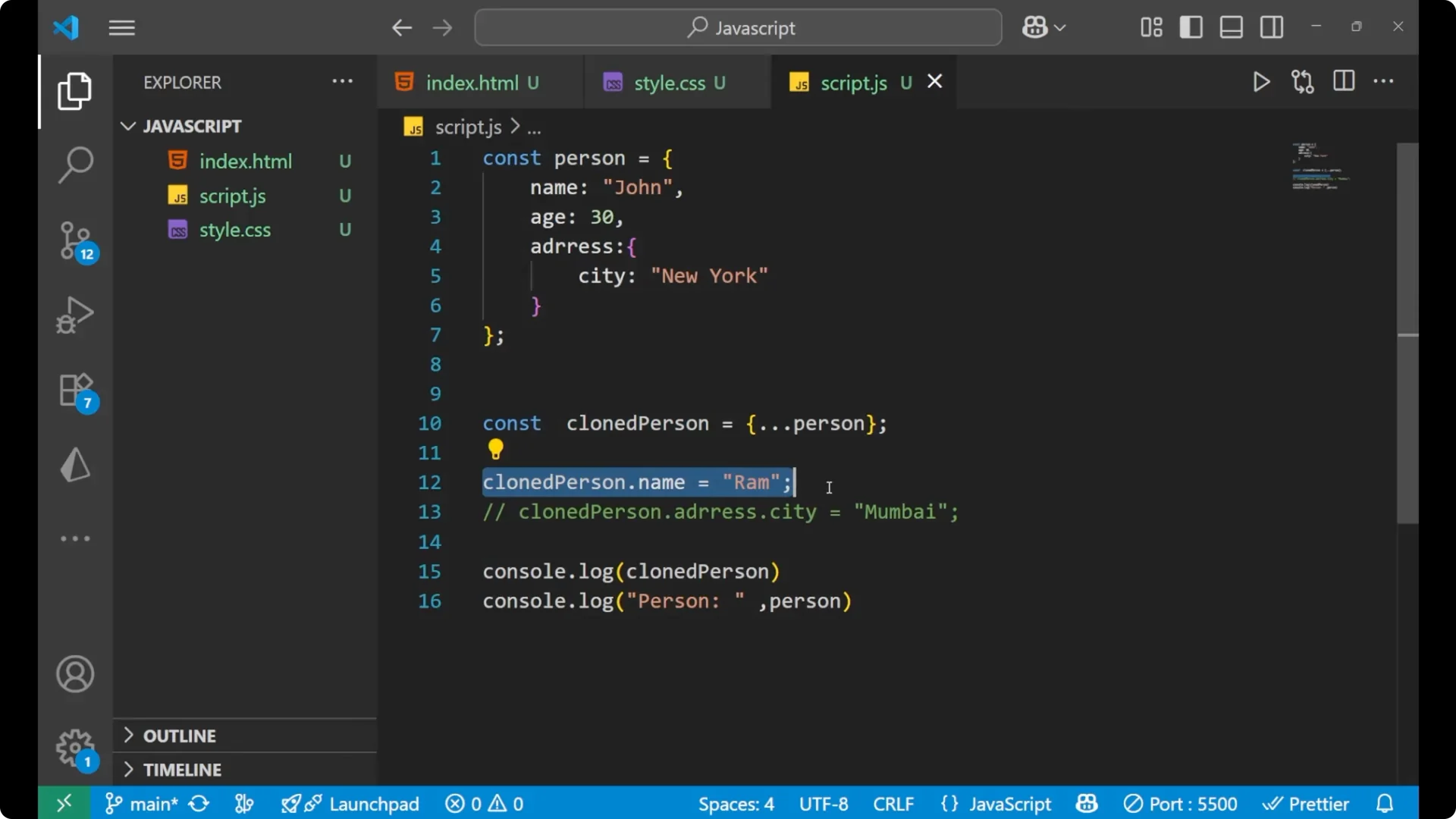
clonedPerson.name = 'Ram';
console.log(clonedPerson.name); // 'Ram'
console.log(person.name); // 'John' - original is not changed
Nested change affects both
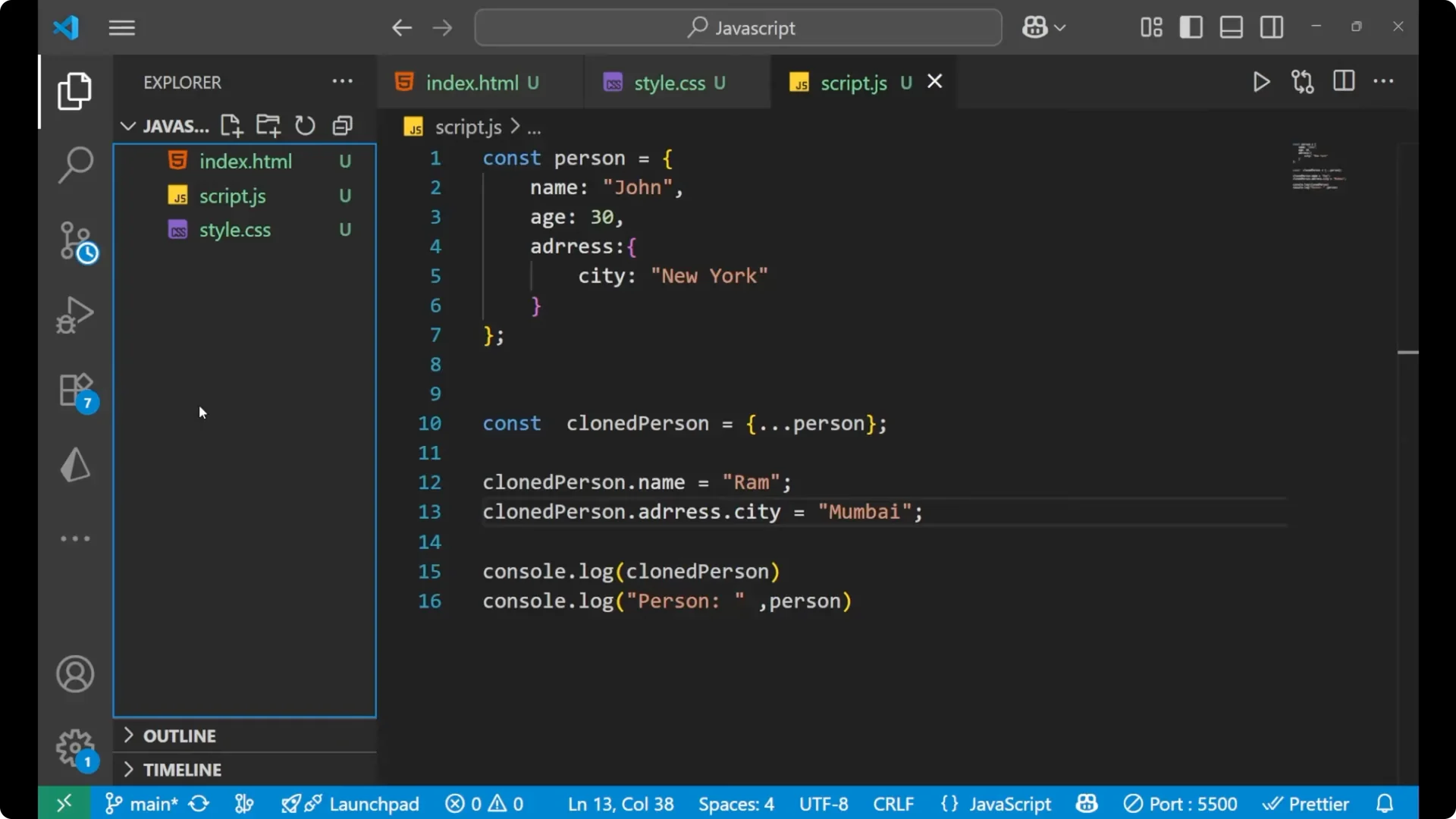
Changing a nested property like `address.city` on the cloned object affects the original too, because the nested object reference is shared.
const person = {
name: 'John',
age: 30,
address: { city: 'New York' }
};
const clonedPerson = { ...person };
// Change nested property on the clone
clonedPerson.address.city = 'Mumbai';
console.log(clonedPerson.address.city); // 'Mumbai'
console.log(person.address.city); // 'Mumbai' - original is also changed
This is one drawback of a
JavaScript shallow copy. Editing deep nested data on the cloned object will also update the original, because the nested structures are still references to the same objects.
Final Thoughts
Use a
JavaScript shallow copy when you want to duplicate top level properties and you are not editing deep nested data. You can clone the original to allow the user to undo the changes, but a shallow clone is only for the first level – not for nested objects.
 I will start with an example object that contains a nested object so we can see the effect of a shallow copy clearly.
I will start with an example object that contains a nested object so we can see the effect of a shallow copy clearly.

 To perform a shallow clone, use the spread operator. The spread operator is denoted by three dots.
To perform a shallow clone, use the spread operator. The spread operator is denoted by three dots.
 This creates a new object with the same top level properties as `person`. The nested `address` object is still the same reference in memory for both `person` and `clonedPerson`.
This creates a new object with the same top level properties as `person`. The nested `address` object is still the same reference in memory for both `person` and `clonedPerson`.
 Create a new object using `{ …person }` to make a shallow clone.
Create a new object using `{ …person }` to make a shallow clone.
 Change a top level property on the clone and verify it does not affect the original.
Change a top level property on the clone and verify it does not affect the original.
 Change a nested property on the clone and observe that it also changes in the original.
Change a nested property on the clone and observe that it also changes in the original.


 Changing a top level property like `name` on the cloned object does not affect the original object, because those primitive values are copied.
Changing a top level property like `name` on the cloned object does not affect the original object, because those primitive values are copied.

 Changing a nested property like `address.city` on the cloned object affects the original too, because the nested object reference is shared.
Changing a nested property like `address.city` on the cloned object affects the original too, because the nested object reference is shared.
 This is one drawback of a JavaScript shallow copy. Editing deep nested data on the cloned object will also update the original, because the nested structures are still references to the same objects.
This is one drawback of a JavaScript shallow copy. Editing deep nested data on the cloned object will also update the original, because the nested structures are still references to the same objects.
