We are going to learn how to build a simple timer using JavaScript like a stopwatch that counts seconds. It is a beginner-friendly project and it is useful in many different projects like quizzes, countdown, or a fitness app. If you also want a quick refresher on loops while practicing basic JS, see
do-while.
JavaScript Stopwatch: HTML
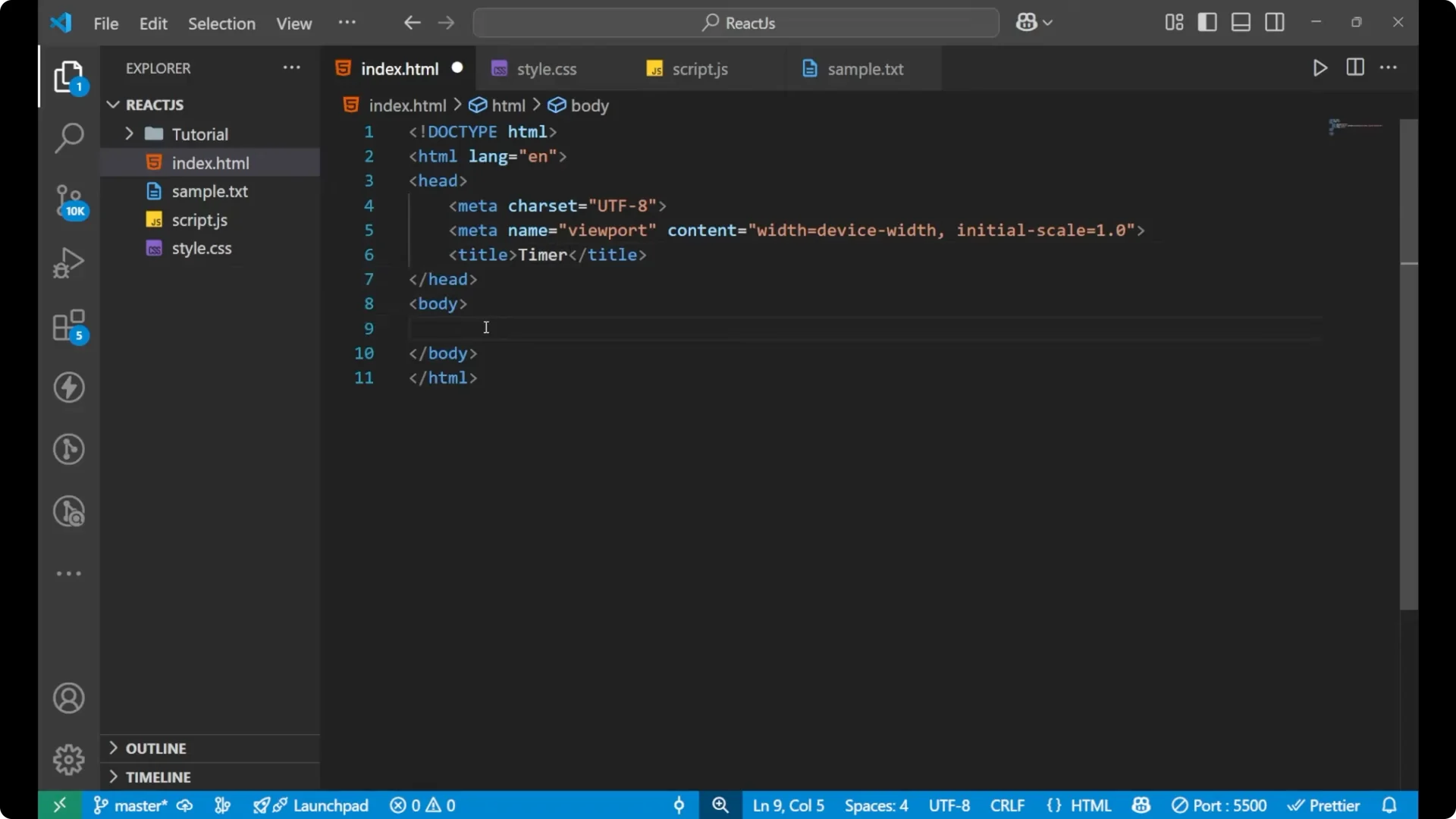
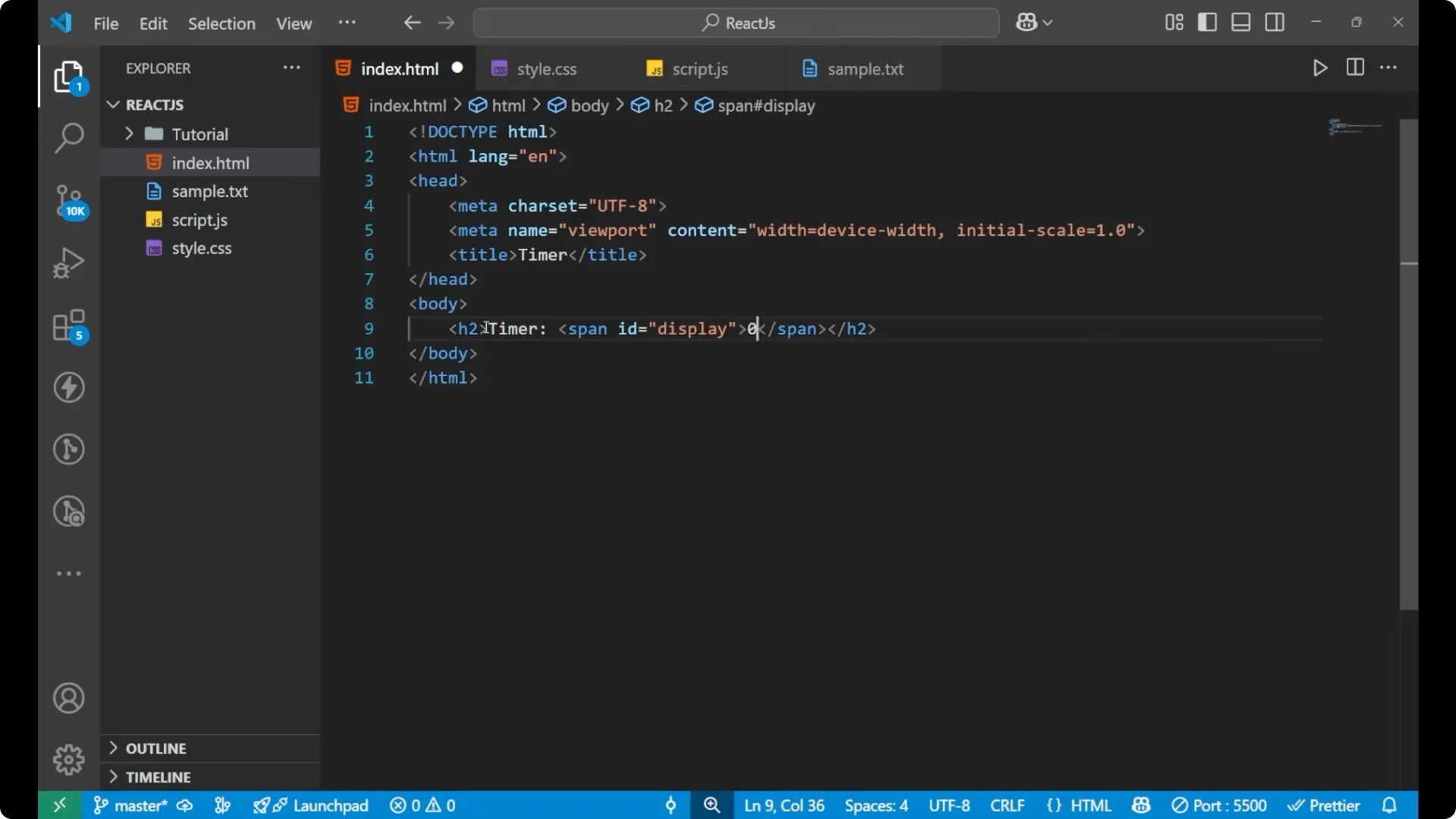
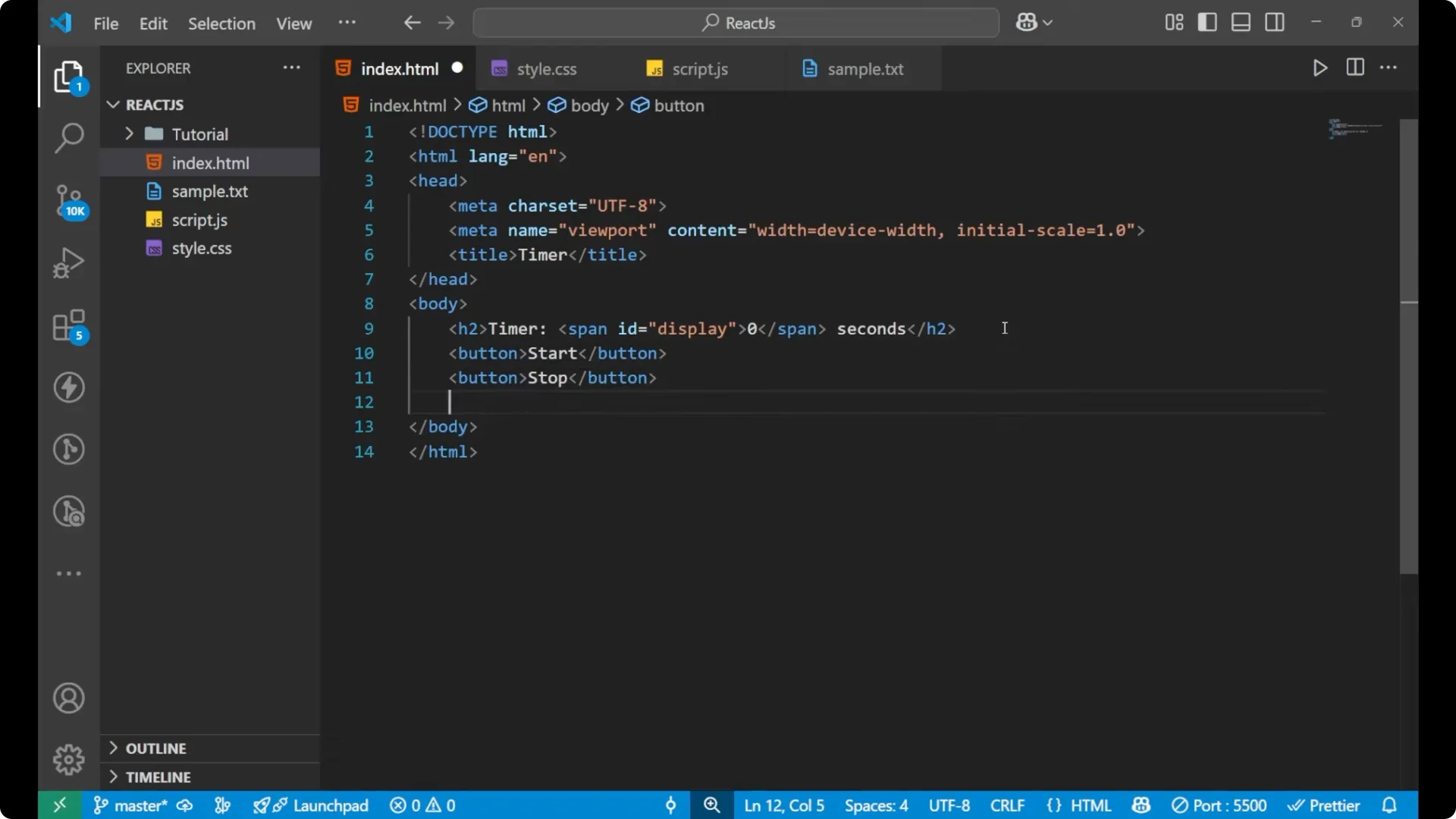
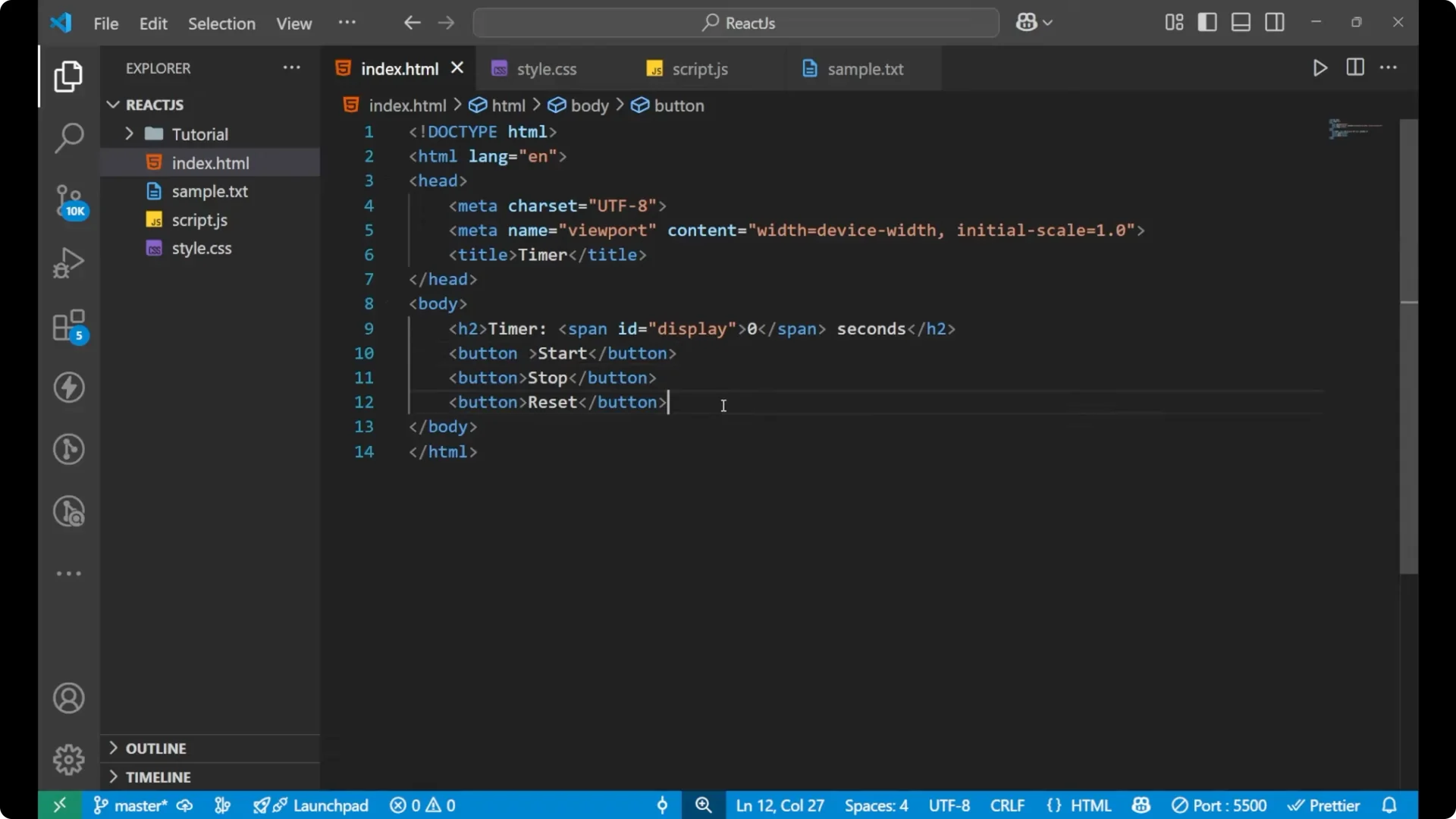
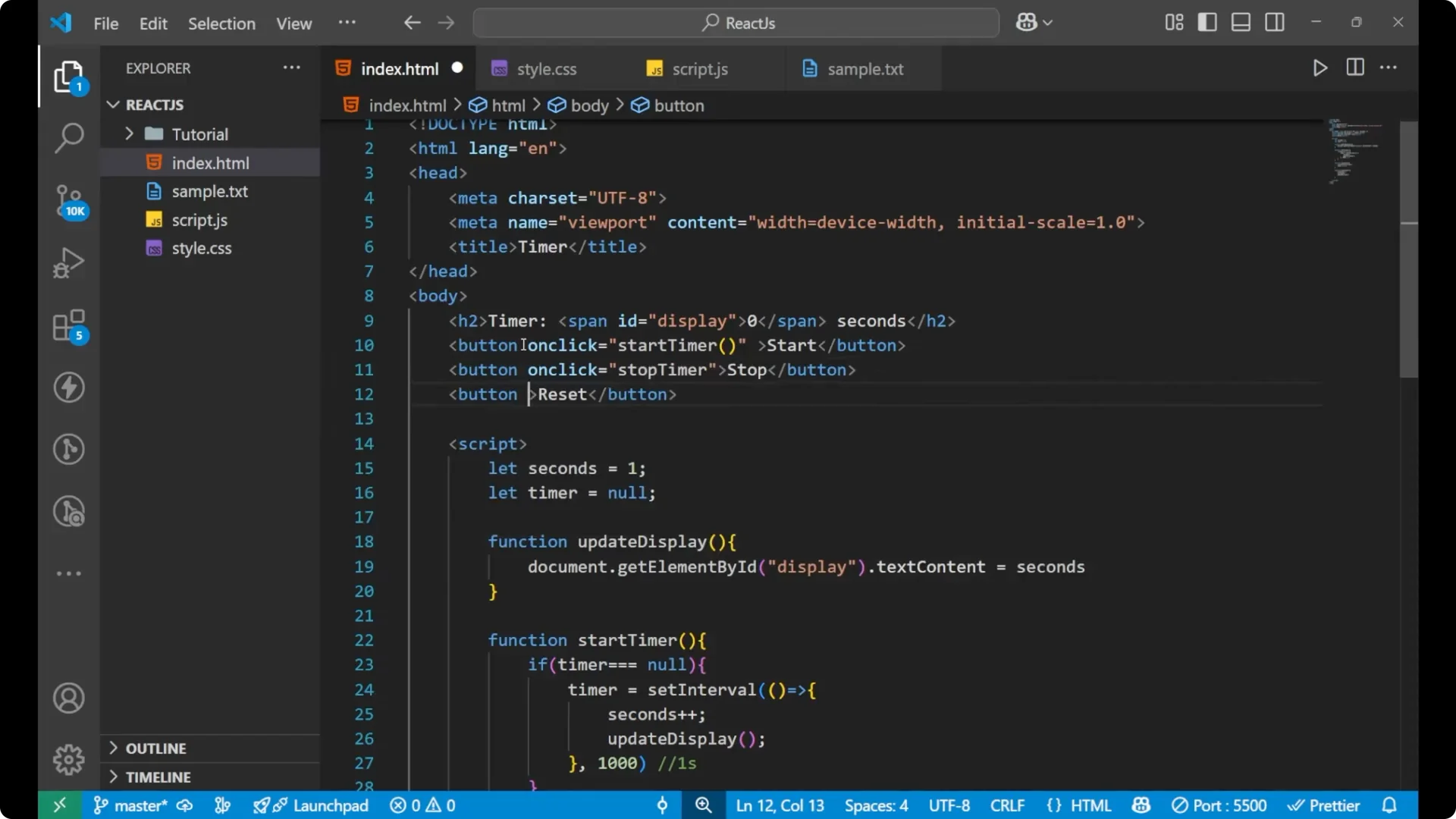
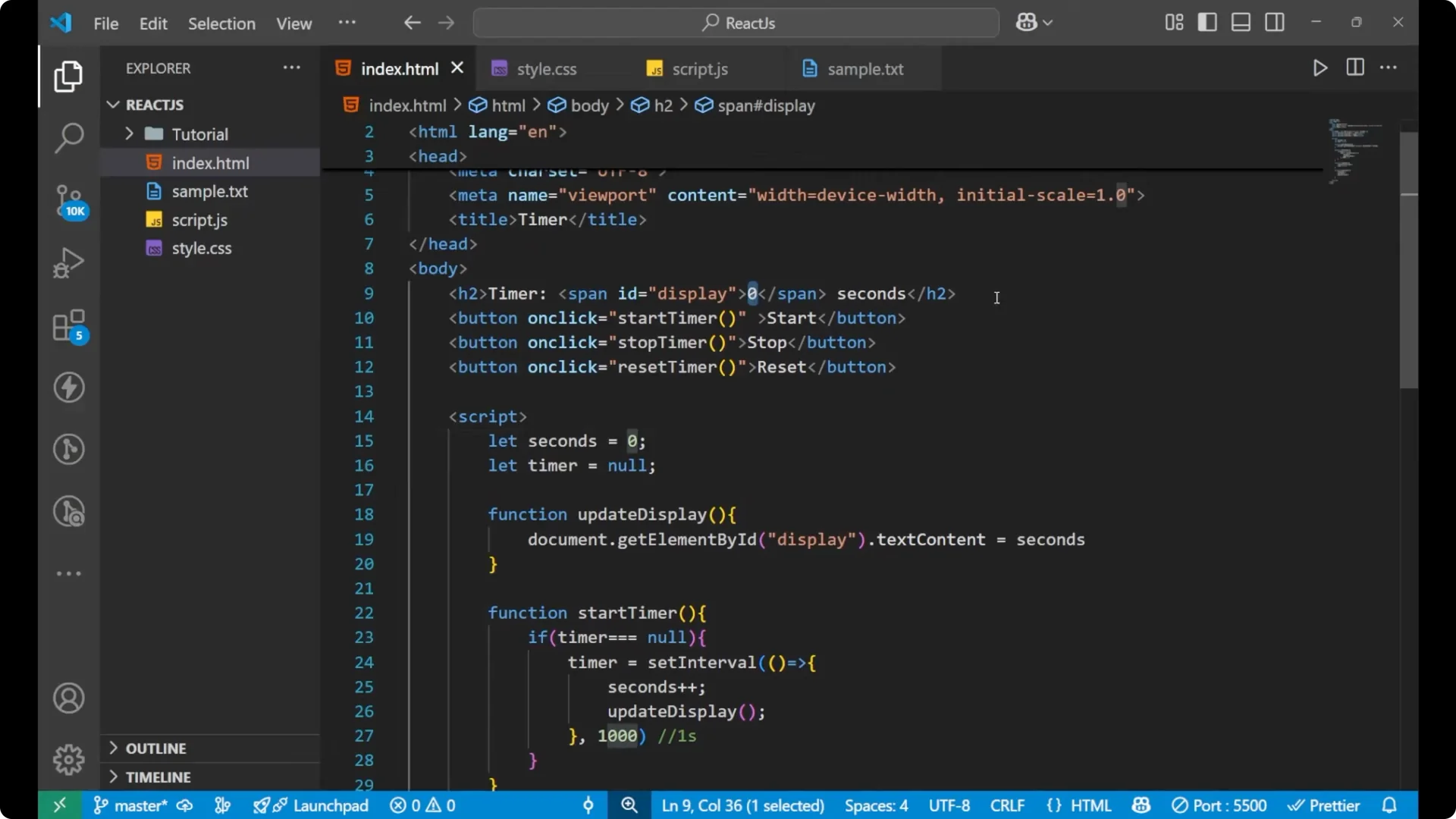
I will start with the HTML part. I will name the document as timer. Create an h2 and write Timer, and then a span. I will give the span an id display and put 0 inside it. After the span I will write the word seconds. Then I will create three buttons: start, stop, and reset.
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>Timer</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Timer</h2>
<span id="display">0</span> seconds
<div>
<button onclick="startTimer()">Start</button>
<button onclick="stopTimer()">Stop</button>
<button onclick="resetTimer()">Reset</button>
</div>
<script>
// JavaScript will go here
</script>
</body>
</html>
JavaScript Stopwatch: JavaScript
I’m going to the JavaScript part. I’m not going to work on the CSS – that is your task. My aim is to explain the whole functioning and how we can create it.
Variables and state
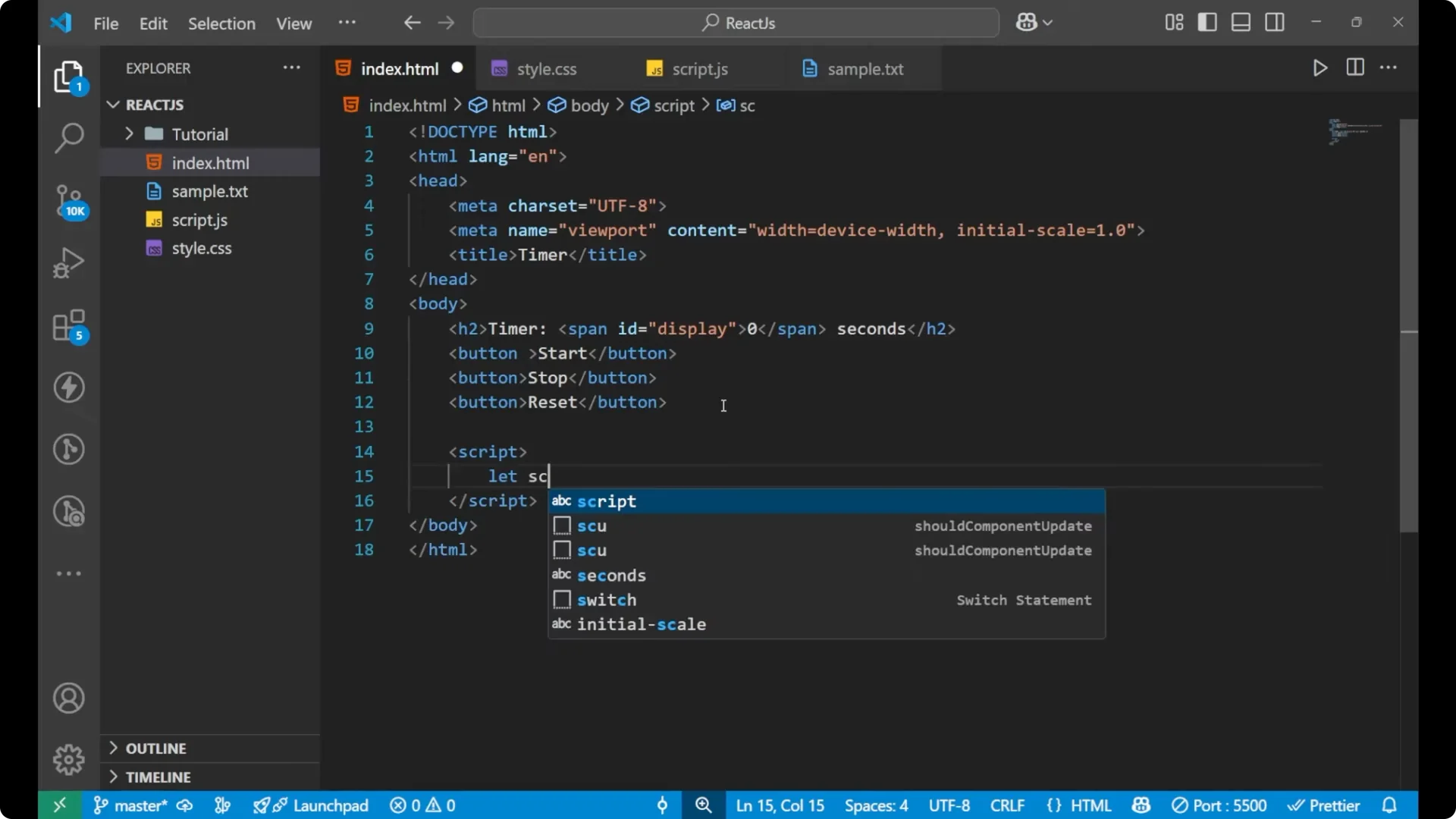
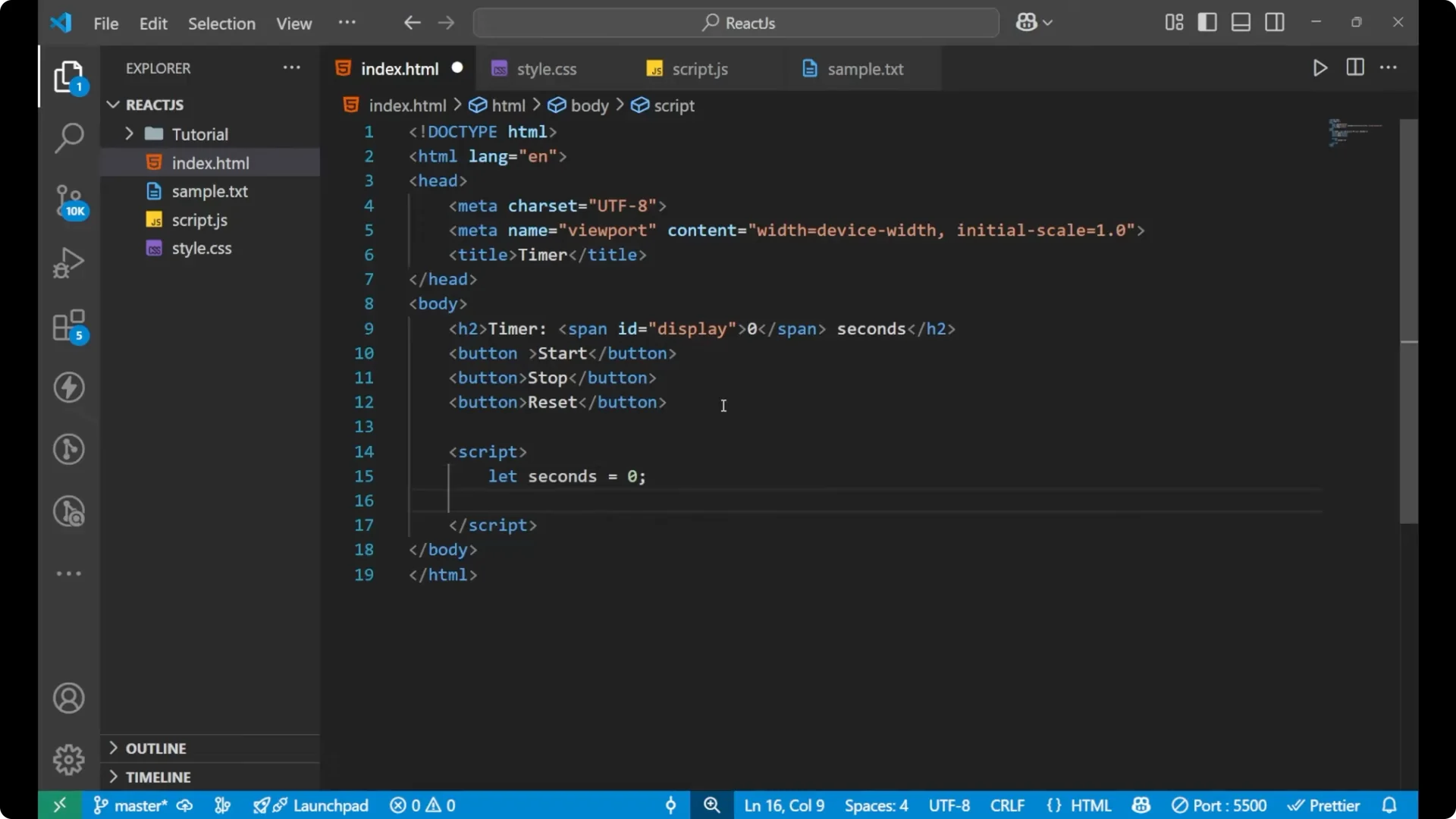
Let seconds equal 0 and let timer equal null. We are initially taking
seconds as 0 and the
timer as
null because the timer is not running.
let seconds = 0;
let timer = null;
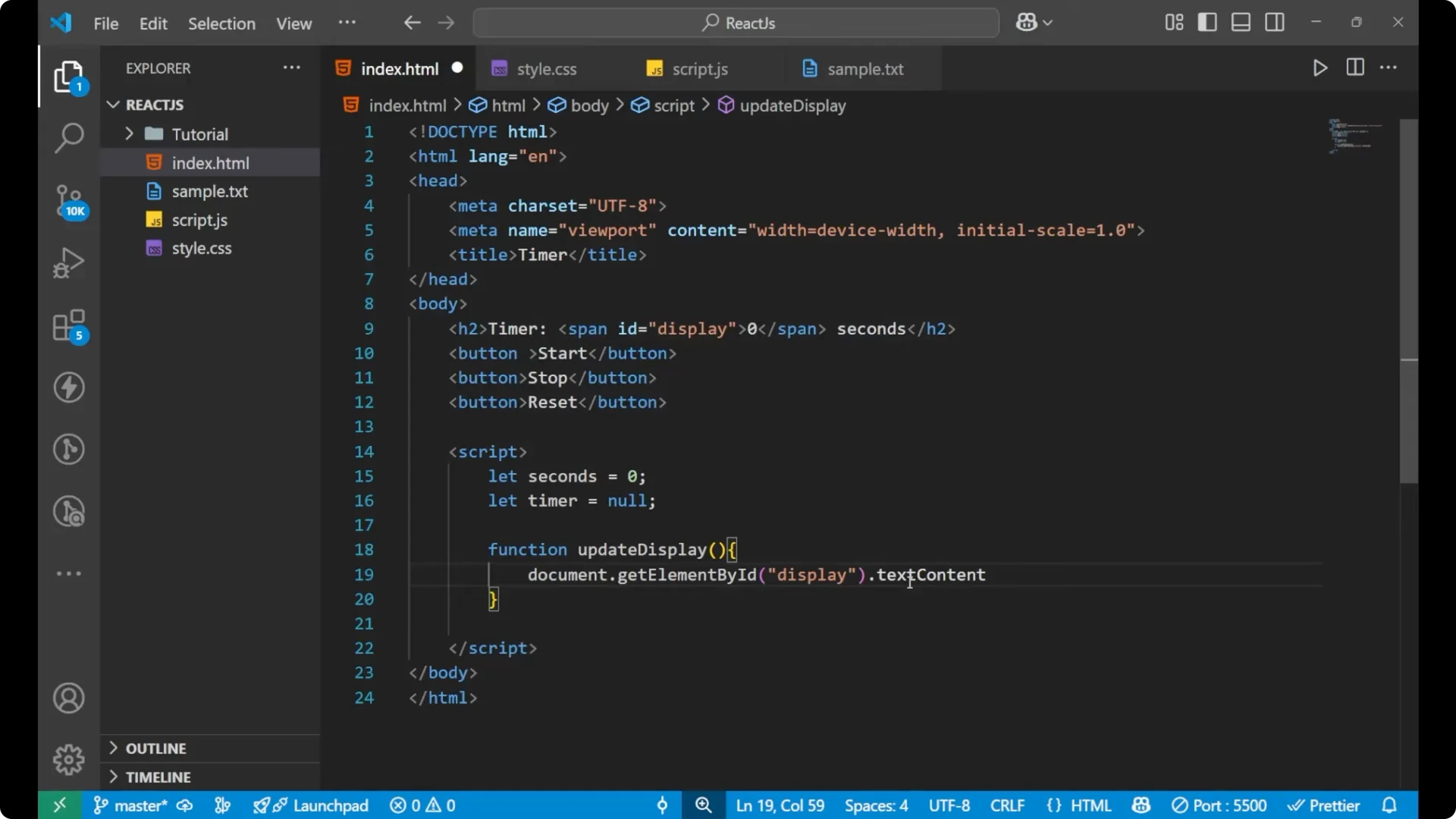
Update the display
Create a function named
updateDisplay that sets the textContent of the element with id display to the current seconds. I want that whenever the timer starts, the value in the display keeps changing.
function updateDisplay() {
document.getElementById('display').textContent = seconds;
}
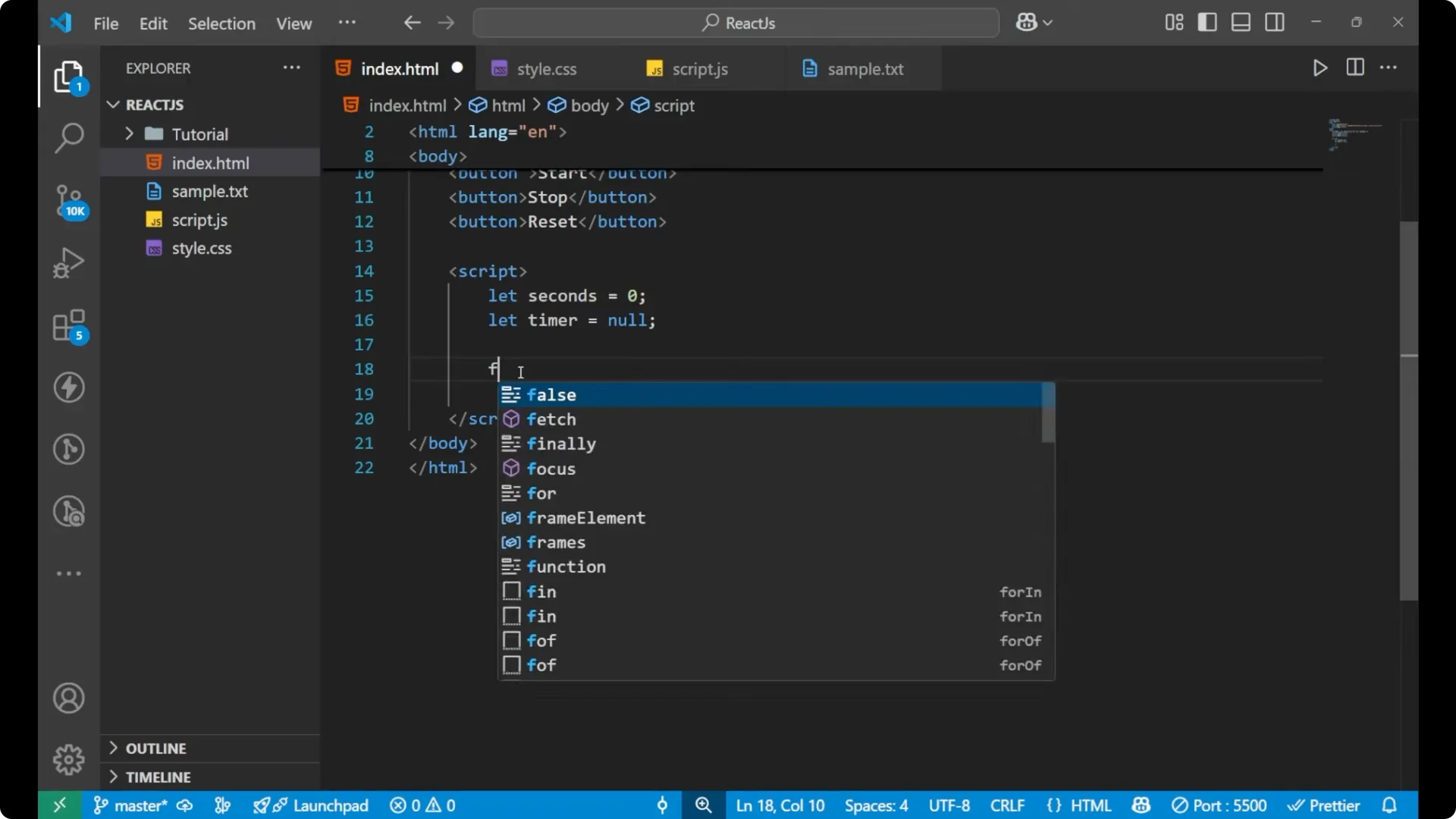
Start the timer
Create a
startTimer function. If
timer === null, set
timer to
setInterval, increment
seconds, and call
updateDisplay every 1000 milliseconds. 1000 milliseconds is 1 second.
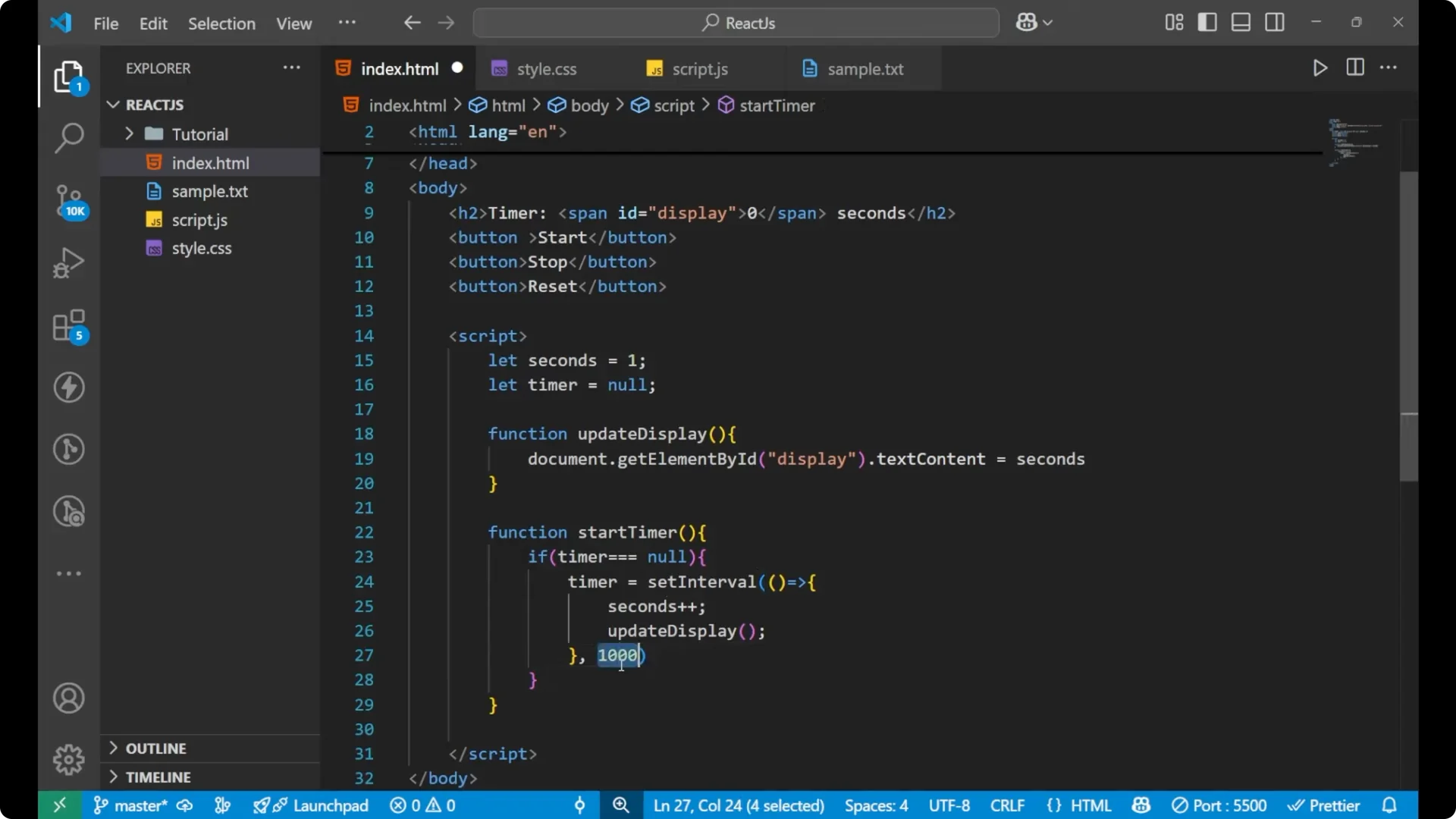
function startTimer() {
if (timer === null) {
timer = setInterval(() => {
seconds++;
updateDisplay();
}, 1000);
}
}
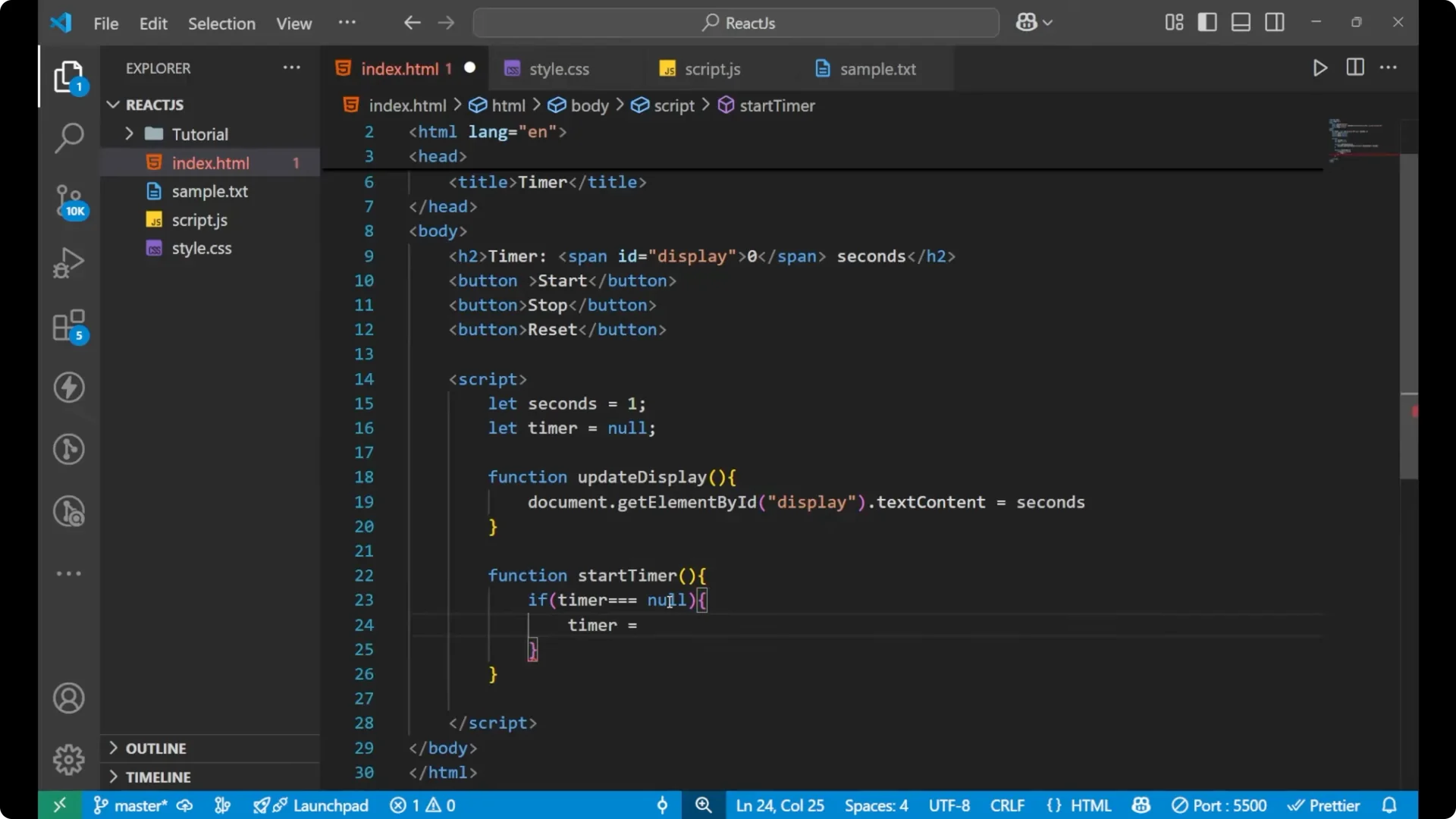
Stop the timer
Create a
stopTimer function. Call
clearInterval(timer) to stop the interval that is running, and then set
timer = null.
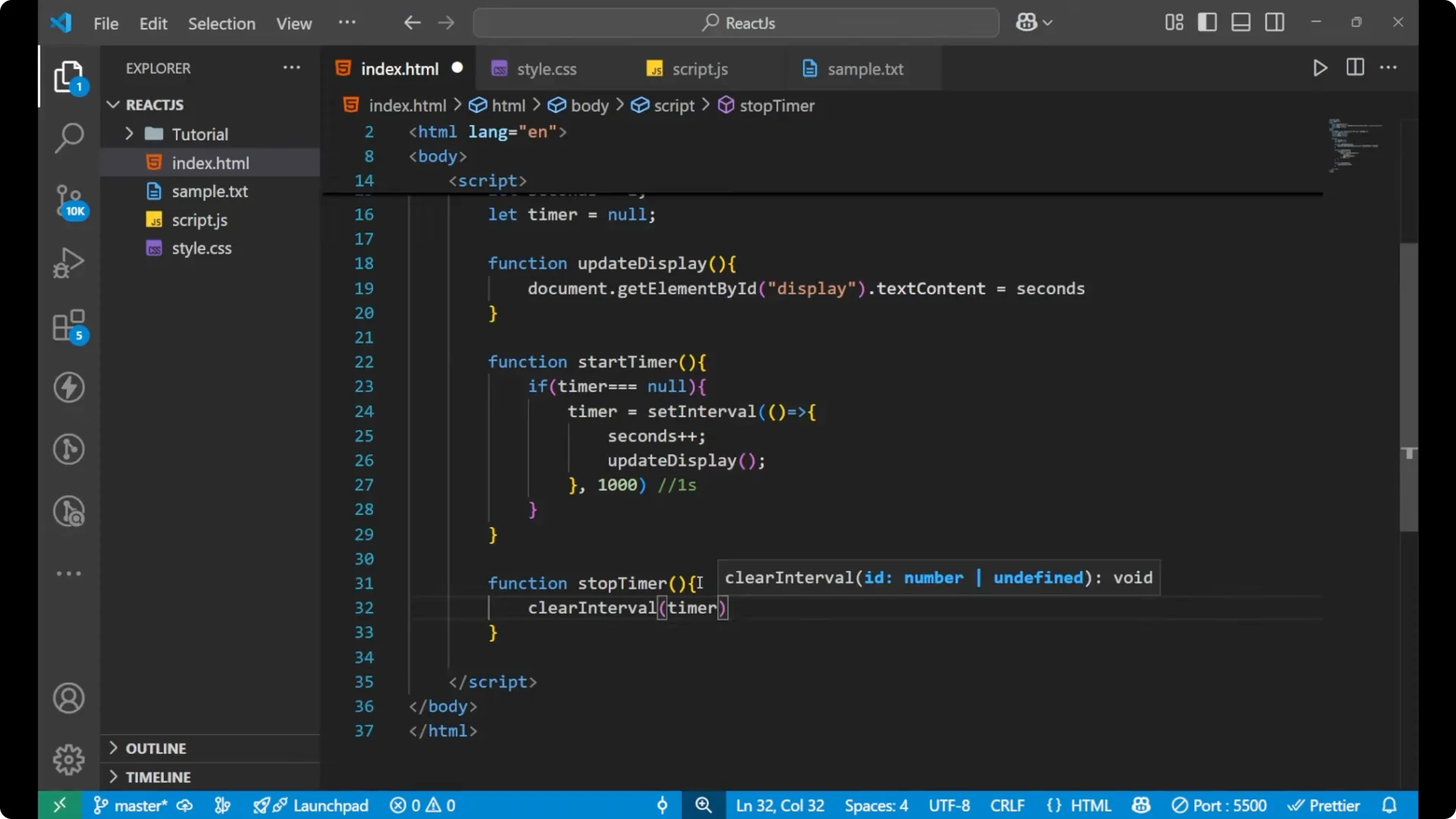
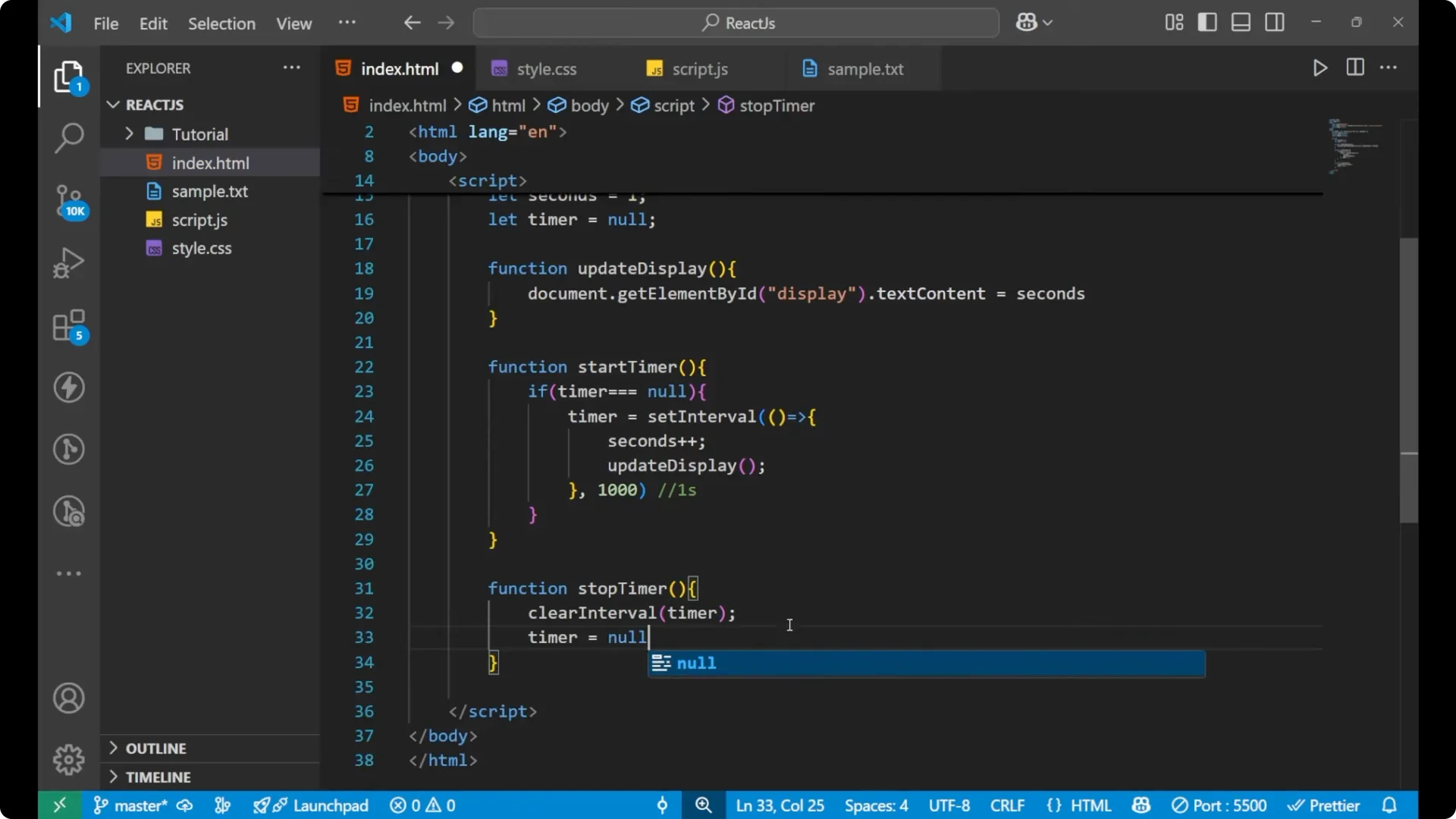
function stopTimer() {
clearInterval(timer);
timer = null;
}
Reset the timer
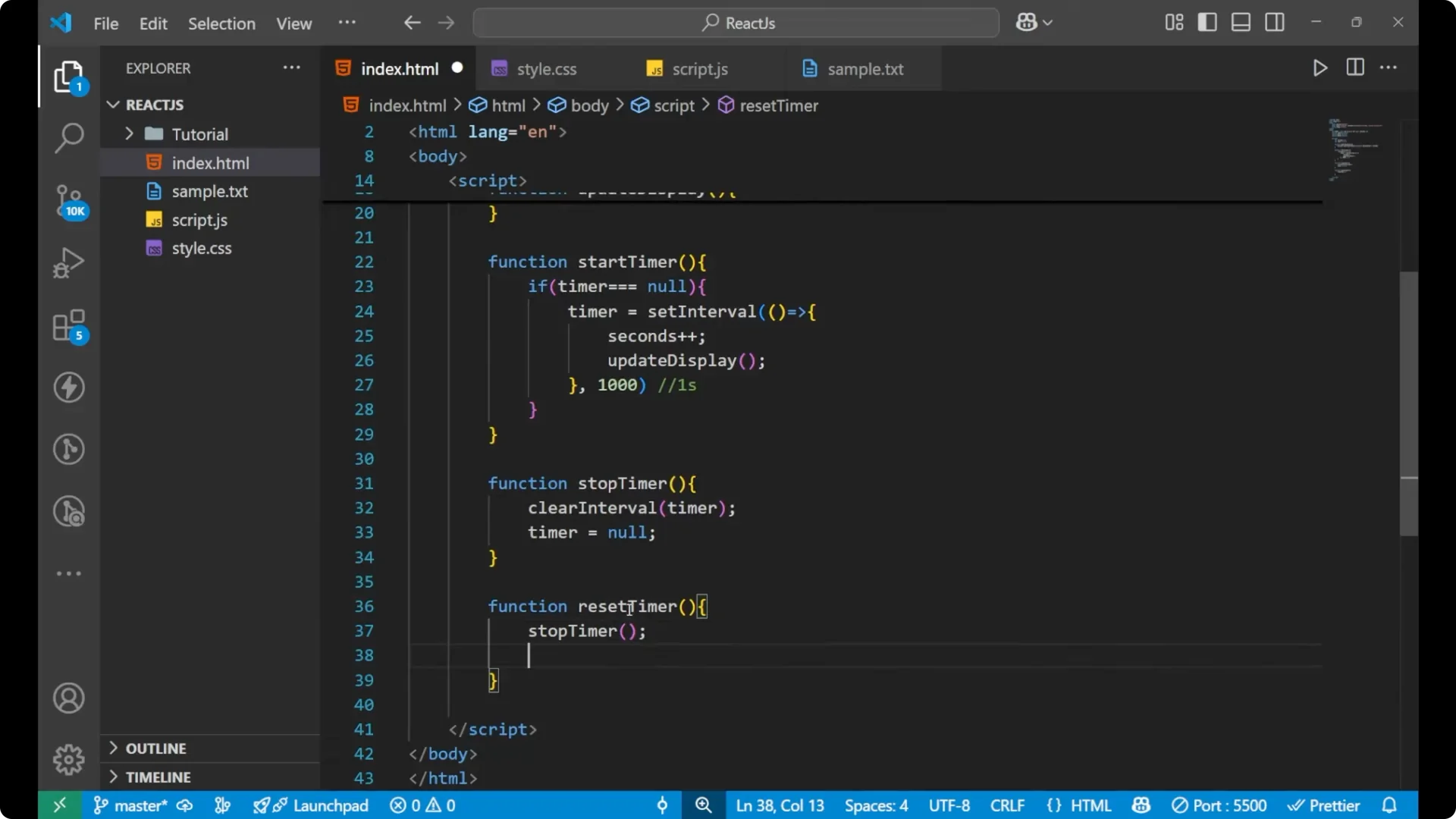
Create a
resetTimer function. First call
stopTimer(), then set
seconds = 0, and finally call
updateDisplay().
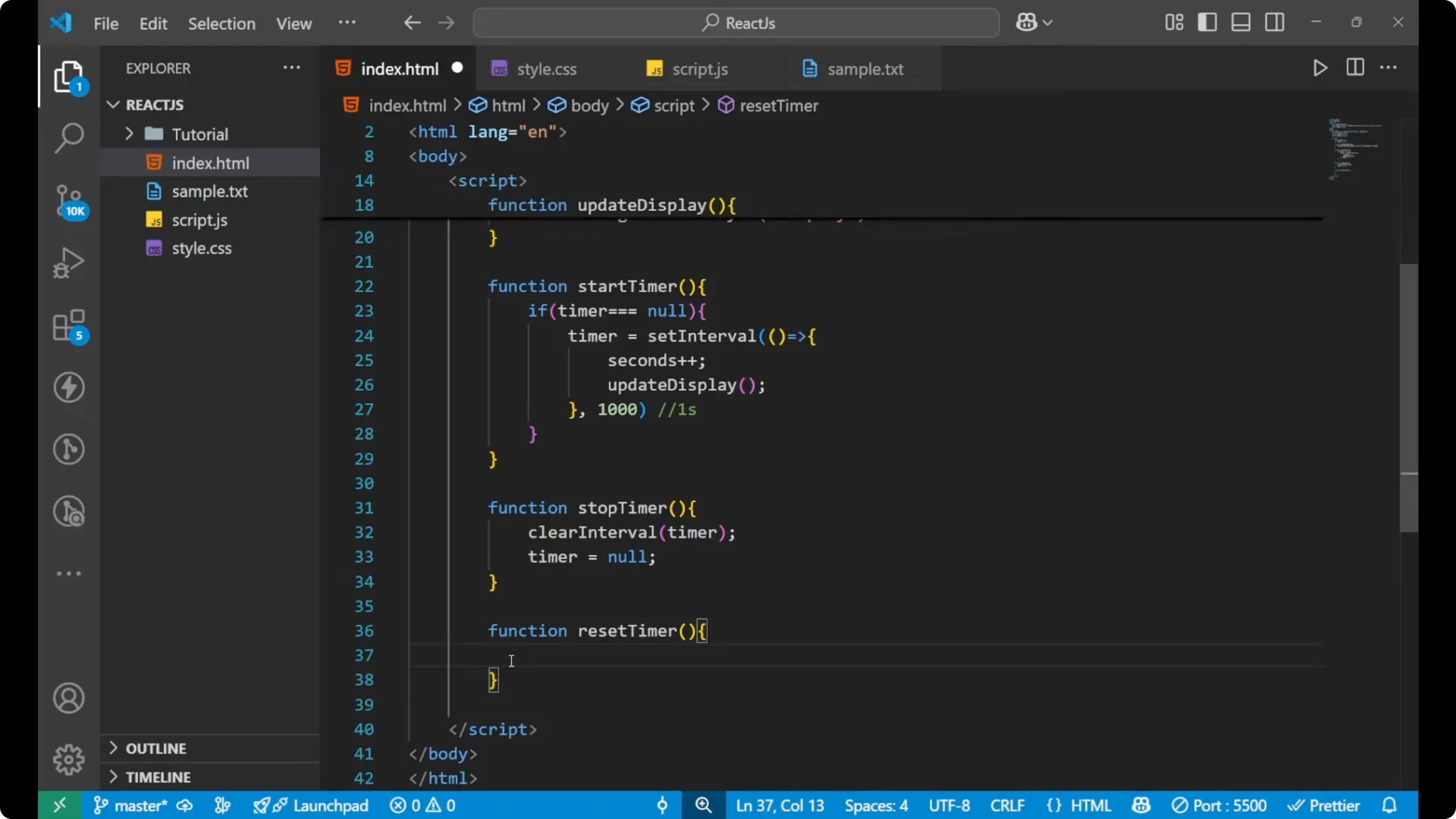
function resetTimer() {
stopTimer();
seconds = 0;
updateDisplay();
}
Here is the complete HTML plus JavaScript put together so you can run it as-is.
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>Timer</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Timer</h2>
<span id="display">0</span> seconds
<div>
<button onclick="startTimer()">Start</button>
<button onclick="stopTimer()">Stop</button>
<button onclick="resetTimer()">Reset</button>
</div>
<script>
let seconds = 0;
let timer = null;
function updateDisplay() {
document.getElementById('display').textContent = seconds;
}
function startTimer() {
if (timer === null) {
timer = setInterval(() => {
seconds++;
updateDisplay();
}, 1000);
}
}
function stopTimer() {
clearInterval(timer);
timer = null;
}
function resetTimer() {
stopTimer();
seconds = 0;
updateDisplay();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
When you connect simple buttons to onclick handlers like this, the same pattern works for UI components such as a
dropdown menu.
How the JavaScript Stopwatch works
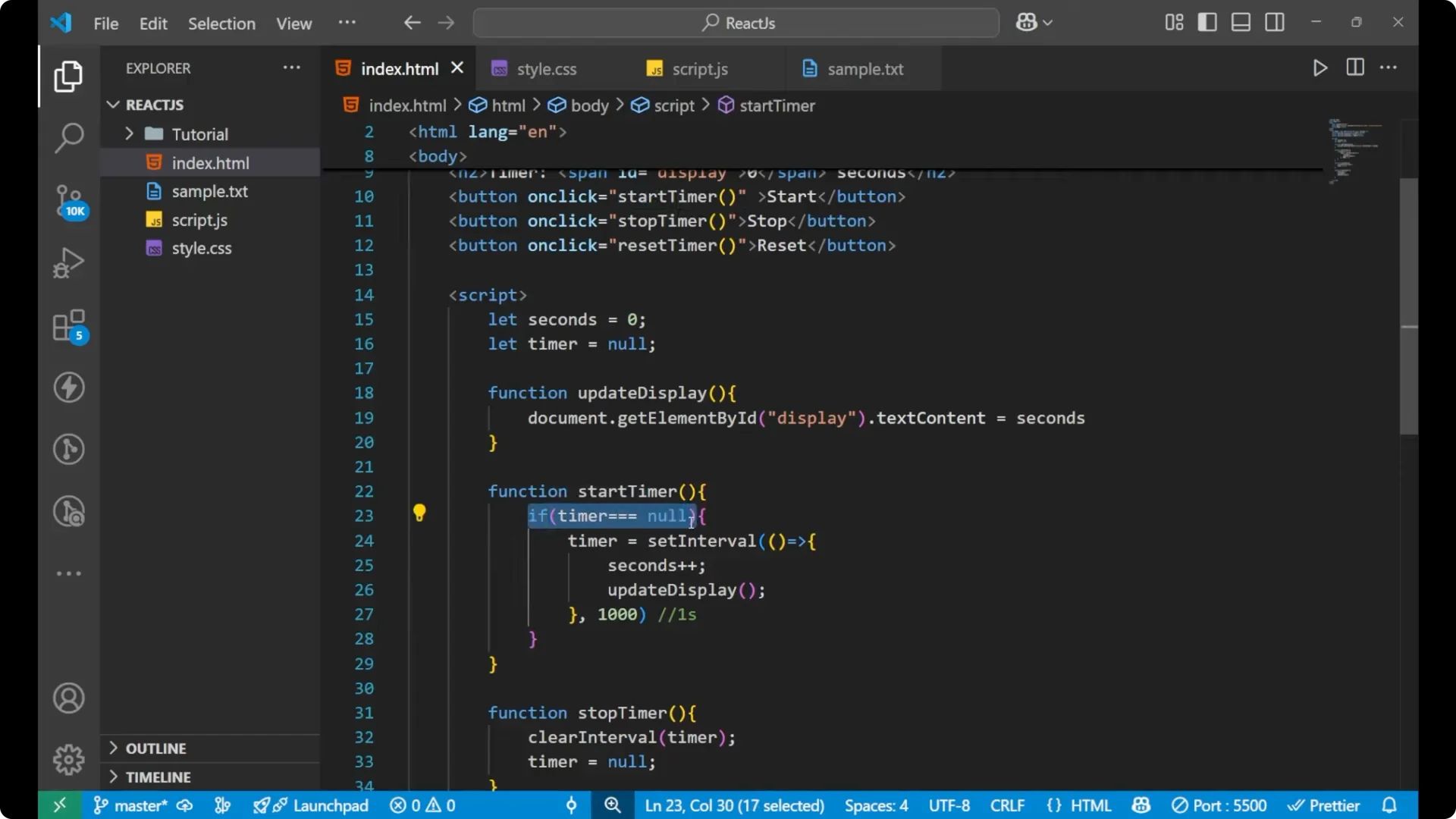
I have put the 0 as the presentation on the main screen where I am getting the timer. On the Start button we are calling
startTimer. This function checks if the timer is
null. If the timer is null, it means it is not having any
setInterval inside it. In that case we put the
setInterval inside it and start increasing the seconds.
The
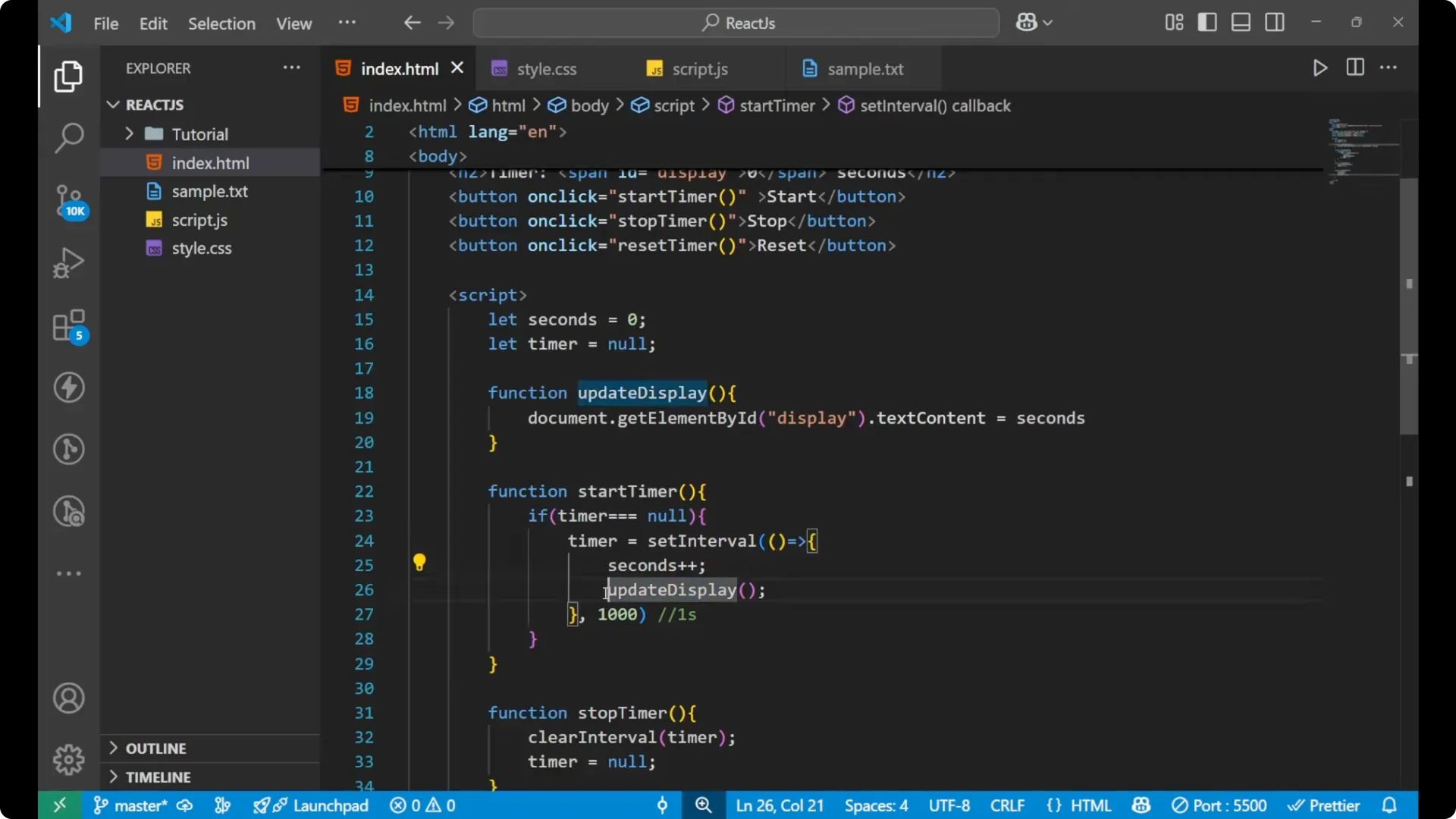
seconds value starts at 0, and every second the interval runs, we increment it and call
updateDisplay. In
updateDisplay we change the
textContent of the display element, and because seconds keeps changing, the number increases every time.
On the Stop button we are calling
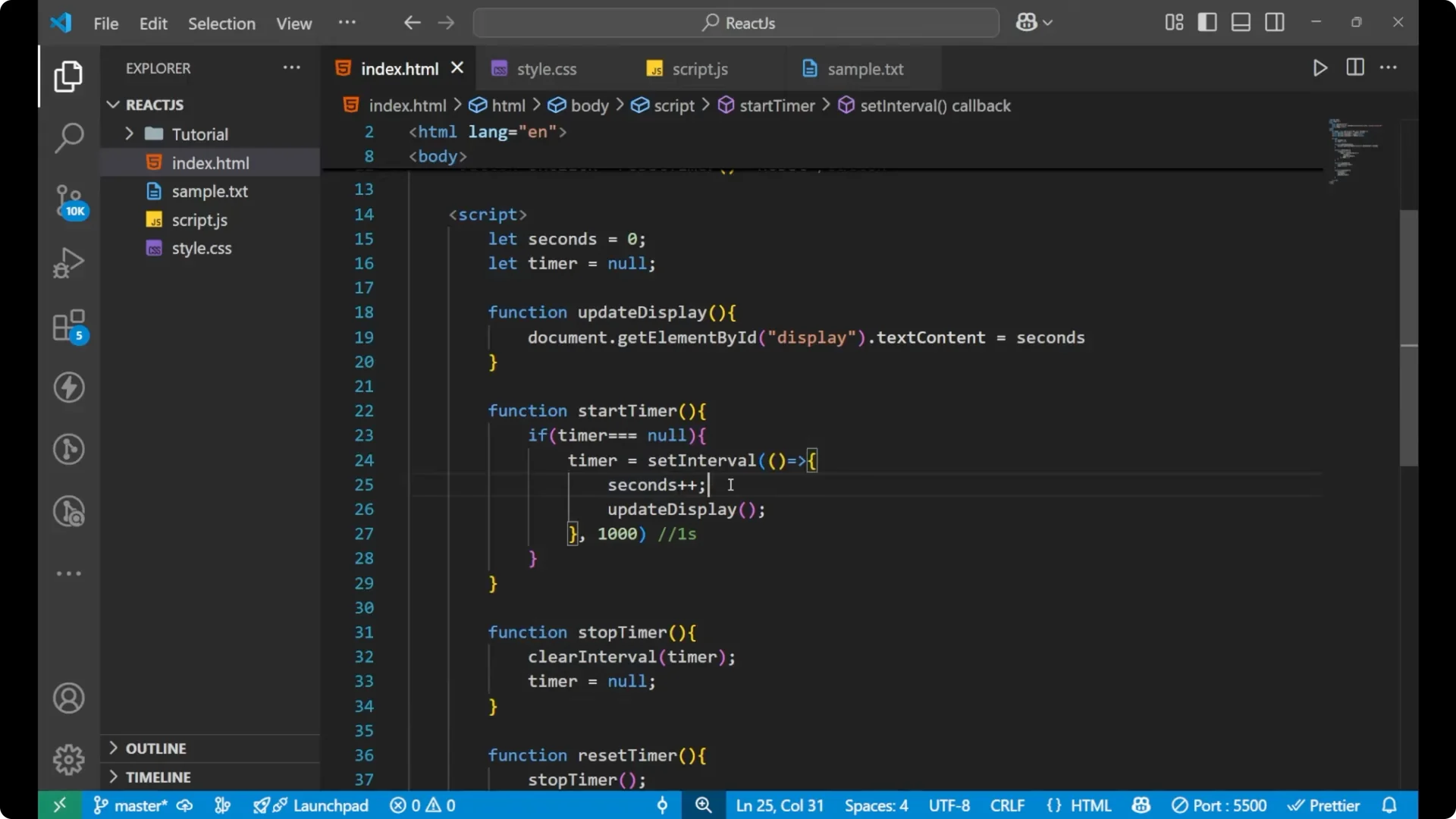
stopTimer. It calls
clearInterval(timer) which removes the setInterval from the timer. Then we put
timer = null again. This stops the changing of the seconds on the screen, but it does not reset the seconds value. The last value still shows on the display.
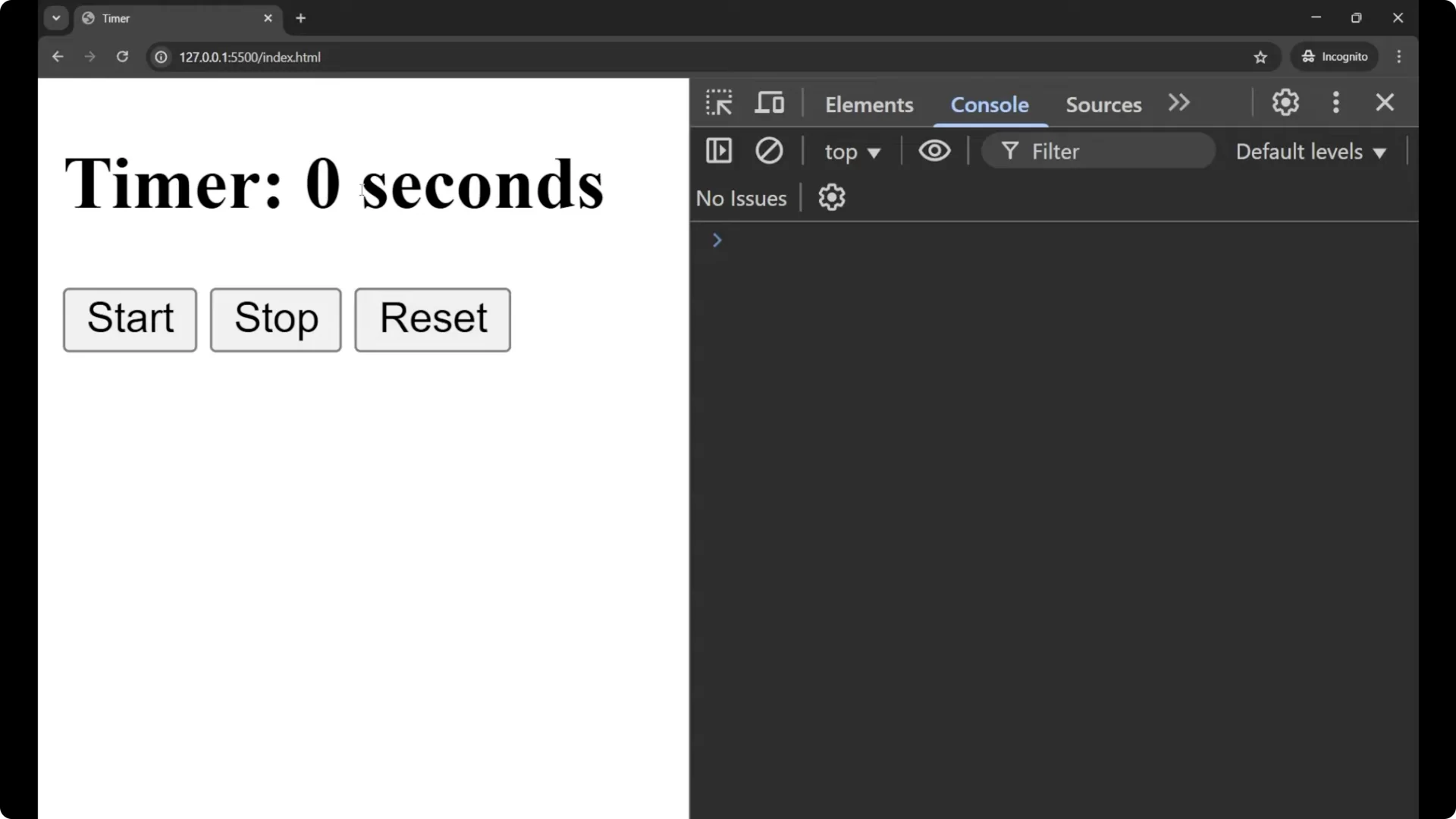
On the Reset button we are calling
resetTimer. First we remove the interval from the timer, then we set
seconds = 0, and then we call
updateDisplay. When I click on Reset you can see the timer goes back to 0.
If you want a good next step after this project, practice method chaining with arrays in
map filter.
Final thoughts
This basic
JavaScript Stopwatch helps you understand how to use functions, how to work with
setInterval and
clearInterval, and how to update the DOM on a timed schedule. It also shows how simple onclick handlers can trigger start, stop, and reset actions cleanly. Keep experimenting by adding minutes and hours, or formatting the output, and you will reinforce the same core ideas.
 I will start with the HTML part. I will name the document as timer. Create an h2 and write Timer, and then a span. I will give the span an id display and put 0 inside it. After the span I will write the word seconds. Then I will create three buttons: start, stop, and reset.
I will start with the HTML part. I will name the document as timer. Create an h2 and write Timer, and then a span. I will give the span an id display and put 0 inside it. After the span I will write the word seconds. Then I will create three buttons: start, stop, and reset.


 I’m going to the JavaScript part. I’m not going to work on the CSS – that is your task. My aim is to explain the whole functioning and how we can create it.
I’m going to the JavaScript part. I’m not going to work on the CSS – that is your task. My aim is to explain the whole functioning and how we can create it.
 Let seconds equal 0 and let timer equal null. We are initially taking seconds as 0 and the timer as null because the timer is not running.
Let seconds equal 0 and let timer equal null. We are initially taking seconds as 0 and the timer as null because the timer is not running.

 Create a function named updateDisplay that sets the textContent of the element with id display to the current seconds. I want that whenever the timer starts, the value in the display keeps changing.
Create a function named updateDisplay that sets the textContent of the element with id display to the current seconds. I want that whenever the timer starts, the value in the display keeps changing.






 Here is the complete HTML plus JavaScript put together so you can run it as-is.
Here is the complete HTML plus JavaScript put together so you can run it as-is.
 When you connect simple buttons to onclick handlers like this, the same pattern works for UI components such as a dropdown menu.
When you connect simple buttons to onclick handlers like this, the same pattern works for UI components such as a dropdown menu.
 I have put the 0 as the presentation on the main screen where I am getting the timer. On the Start button we are calling startTimer. This function checks if the timer is null. If the timer is null, it means it is not having any setInterval inside it. In that case we put the setInterval inside it and start increasing the seconds.
I have put the 0 as the presentation on the main screen where I am getting the timer. On the Start button we are calling startTimer. This function checks if the timer is null. If the timer is null, it means it is not having any setInterval inside it. In that case we put the setInterval inside it and start increasing the seconds.
 The seconds value starts at 0, and every second the interval runs, we increment it and call updateDisplay. In updateDisplay we change the textContent of the display element, and because seconds keeps changing, the number increases every time.
The seconds value starts at 0, and every second the interval runs, we increment it and call updateDisplay. In updateDisplay we change the textContent of the display element, and because seconds keeps changing, the number increases every time.
 On the Stop button we are calling stopTimer. It calls clearInterval(timer) which removes the setInterval from the timer. Then we put timer = null again. This stops the changing of the seconds on the screen, but it does not reset the seconds value. The last value still shows on the display.
On the Stop button we are calling stopTimer. It calls clearInterval(timer) which removes the setInterval from the timer. Then we put timer = null again. This stops the changing of the seconds on the screen, but it does not reset the seconds value. The last value still shows on the display.
 On the Reset button we are calling resetTimer. First we remove the interval from the timer, then we set seconds = 0, and then we call updateDisplay. When I click on Reset you can see the timer goes back to 0.
On the Reset button we are calling resetTimer. First we remove the interval from the timer, then we set seconds = 0, and then we call updateDisplay. When I click on Reset you can see the timer goes back to 0.
 If you want a good next step after this project, practice method chaining with arrays in map filter.
If you want a good next step after this project, practice method chaining with arrays in map filter.
