We will learn about how we can take the user input with the help of the prompt method in JavaScript. Your prompt method opens a popup where the user can enter some text. One thing which is very important about prompt is that it
always returns a string. If the user presses Cancel, in that case it returns
null. We can use that null in our conditions.
JavaScript Prompt Input Handling: What prompt returns
Prompt returns a string for any input, so either the user inputs a number or a string it will always return a string. If the user presses Cancel in the prompt, in that case you get a null from JavaScript. We can use that to decide if there is any need to do further condition checking.
JavaScript Prompt Input Handling: Getting and Validating Age Input
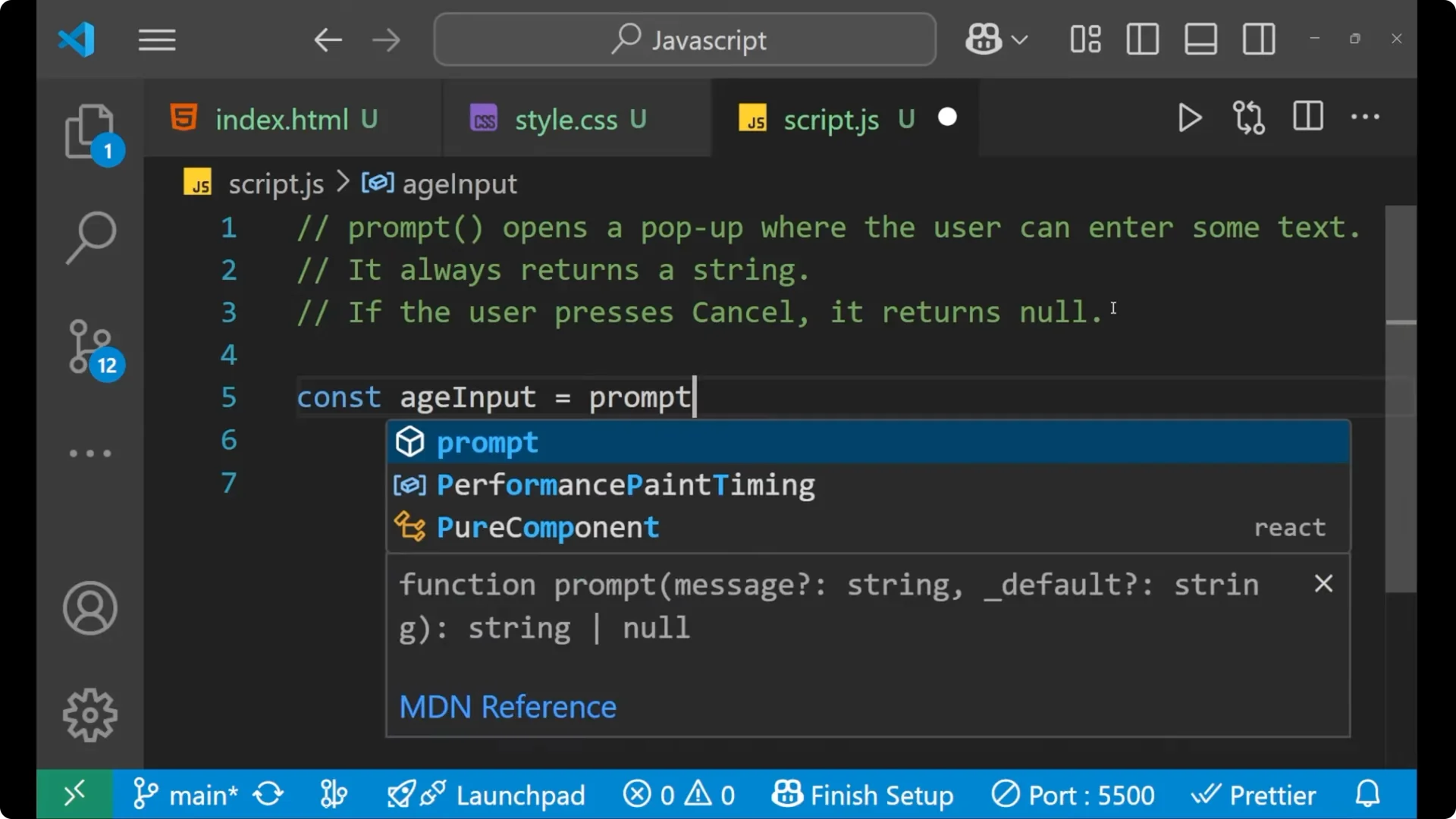
Let’s take a variable and read the input.
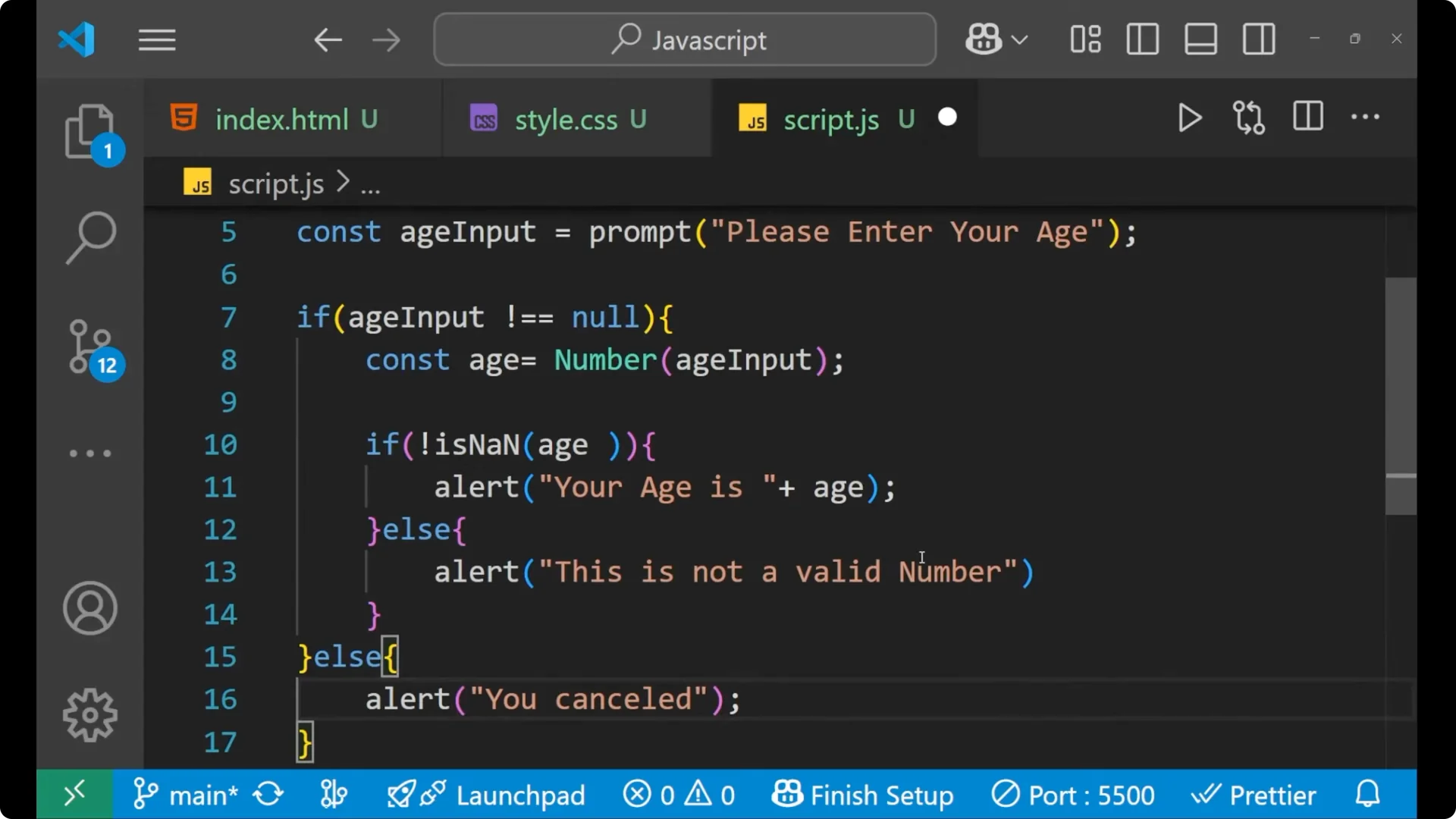
const ageInput = prompt("Please enter your age");
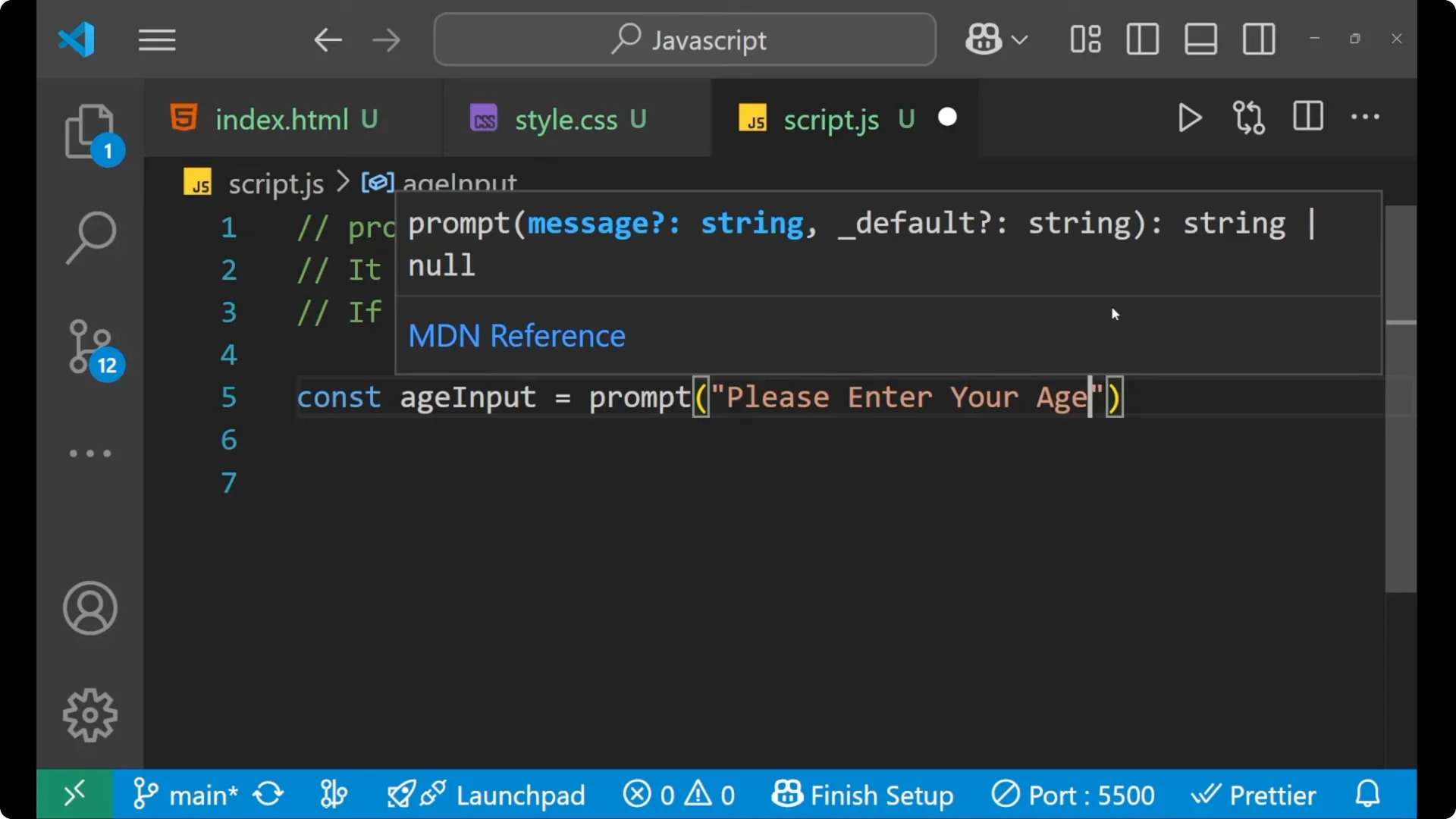
After that we can put the condition like if `ageInput !== null`. If the user presses the Cancel button in that case it returns a null that he or she has not entered anything, they have cancelled it. If they cancelled, there is no need to do further checks.
Inside the branch where input is present, convert the string to a number. Since prompt returns a string, for converting it into a number we will write `Number(ageInput)` because age will be in number.
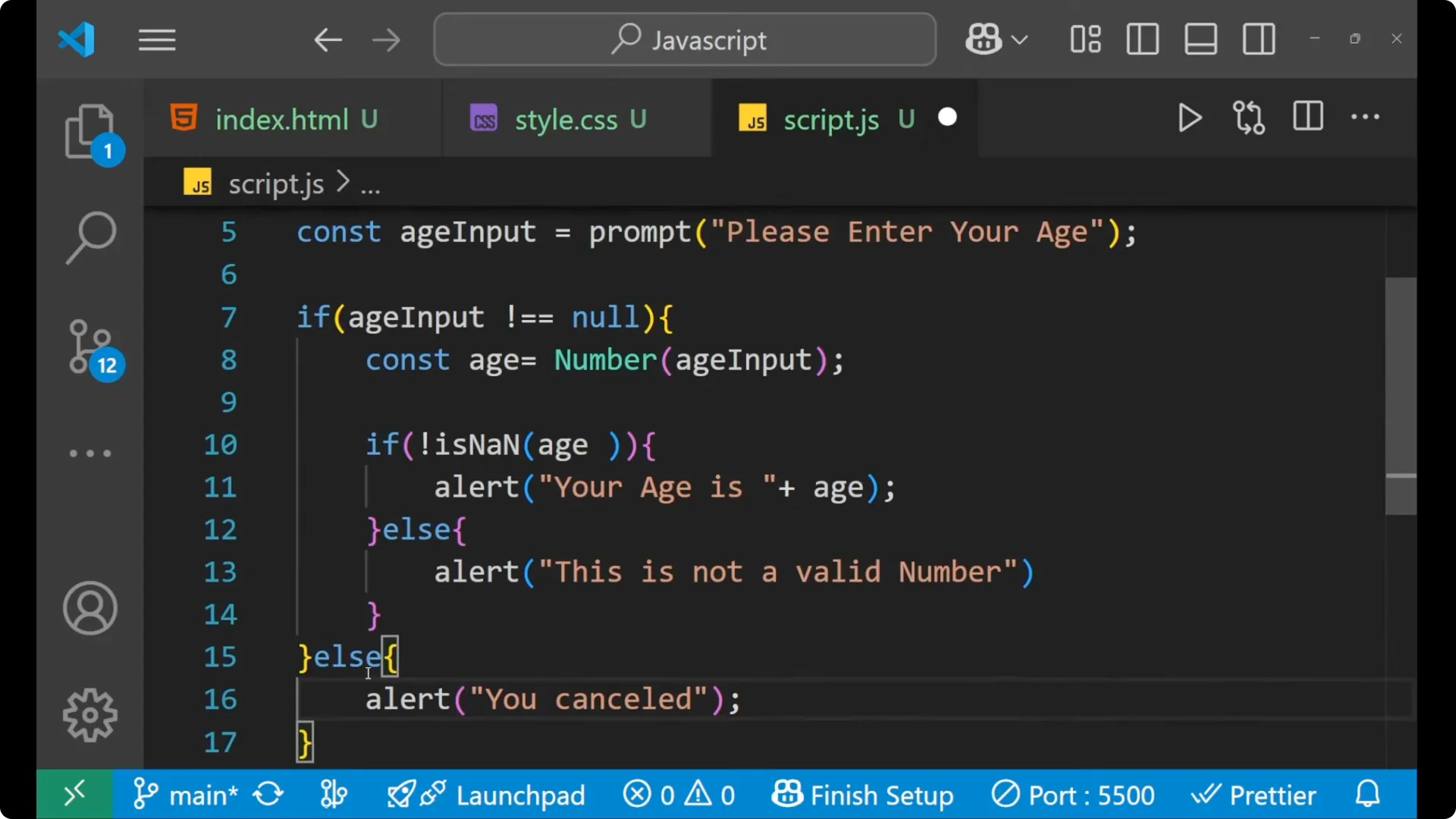
if (ageInput !== null) {
const age = Number(ageInput);
// if your age is not a number
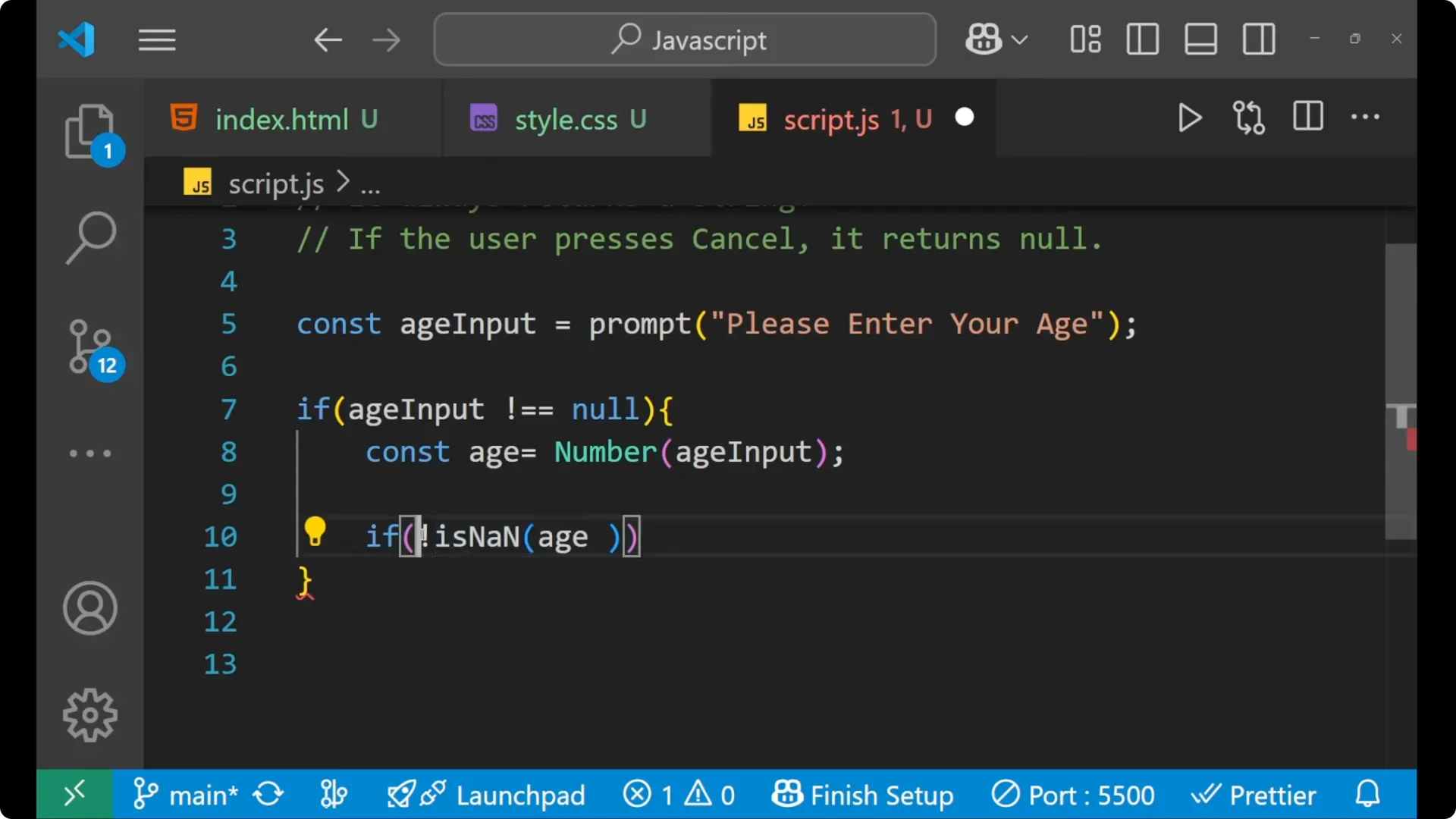
if (!isNaN(age)) {
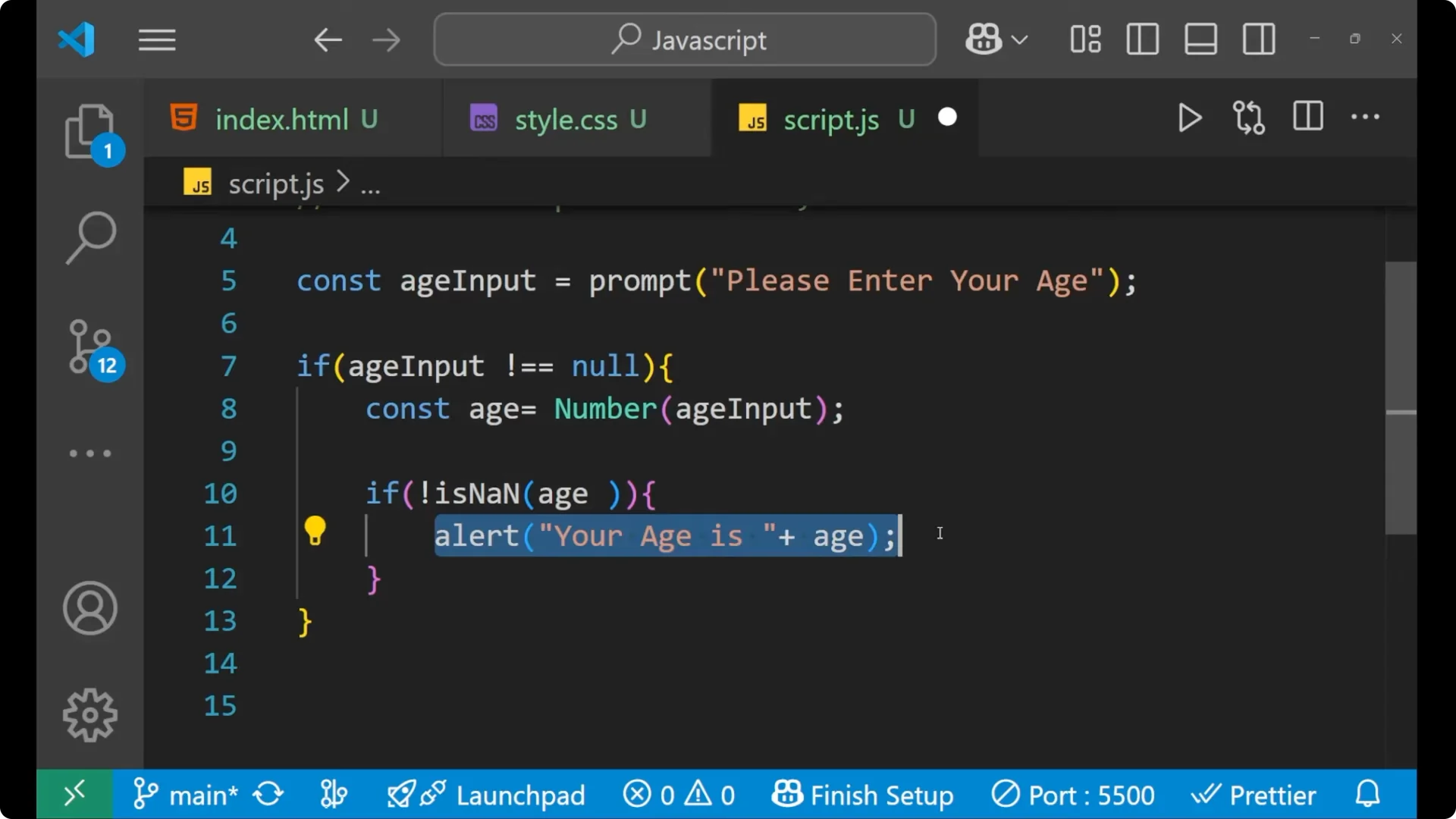
alert("Your age is " + age);
} else {
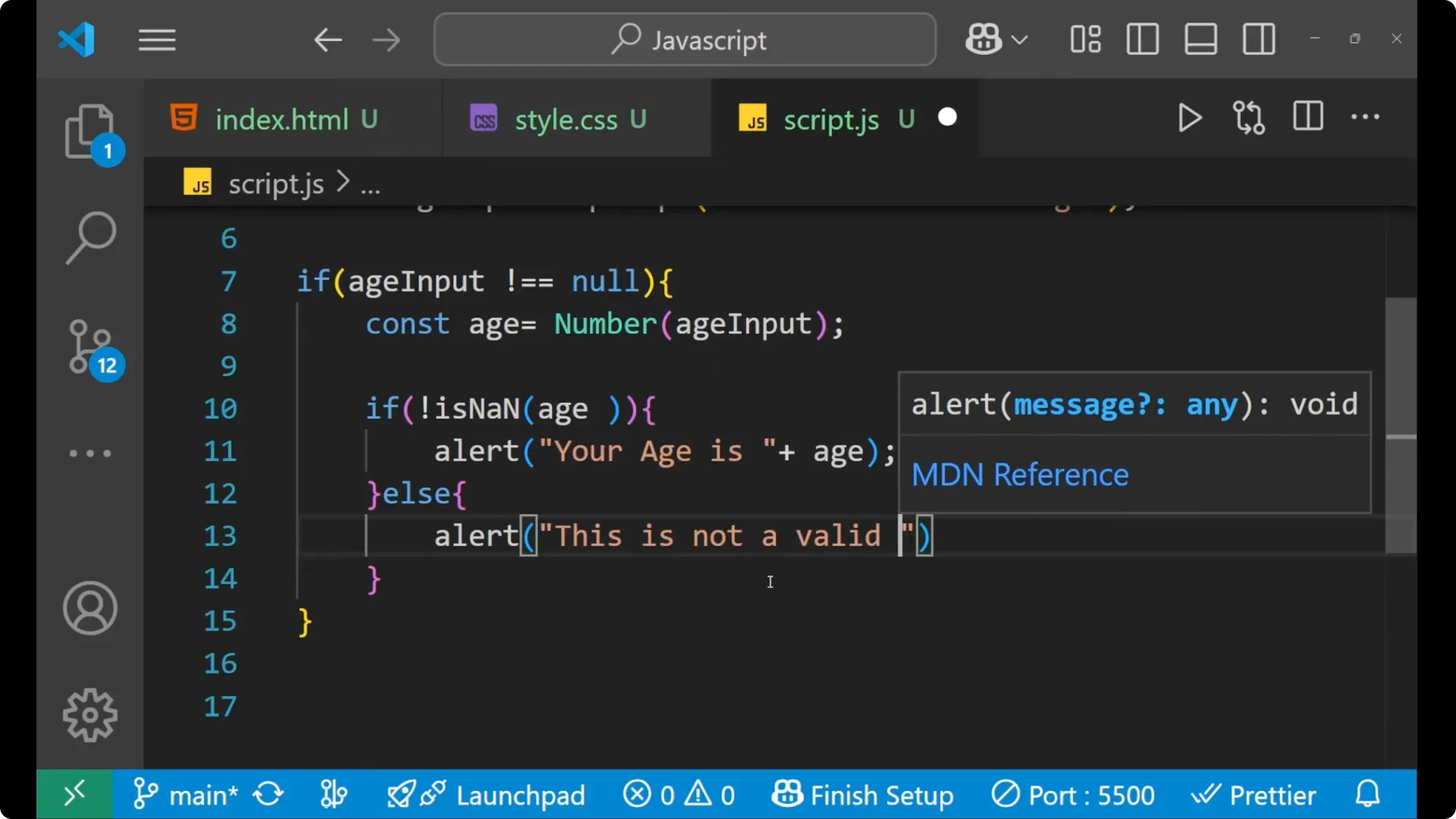
alert("This is not a valid number.");
}
} else {
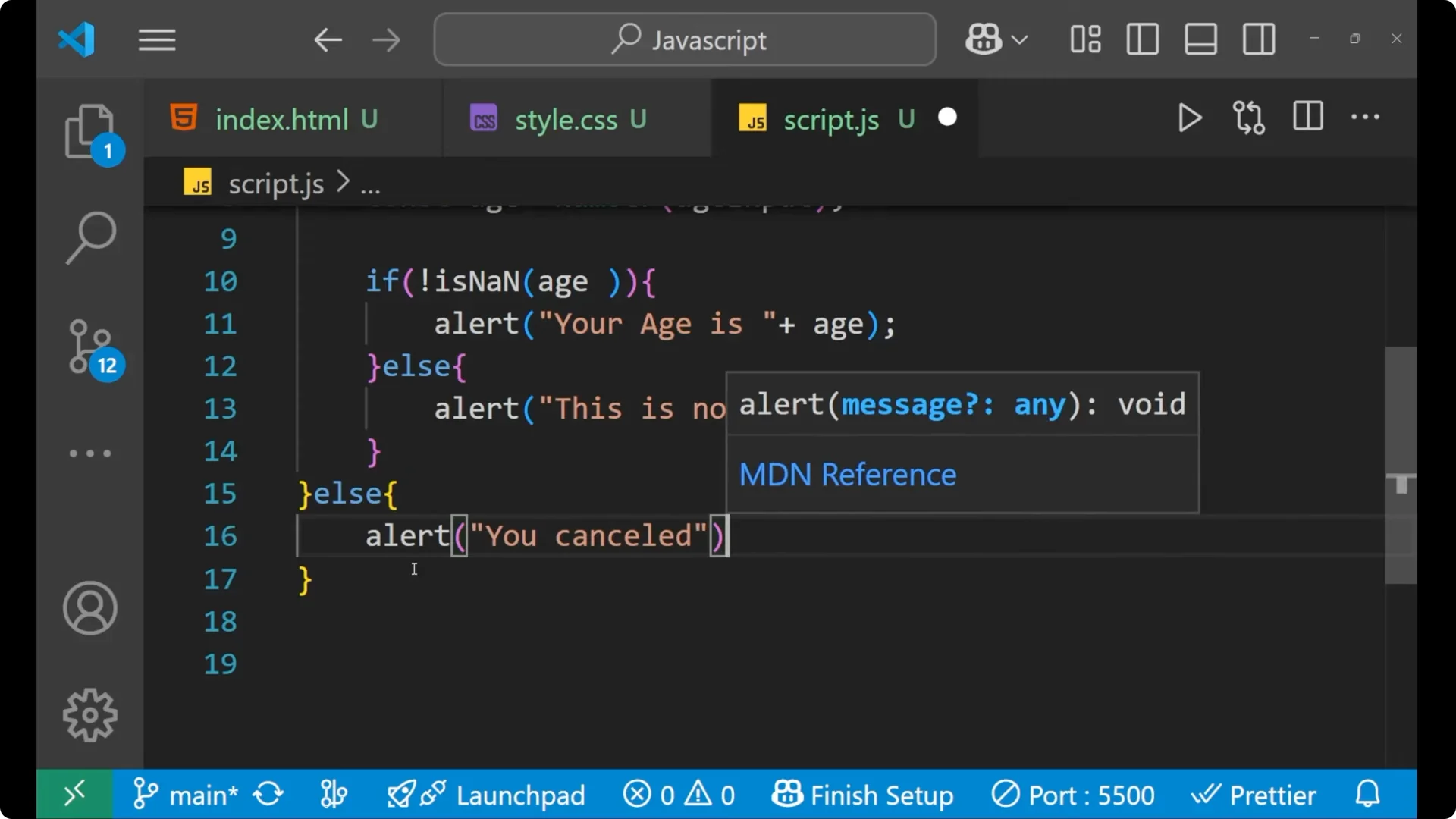
alert("You cancelled.");
}
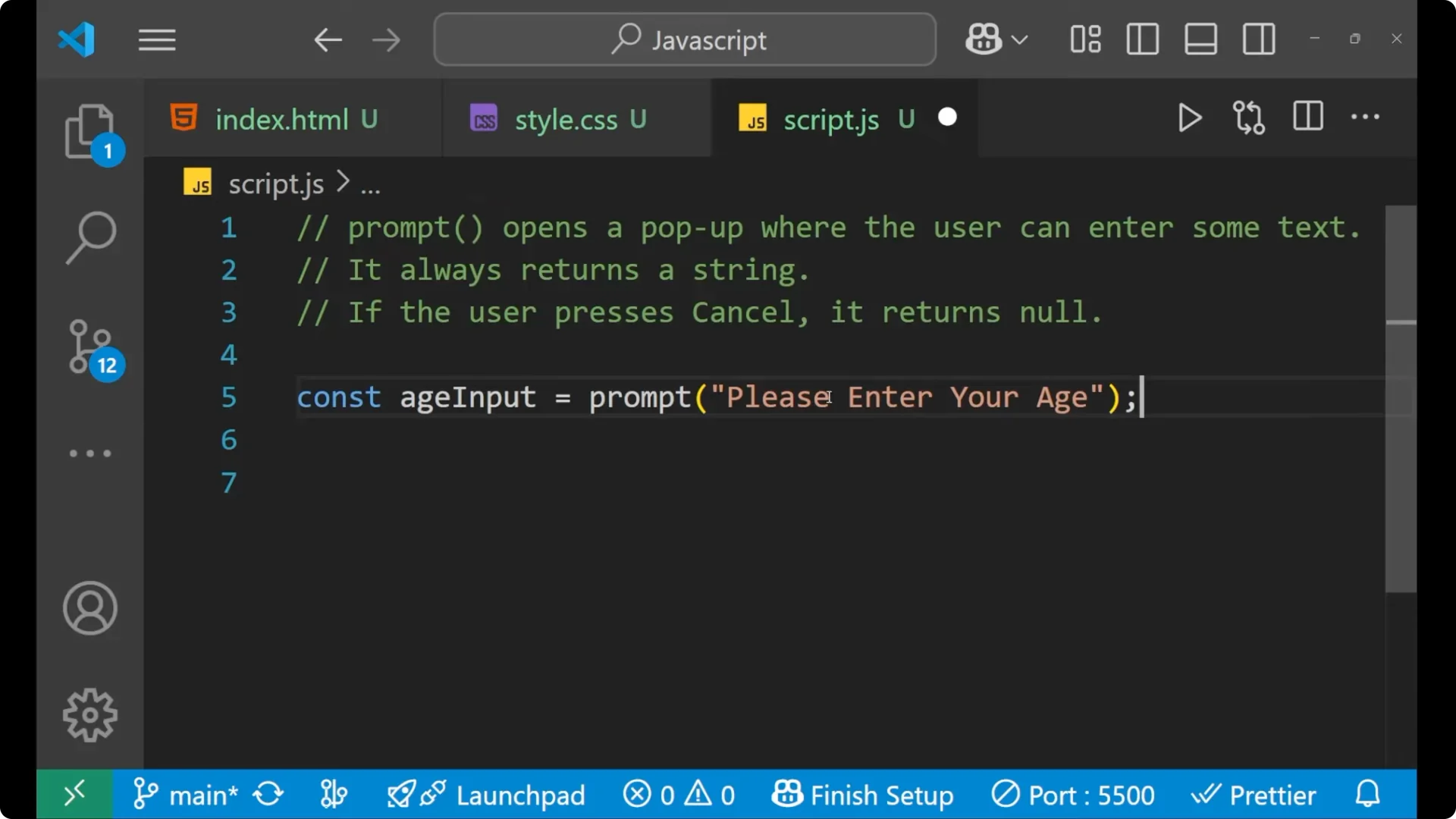
JavaScript Prompt Input Handling: Step-by-step
Take a variable: `const ageInput = prompt(“Please enter your age”);`
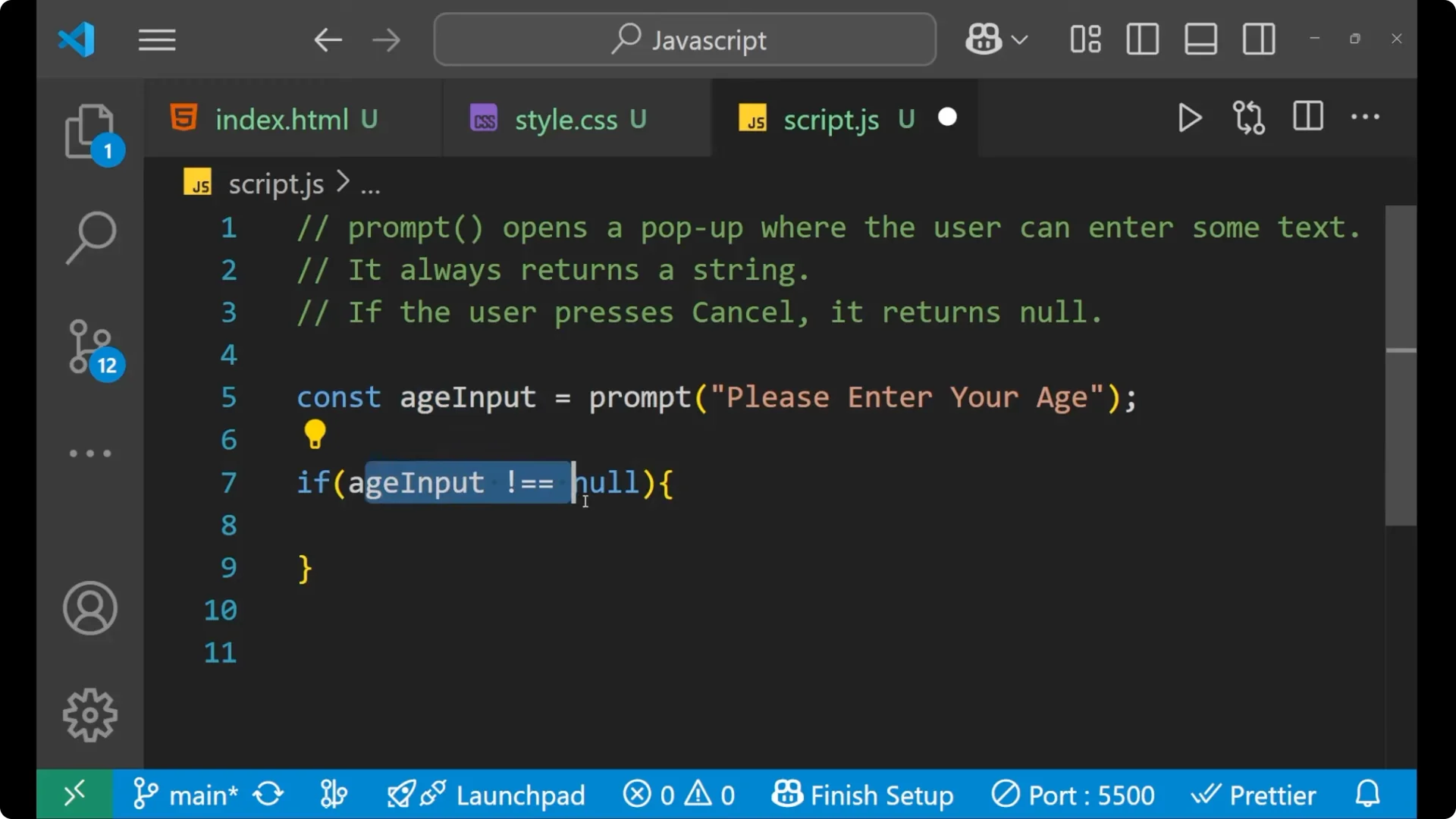
Put the condition `if (ageInput !== null)` so that further condition checking only happens when input is not null.
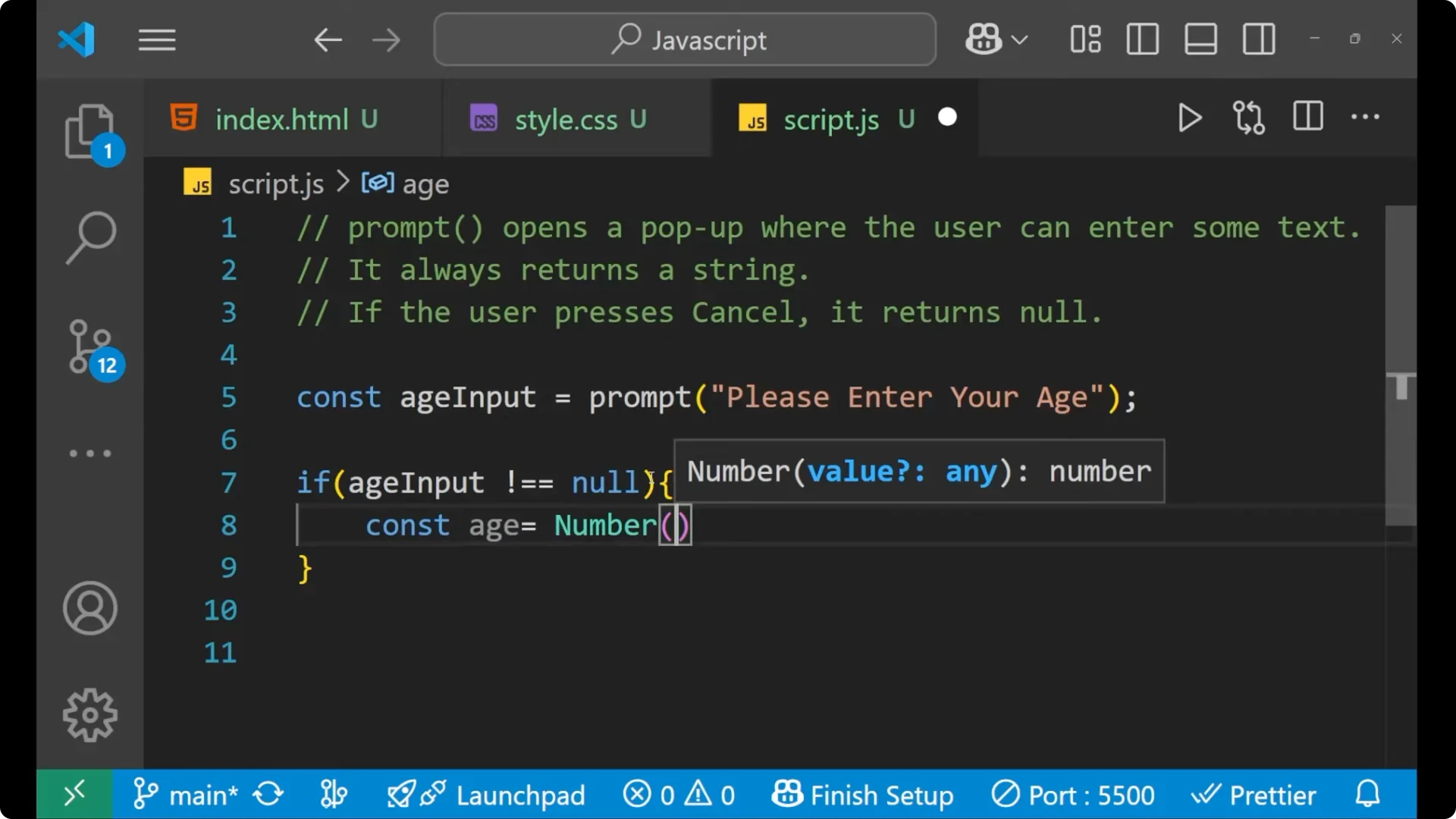
Write `const age = Number(ageInput)` because that particular input has stored inside `ageInput`, and we want a number.
Put the condition that checks numeric input. If `isNaN(age)` means your age is
not a number, so we put the exclamation mark which says that your particular age is a number: `if (!isNaN(age)) { … }`.
In such case you will give the alert as `Your age is ` plus the computed age.
Else you say `alert(“This is not a valid number.”)` because in case the user made the input as some string like `hello` in the age section, it will not be able to convert it into a number.
Else for the condition that `ageInput === null`, make the alert as `You cancelled` so that every edge case is covered.
Full example
<!doctype html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
const ageInput = prompt("Please enter your age");
if (ageInput !== null) {
const age = Number(ageInput);
if (!isNaN(age)) {
alert("Your age is " + age);
} else {
alert("This is not a valid number.");
}
} else {
alert("You cancelled.");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
If you enter `12` and click OK, it shows that your age is 12. If you enter a string like `hello` and click OK, it says that this is not a valid number. If you click Cancel, it says that you cancelled, which means every edge case is working properly.
Final Thoughts on JavaScript Prompt Input Handling
Prompt is simple to use for quick input. It
always returns a string, and Cancel gives you
null. Convert the input with `Number(…)`, check `!isNaN(…)` to confirm it is numeric, show the result for valid input, report an invalid number for non numeric input, and handle the cancel case explicitly. This is the whole logic we need to take user input with the help of JavaScript prompt.

 Prompt returns a string for any input, so either the user inputs a number or a string it will always return a string. If the user presses Cancel in the prompt, in that case you get a null from JavaScript. We can use that to decide if there is any need to do further condition checking.
Prompt returns a string for any input, so either the user inputs a number or a string it will always return a string. If the user presses Cancel in the prompt, in that case you get a null from JavaScript. We can use that to decide if there is any need to do further condition checking.
 Let’s take a variable and read the input.
Let’s take a variable and read the input.
 After that we can put the condition like if `ageInput !== null`. If the user presses the Cancel button in that case it returns a null that he or she has not entered anything, they have cancelled it. If they cancelled, there is no need to do further checks.
Inside the branch where input is present, convert the string to a number. Since prompt returns a string, for converting it into a number we will write `Number(ageInput)` because age will be in number.
After that we can put the condition like if `ageInput !== null`. If the user presses the Cancel button in that case it returns a null that he or she has not entered anything, they have cancelled it. If they cancelled, there is no need to do further checks.
Inside the branch where input is present, convert the string to a number. Since prompt returns a string, for converting it into a number we will write `Number(ageInput)` because age will be in number.

 Put the condition `if (ageInput !== null)` so that further condition checking only happens when input is not null.
Put the condition `if (ageInput !== null)` so that further condition checking only happens when input is not null.
 Write `const age = Number(ageInput)` because that particular input has stored inside `ageInput`, and we want a number.
Write `const age = Number(ageInput)` because that particular input has stored inside `ageInput`, and we want a number.
 Put the condition that checks numeric input. If `isNaN(age)` means your age is not a number, so we put the exclamation mark which says that your particular age is a number: `if (!isNaN(age)) { … }`.
Put the condition that checks numeric input. If `isNaN(age)` means your age is not a number, so we put the exclamation mark which says that your particular age is a number: `if (!isNaN(age)) { … }`.
 In such case you will give the alert as `Your age is ` plus the computed age.
In such case you will give the alert as `Your age is ` plus the computed age.
 Else you say `alert(“This is not a valid number.”)` because in case the user made the input as some string like `hello` in the age section, it will not be able to convert it into a number.
Else you say `alert(“This is not a valid number.”)` because in case the user made the input as some string like `hello` in the age section, it will not be able to convert it into a number.
 Else for the condition that `ageInput === null`, make the alert as `You cancelled` so that every edge case is covered.
Else for the condition that `ageInput === null`, make the alert as `You cancelled` so that every edge case is covered.

 If you enter `12` and click OK, it shows that your age is 12. If you enter a string like `hello` and click OK, it says that this is not a valid number. If you click Cancel, it says that you cancelled, which means every edge case is working properly.
If you enter `12` and click OK, it shows that your age is 12. If you enter a string like `hello` and click OK, it says that this is not a valid number. If you click Cancel, it says that you cancelled, which means every edge case is working properly.
