We are going to learn how to parse JSON data in JavaScript. It is a
must-know concept if you are working with APIs and storing data or just building modern apps. I will explain everything from scratch.
Imagine someone sends you a letter in a code language and you need to decode it before you can understand the message. That is exactly what we do with JSON. We use the
JSON.parse method to decode the data.
JSON.parse in JavaScript
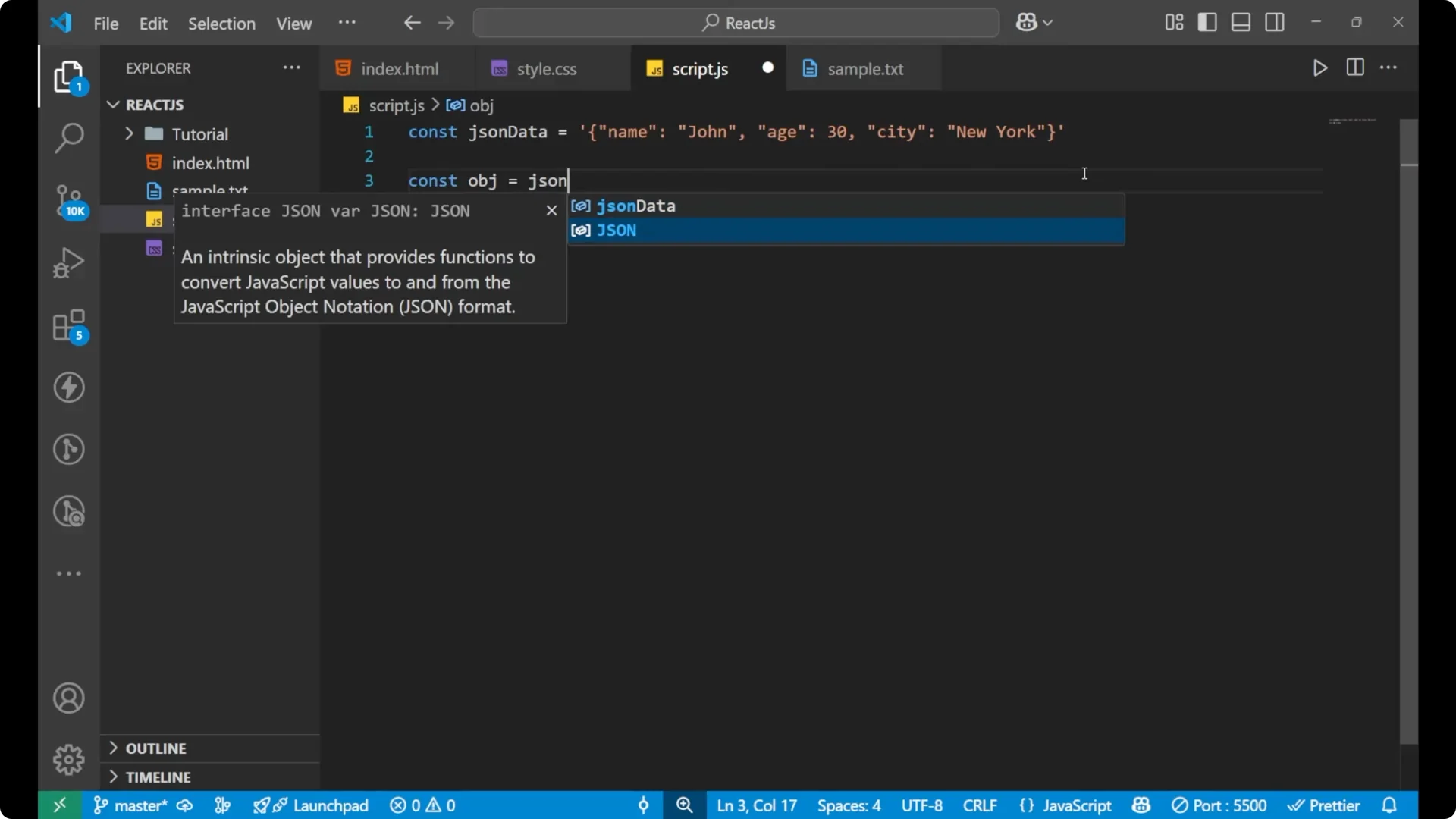
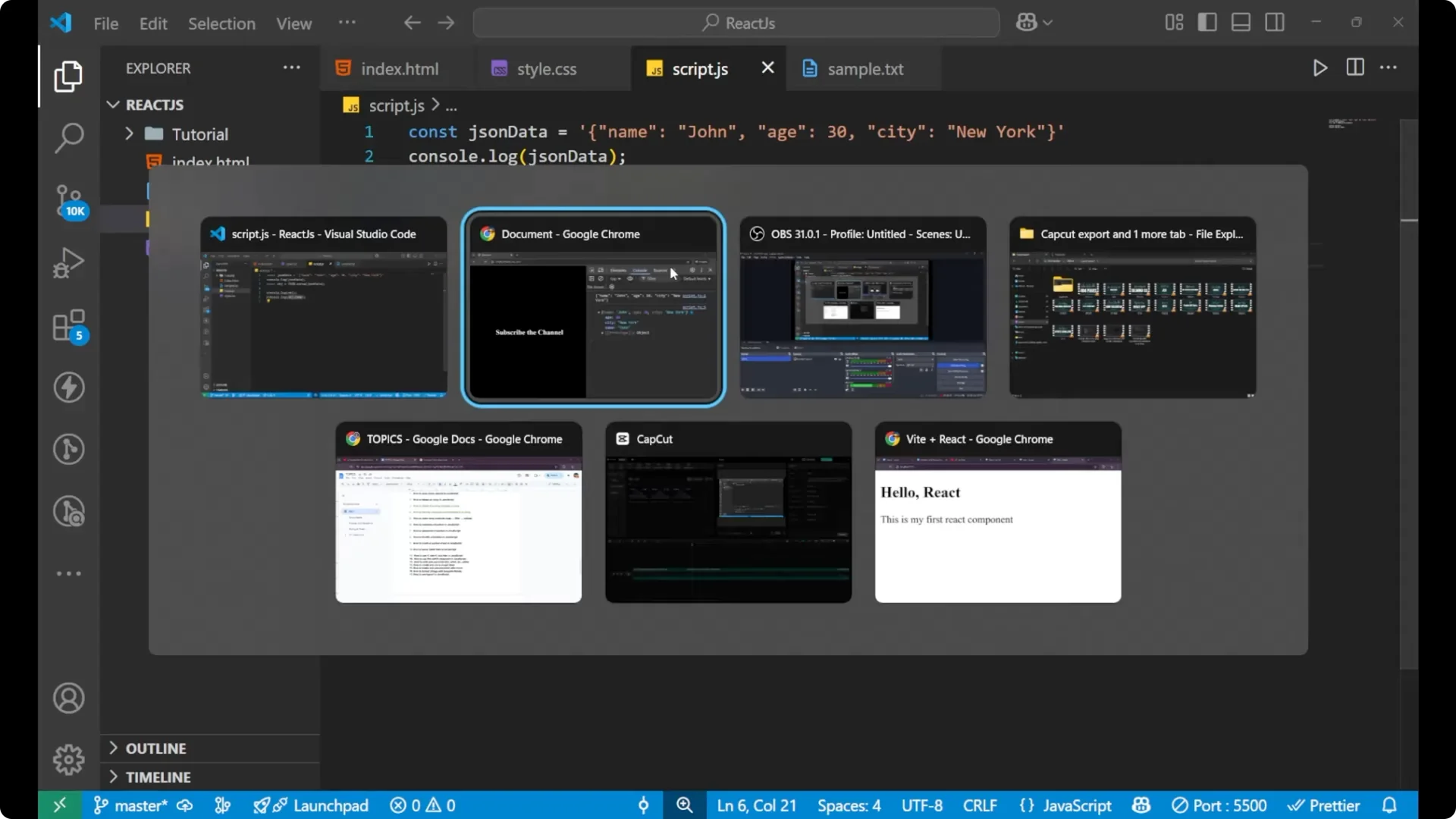
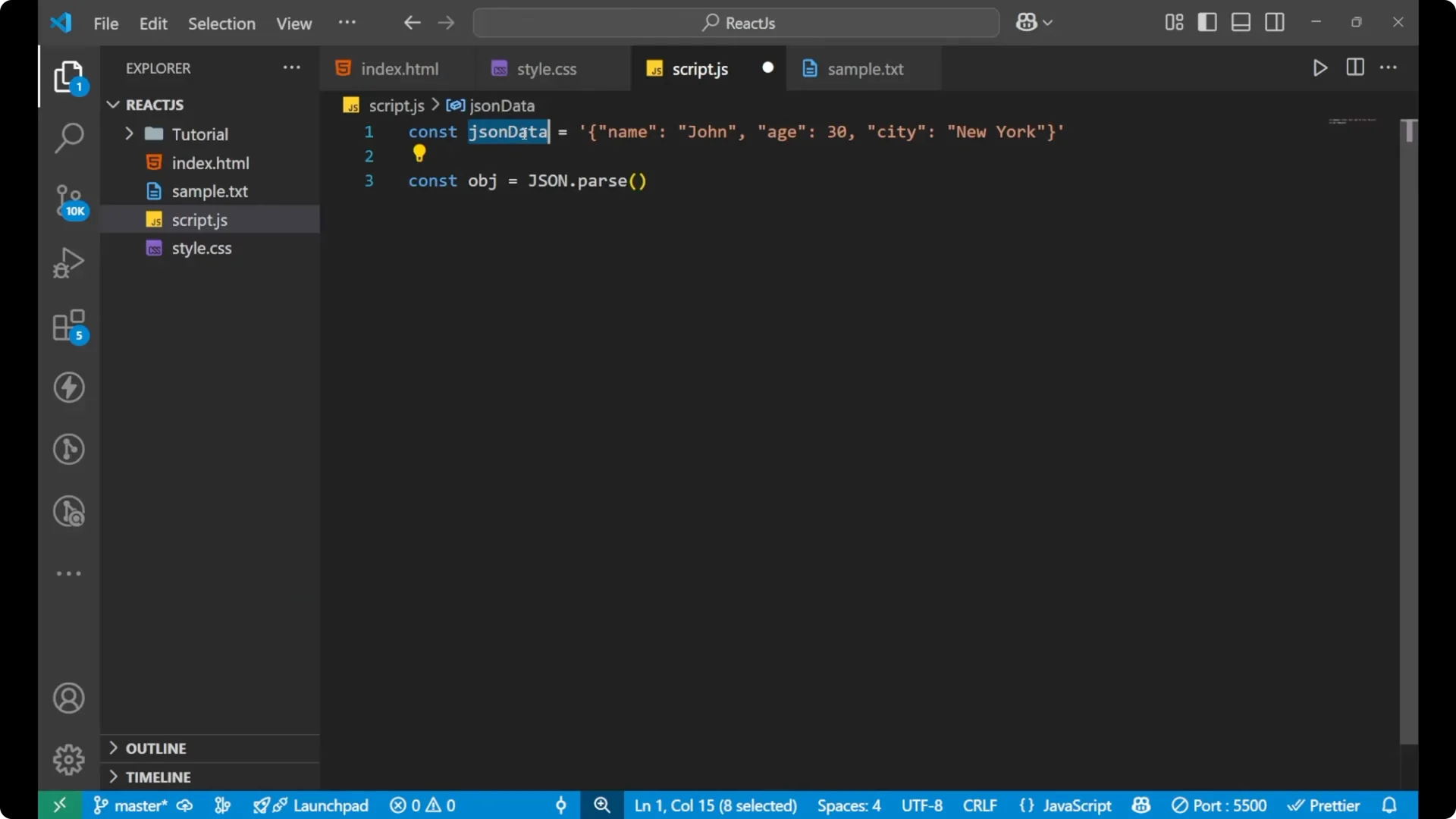
Suppose we have some JSON data as a string. It looks like an object inside, but the whole thing is actually a string because it is wrapped in quotation marks. To convert it and see the actual object from the string, you need to use
JSON.parse.
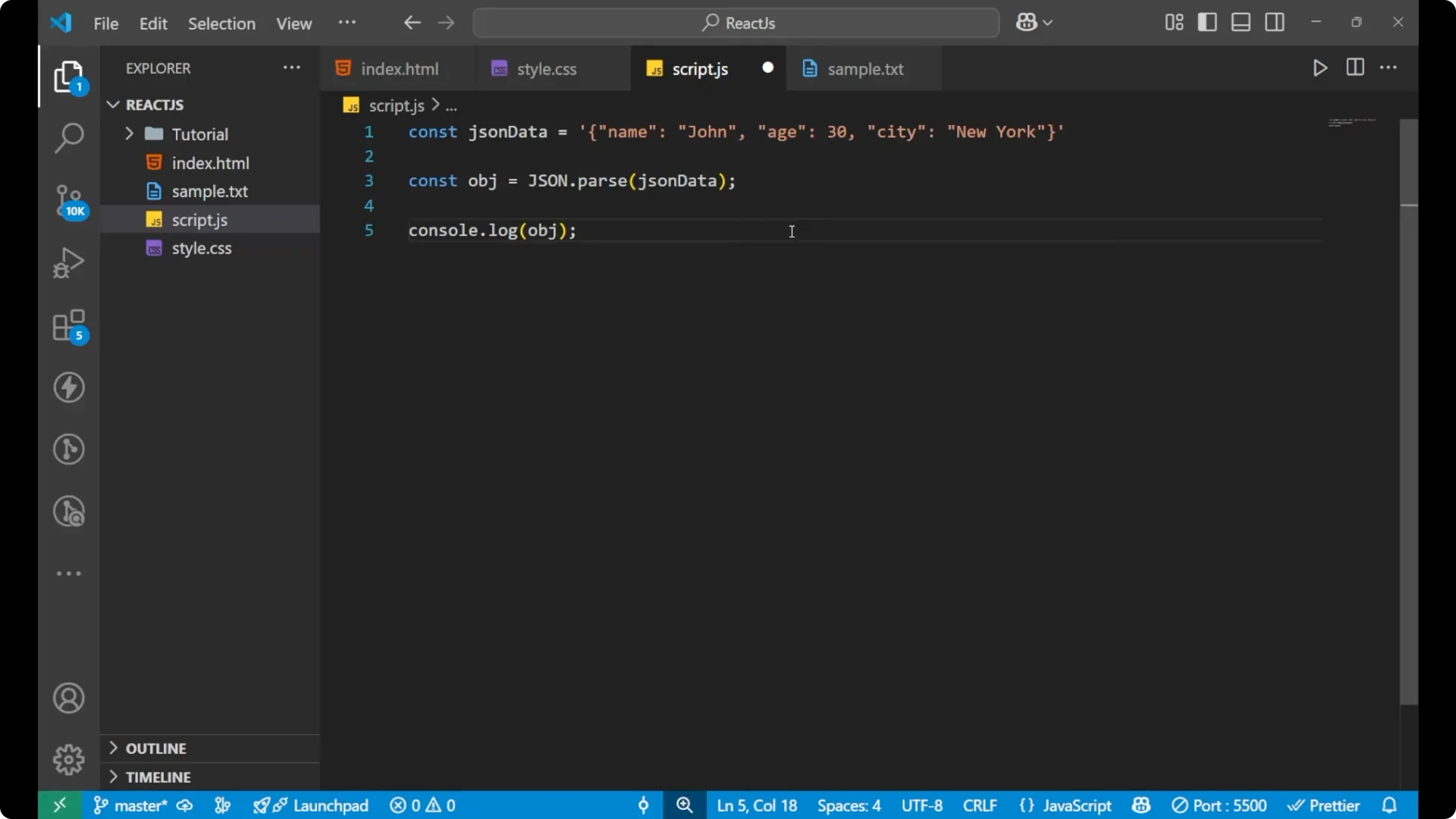
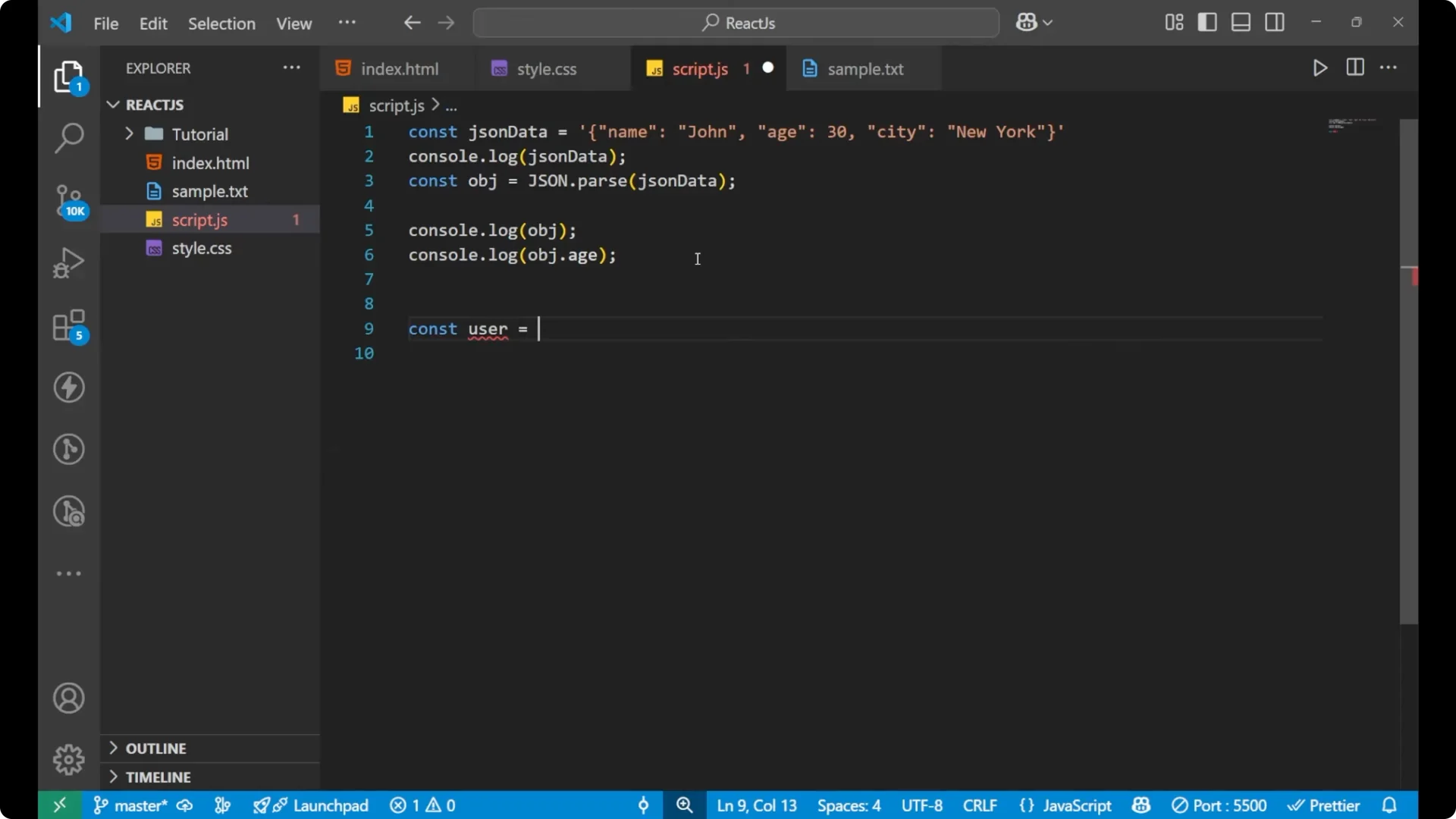
const jsonData = '{"name":"John","age":30}';
// Convert the JSON string to a real object
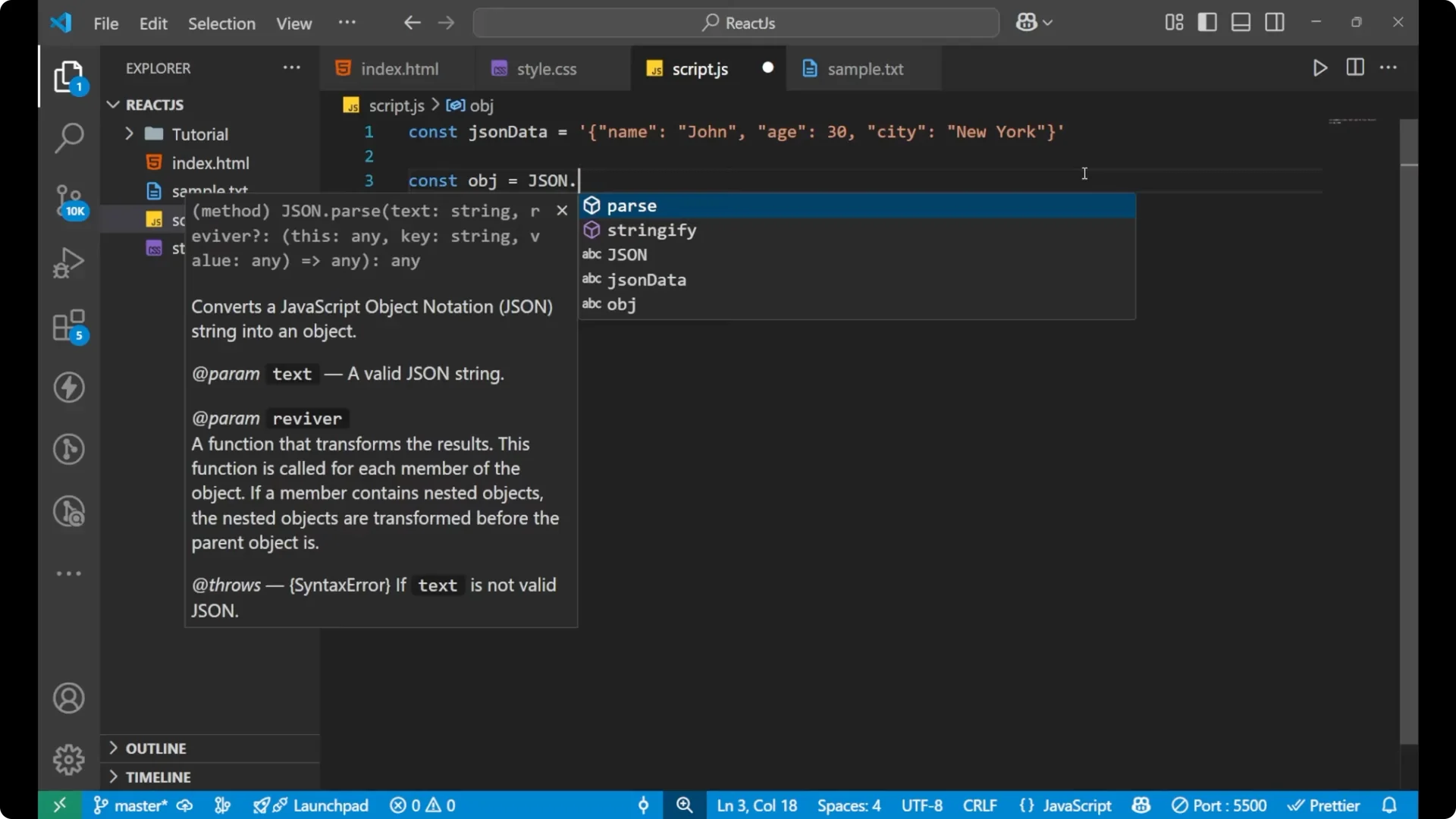
const obj = JSON.parse(jsonData);
// Compare string vs object in the console
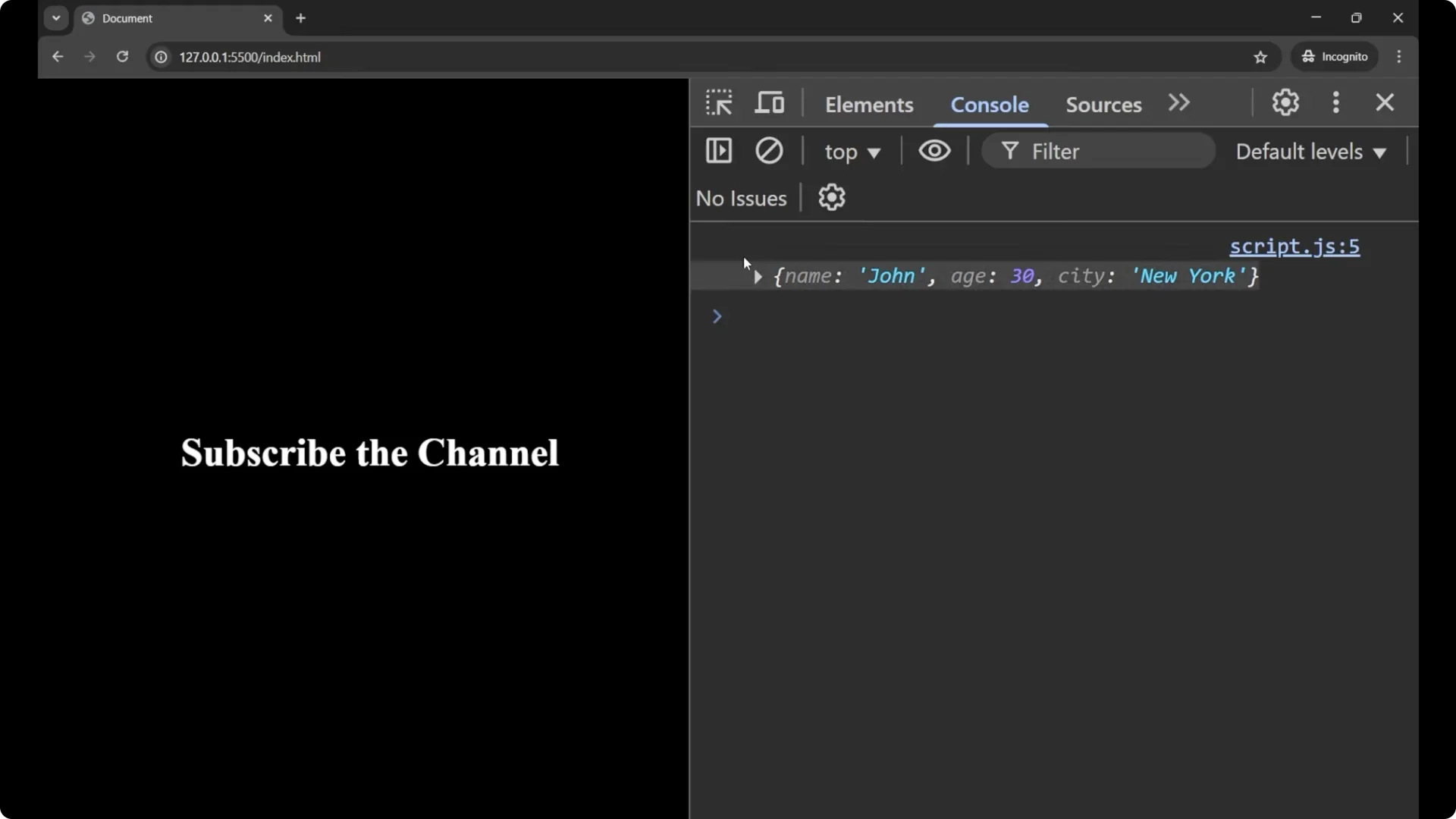
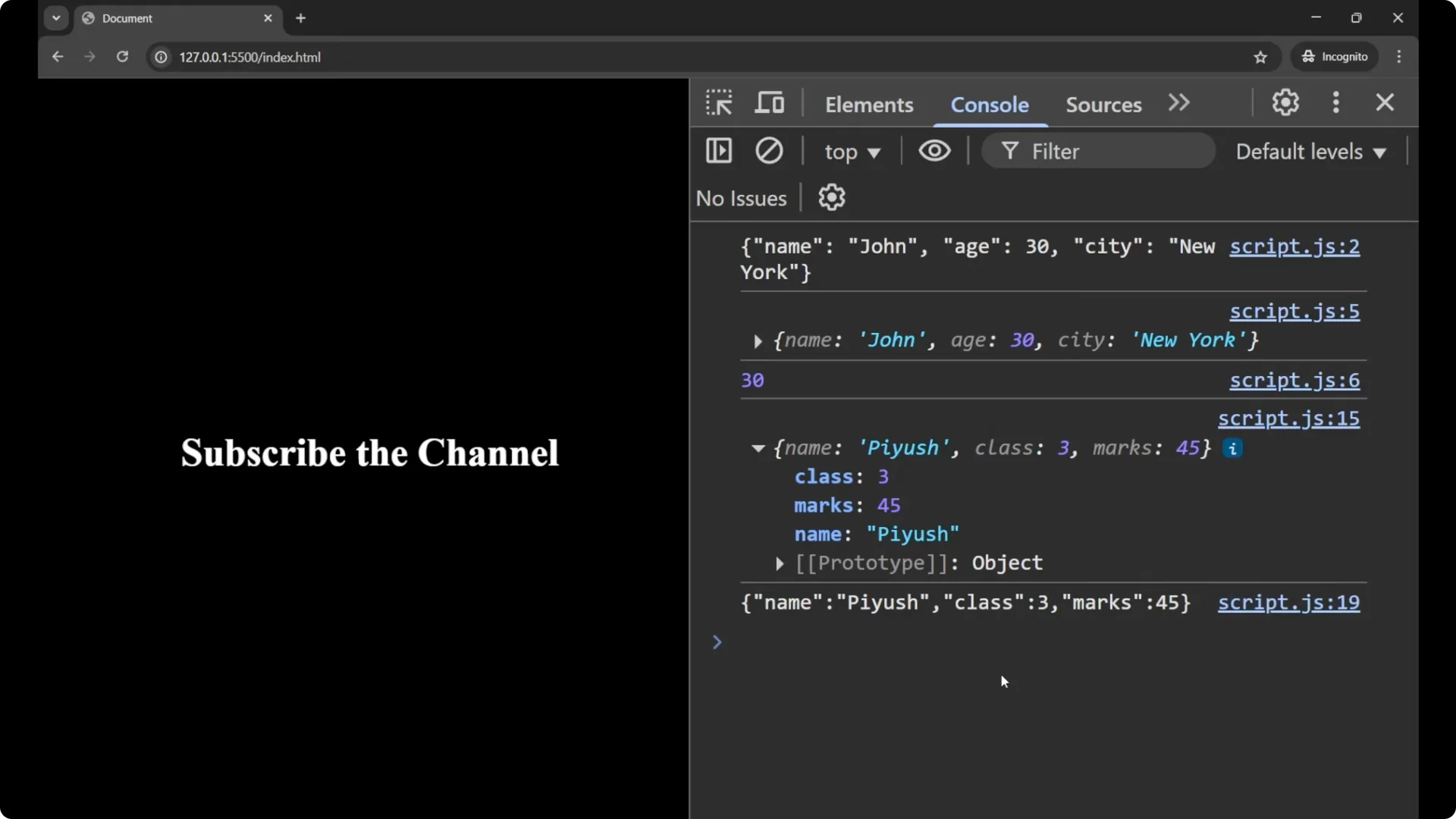
console.log(jsonData); // still a string
console.log(obj); // now an object
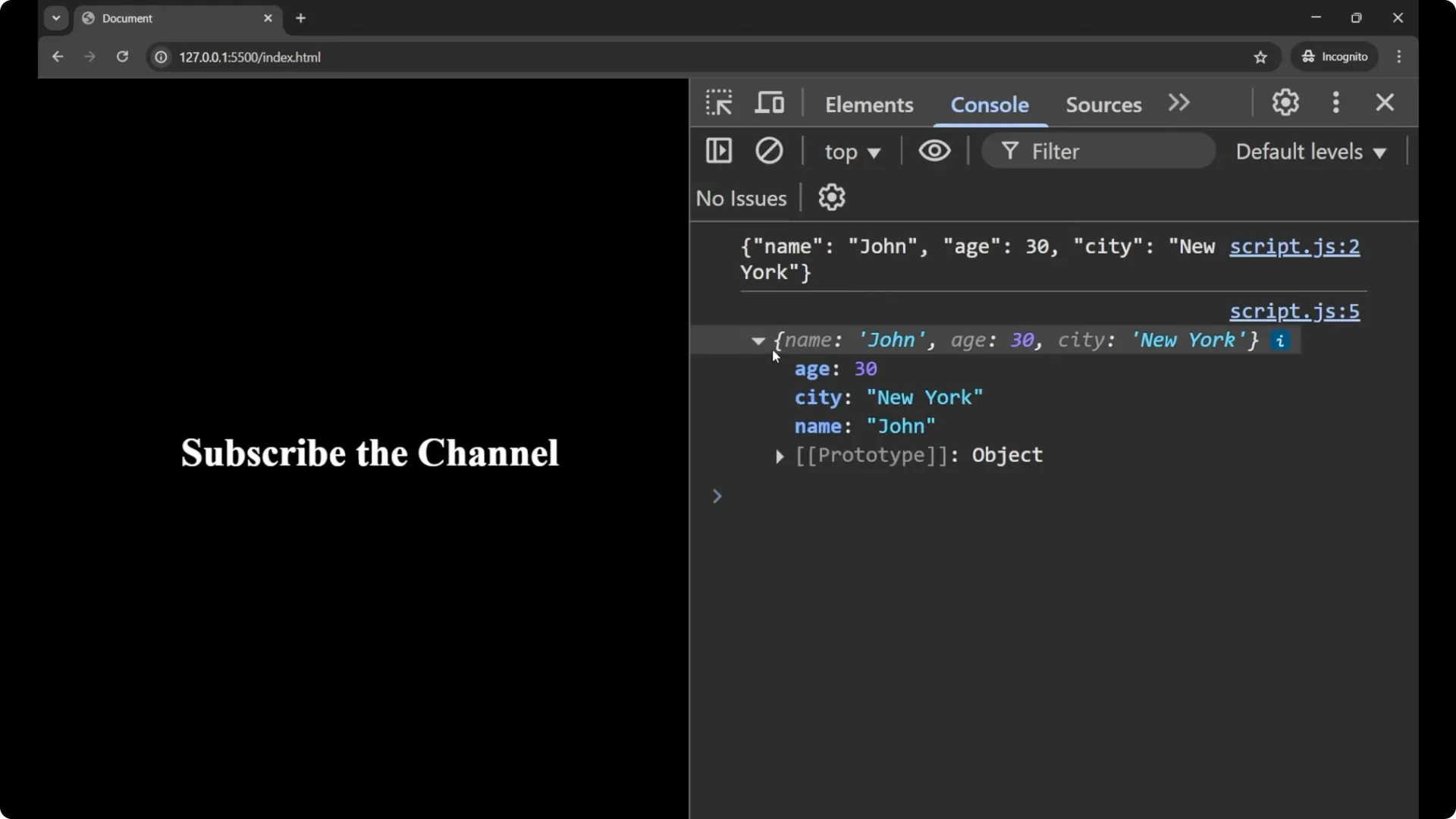
If you print only the original string, you just get a string and you cannot do anything with it in terms of property access. After parsing, you can use the data. For example:
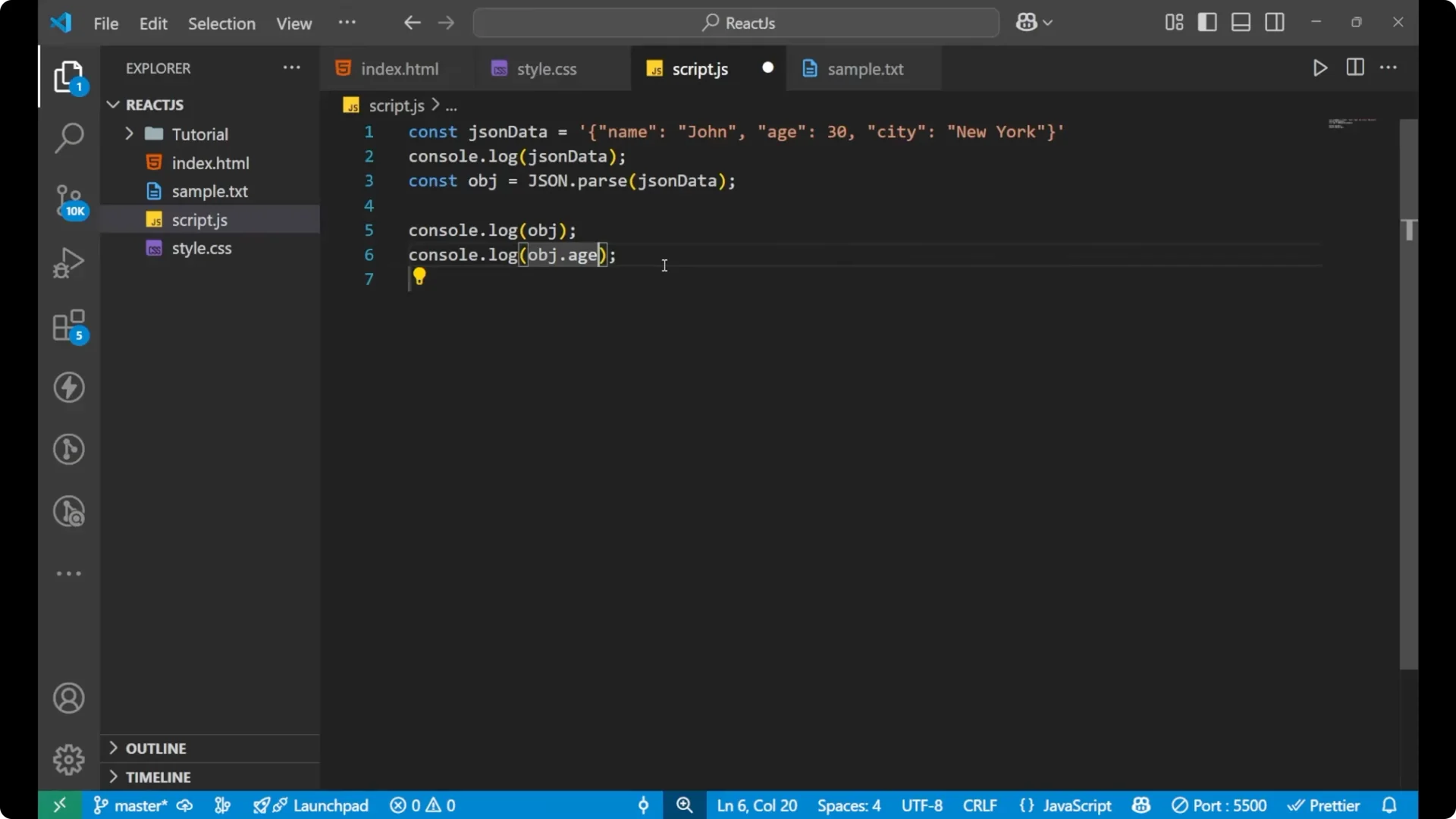
console.log(obj.name); // John
console.log(obj.age); // 30
Step-by-step parsing
Write the JSON string in a variable.
Write
JSON in capital letters, add `.parse(…)`.
Pass the variable holding the JSON string into `parse`.
Assign the result to a variable like `obj`.
Print `obj` with `console.log`.
Access properties like `obj.name` or `obj.age`.
For a deeper look at parsing, check
more on parsing.
From object to JSON string
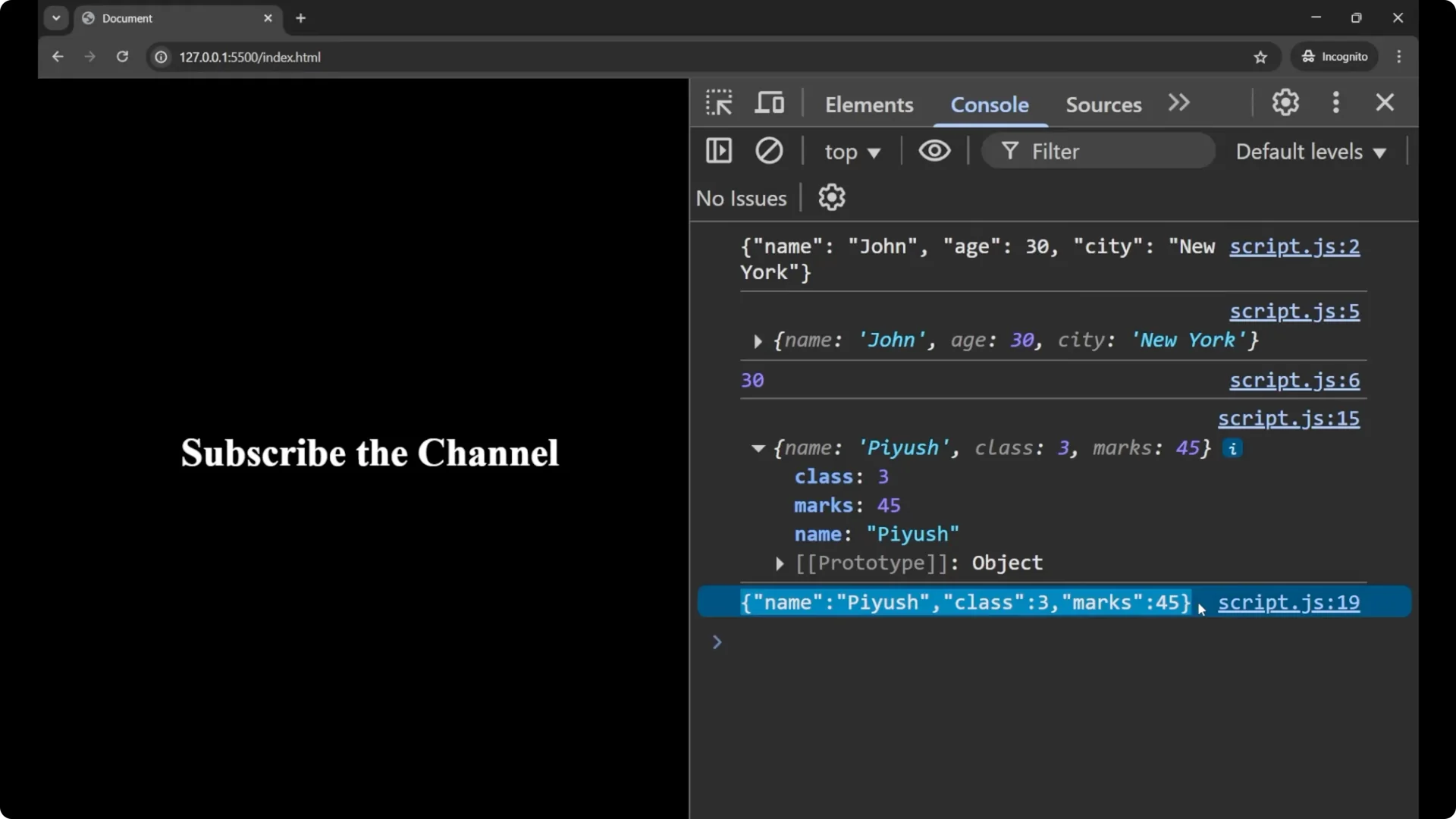
If I want to convert an object to a JSON string, it is just the reverse of what we did above. This time I am creating an object.
const user = {
name: 'fuse',
class: 3,
marks: 45
};
// The original object
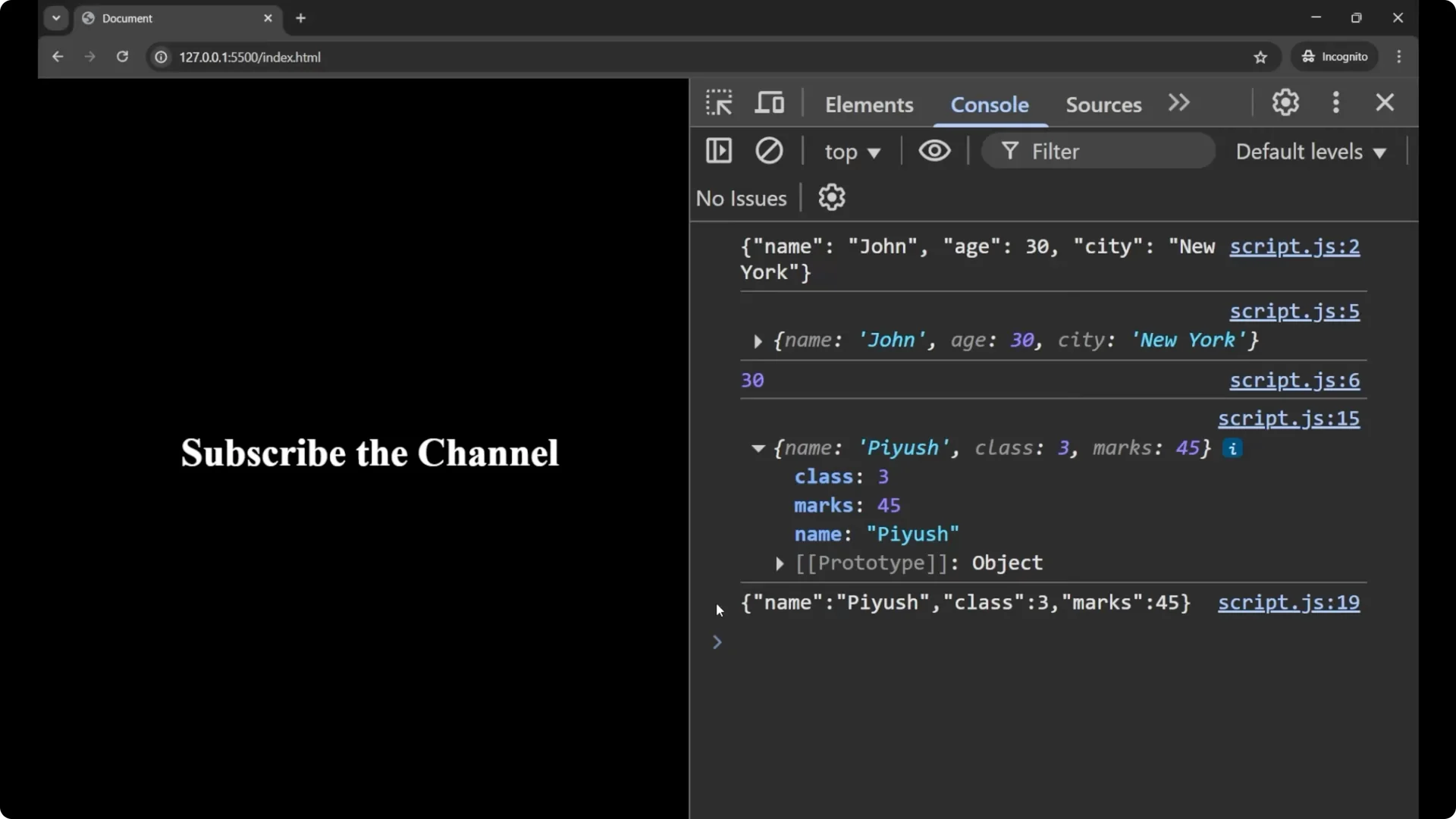
console.log(user);
// Convert the object into a JSON string
const jsonString = JSON.stringify(user);
// The result is a string
console.log(jsonString);
// => '{"name":"fuse","class":3,"marks":45}'
 JSON.stringify
JSON.stringify is the opposite of
JSON.parse, and you use it when you want to send or store data. It converts the object to a JSON string. It is useful when sending data to a server or saving to local storage in your app, for example before populating a
dropdown menu.
Step-by-step stringify
Create a regular JavaScript object.
Call
JSON.stringify with that object.
Assign the result to a variable like `jsonString`.
Print both the original object and the resulting string to see the difference.
Final thoughts
JSON.parse converts a JSON string into a usable JavaScript object, and
JSON.stringify converts a JavaScript object into a JSON string. Parse when you receive data as a string and need to work with it as an object. Stringify when you need to send or store the data as a string. If you want a quick refresher on basic loops while you practice working with parsed collections, see
do while.
 Suppose we have some JSON data as a string. It looks like an object inside, but the whole thing is actually a string because it is wrapped in quotation marks. To convert it and see the actual object from the string, you need to use JSON.parse.
Suppose we have some JSON data as a string. It looks like an object inside, but the whole thing is actually a string because it is wrapped in quotation marks. To convert it and see the actual object from the string, you need to use JSON.parse.
 If you print only the original string, you just get a string and you cannot do anything with it in terms of property access. After parsing, you can use the data. For example:
If you print only the original string, you just get a string and you cannot do anything with it in terms of property access. After parsing, you can use the data. For example:

 Write the JSON string in a variable.
Write JSON in capital letters, add `.parse(…)`.
Pass the variable holding the JSON string into `parse`.
Assign the result to a variable like `obj`.
Print `obj` with `console.log`.
Access properties like `obj.name` or `obj.age`.
Write the JSON string in a variable.
Write JSON in capital letters, add `.parse(…)`.
Pass the variable holding the JSON string into `parse`.
Assign the result to a variable like `obj`.
Print `obj` with `console.log`.
Access properties like `obj.name` or `obj.age`.





 For a deeper look at parsing, check more on parsing.
For a deeper look at parsing, check more on parsing.
 If I want to convert an object to a JSON string, it is just the reverse of what we did above. This time I am creating an object.
If I want to convert an object to a JSON string, it is just the reverse of what we did above. This time I am creating an object.
 JSON.stringify is the opposite of JSON.parse, and you use it when you want to send or store data. It converts the object to a JSON string. It is useful when sending data to a server or saving to local storage in your app, for example before populating a dropdown menu.
JSON.stringify is the opposite of JSON.parse, and you use it when you want to send or store data. It converts the object to a JSON string. It is useful when sending data to a server or saving to local storage in your app, for example before populating a dropdown menu.
 Create a regular JavaScript object.
Call JSON.stringify with that object.
Assign the result to a variable like `jsonString`.
Print both the original object and the resulting string to see the difference.
Create a regular JavaScript object.
Call JSON.stringify with that object.
Assign the result to a variable like `jsonString`.
Print both the original object and the resulting string to see the difference.




