Accessing HTML elements using JavaScript is the most important and fundamental topic by which we can perform
DOM manipulation and other work with JavaScript. I will show simple ways to select elements and then change their text or styles.
I have some of the HTML part here. The first is a heading whose id is page-title. The next two lines are paragraphs, and their class is intro. The third is a button whose id is my-button.
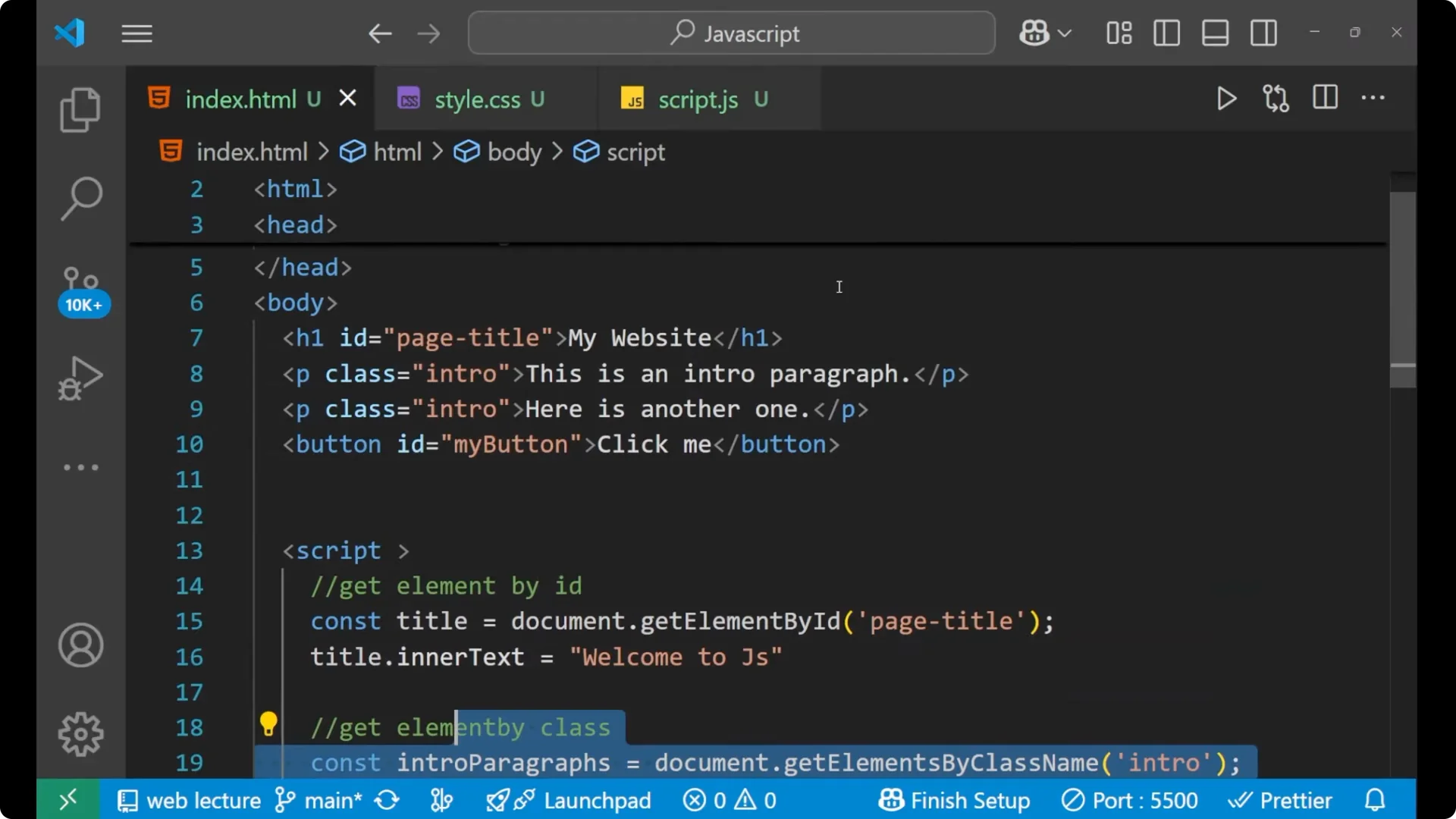
<h1 id="page-title">My Website</h1>
<p class="intro">This is the first intro paragraph.</p>
<p class="intro">This is the second intro paragraph.</p>
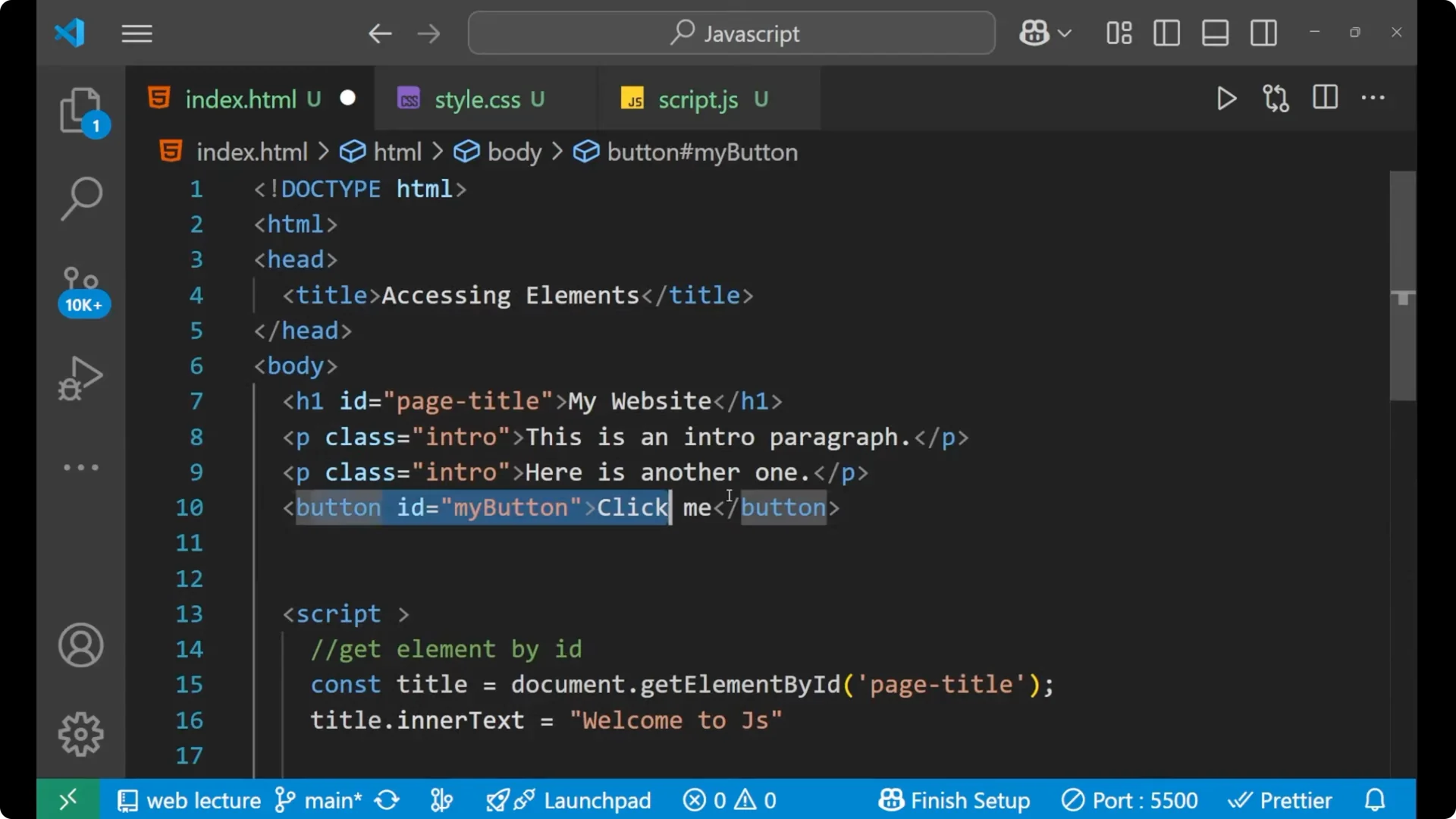
<button id="my-button">Press Me</button>
JavaScript DOM Selection by ID with getElementById
The first method to access an element is by using the
document object. The document represents the whole browser page. Then you use the
getElementById method to get an element by its id.
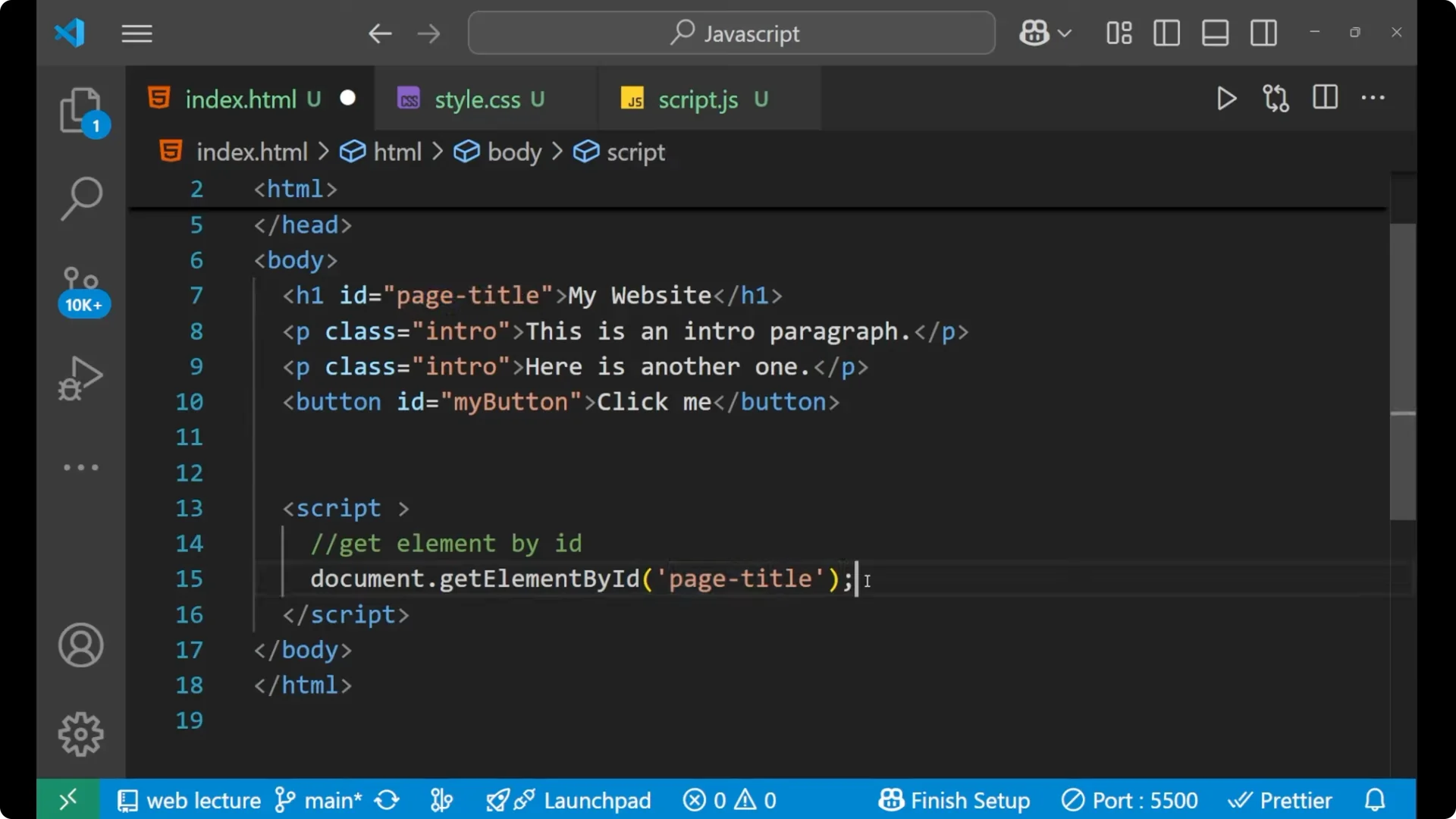
Select the element by id.
Store it inside a variable.
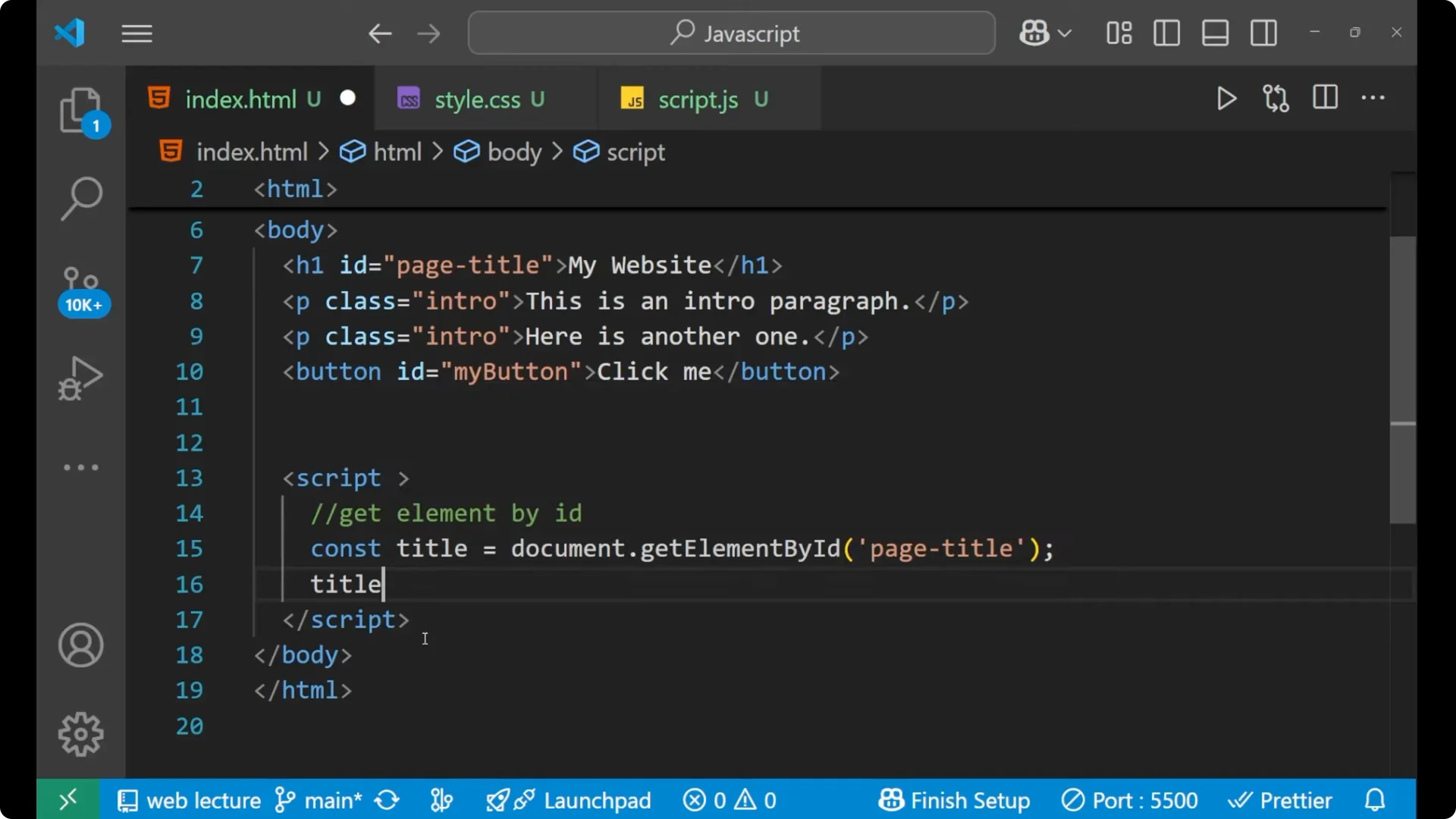
Change its inner text.
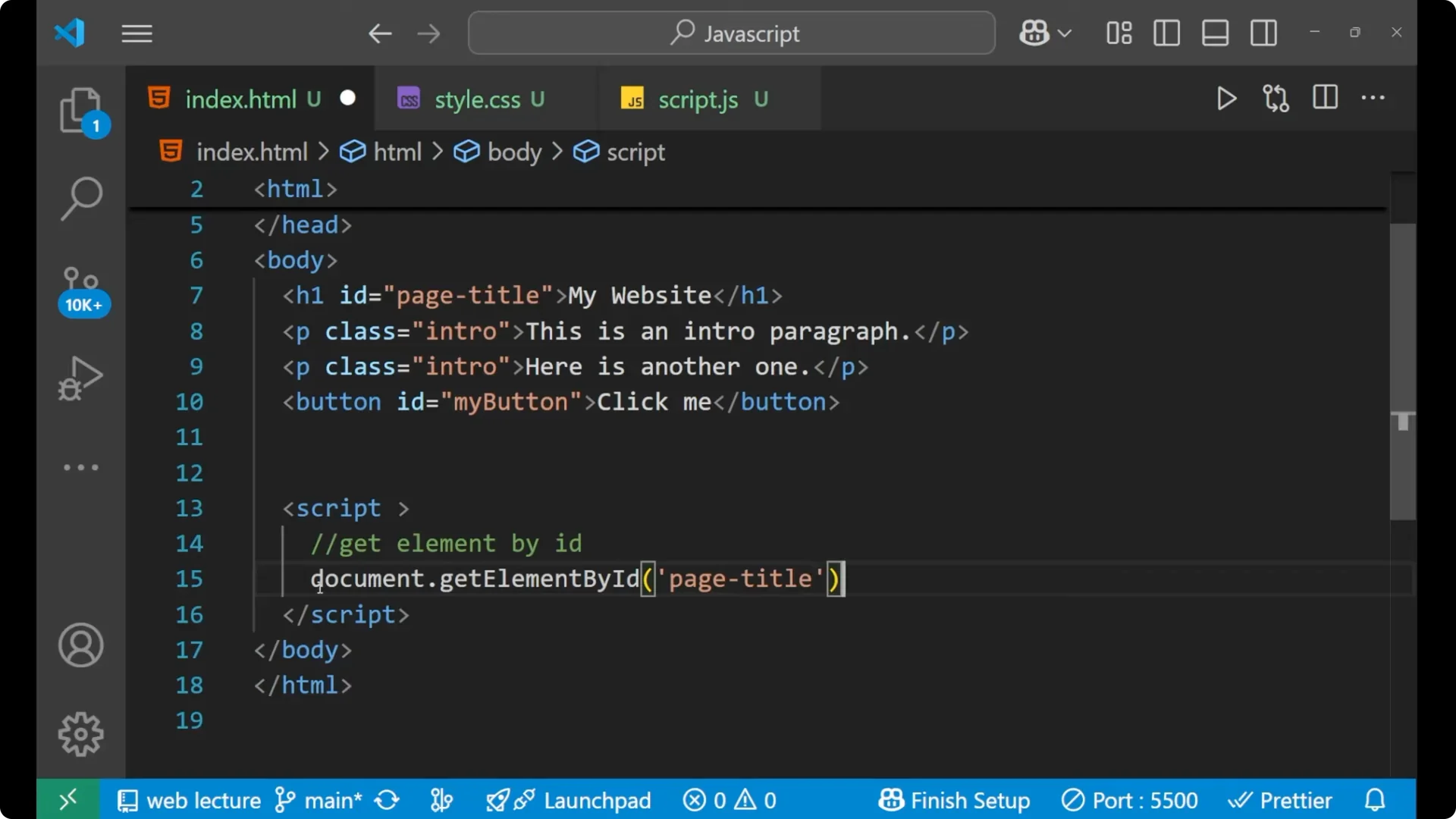
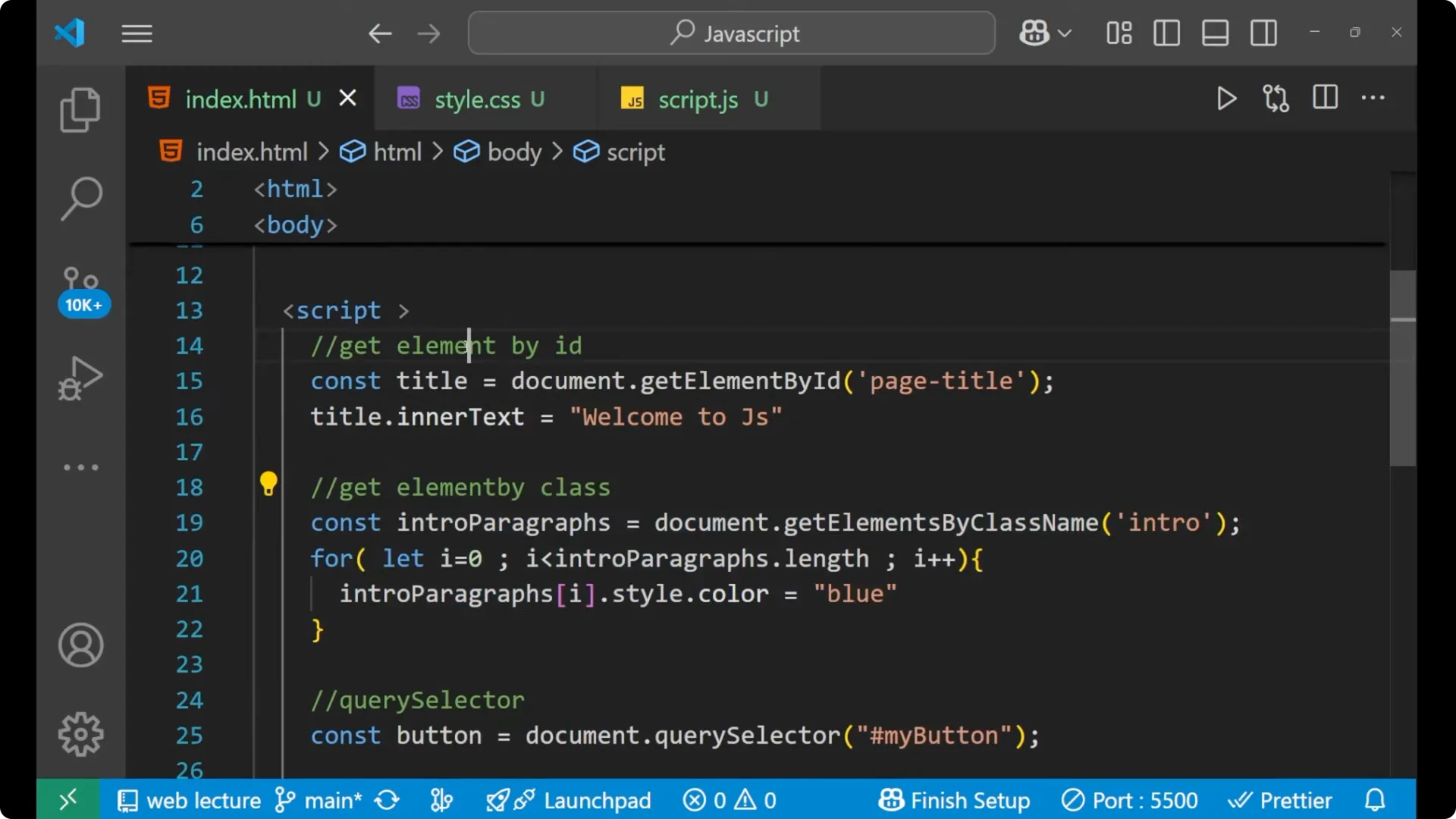
const title = document.getElementById('page-title');
// Perform an operation on it
title.innerText = 'Welcome to JS';
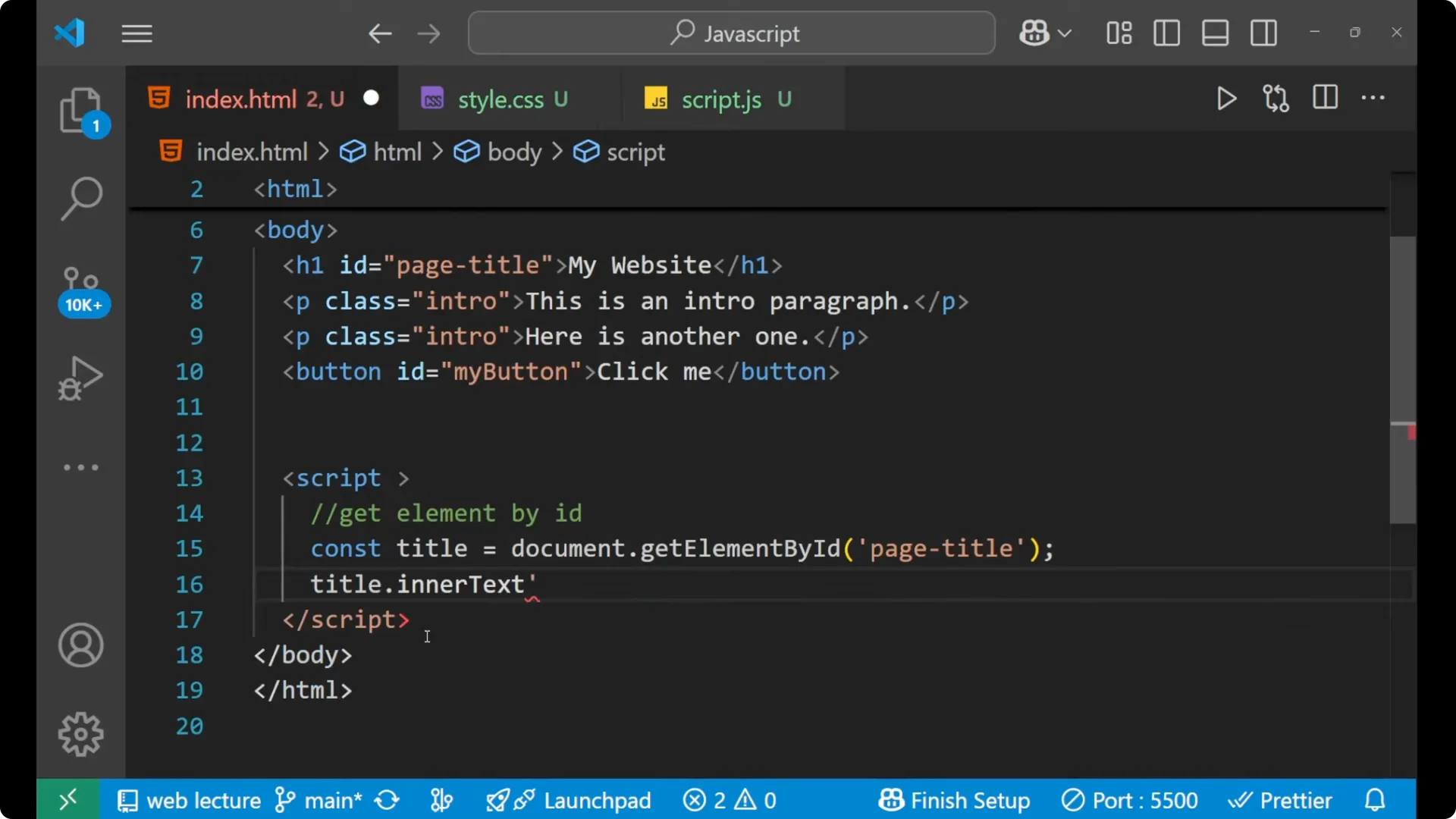
Earlier it was My Website and now it is Welcome to JS. We can simply change the HTML part with the help of JavaScript by performing
DOM manipulation and using
document.getElementById.

JavaScript DOM Selection by Class with getElementsByClassName
The second method is getting elements with the help of class using
getElementsByClassName. For selecting elements with a class, this returns a live HTMLCollection, so we typically loop over it.
Select all elements with the class intro.
Store them in a variable.
Loop through the collection up to its length.
Change the style for each indexed element.
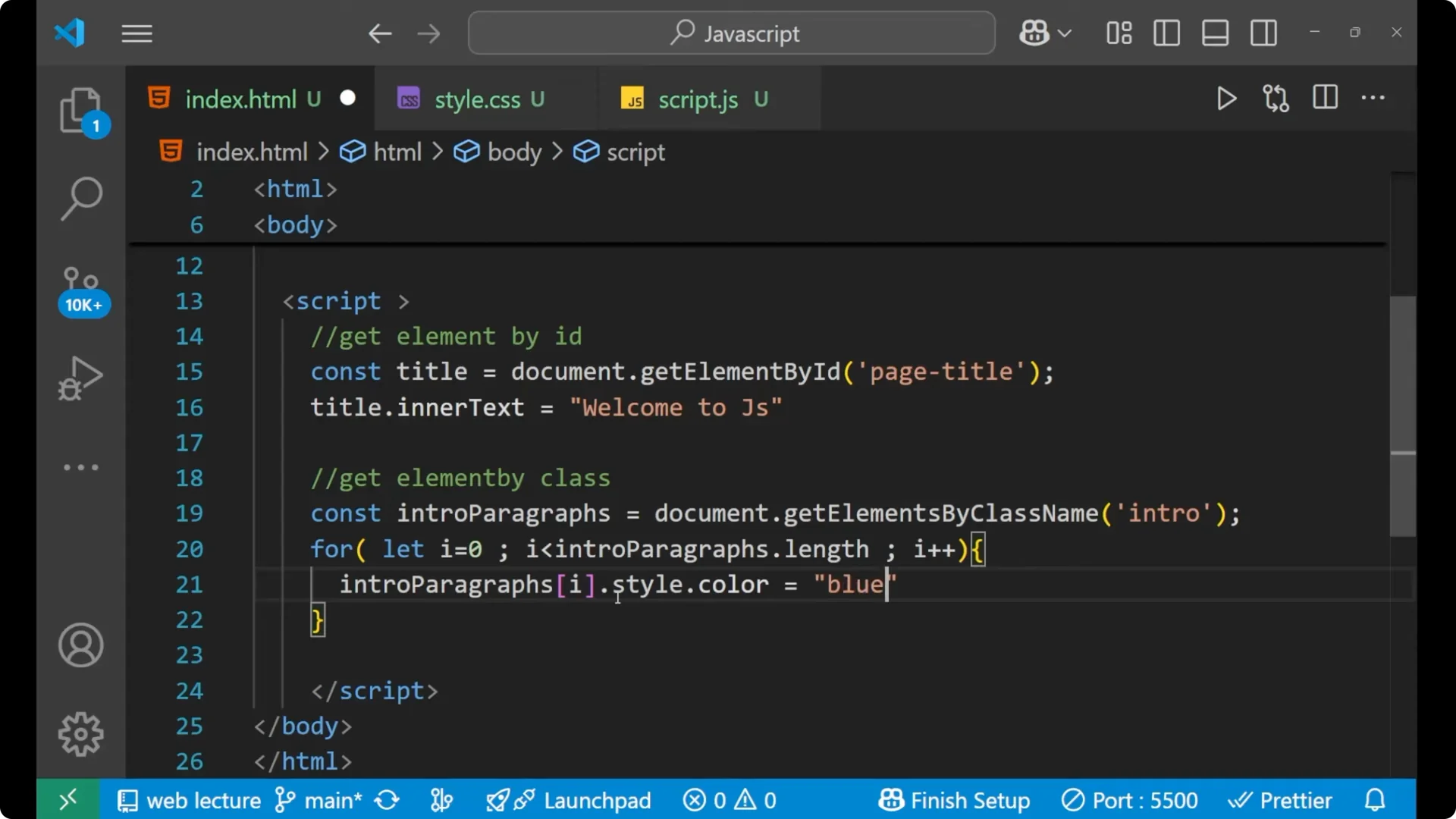
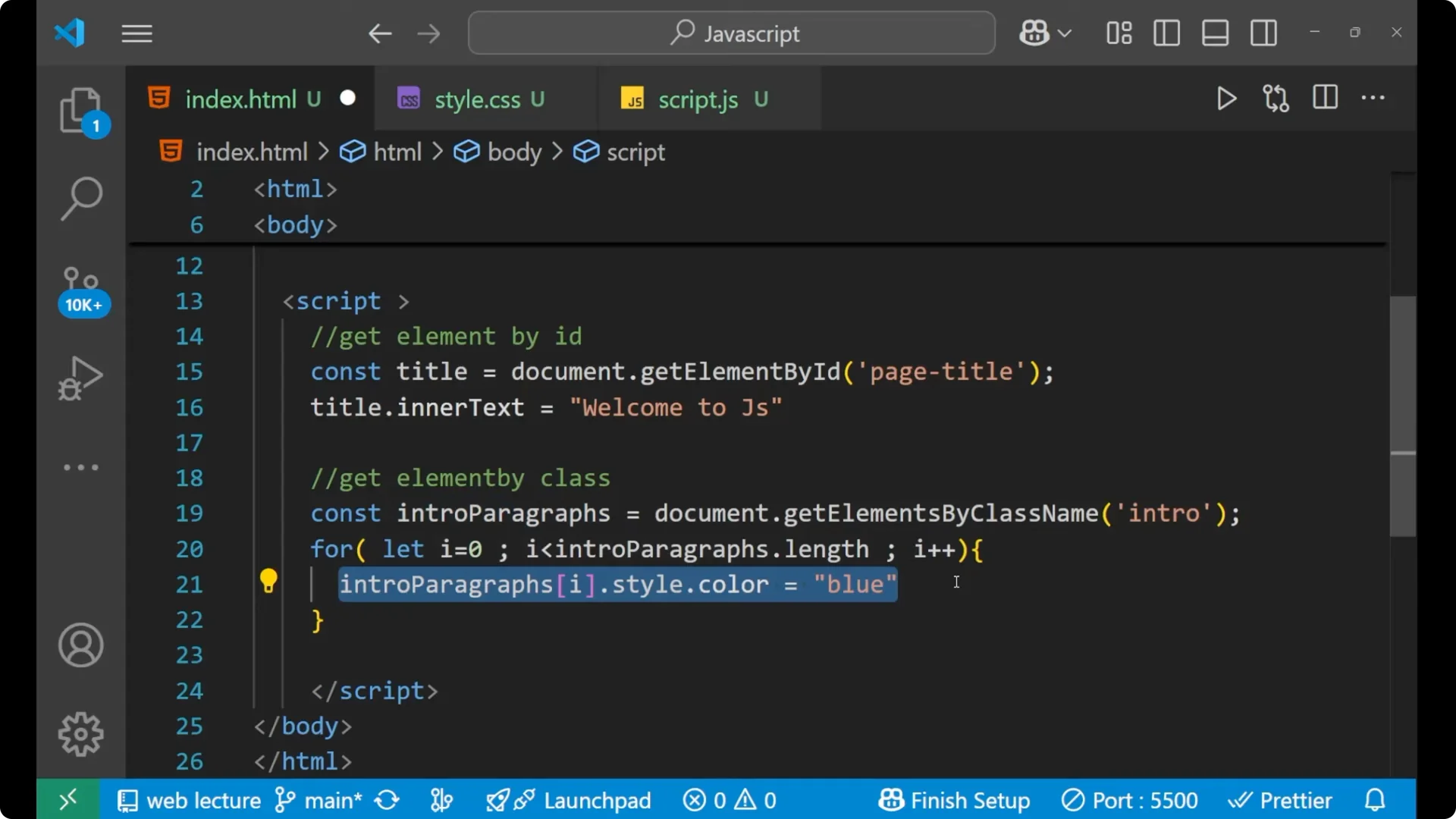
const introParagraphs = document.getElementsByClassName('intro');
for (let i = 0; i < introParagraphs.length; i++) {
introParagraphs[i].style.color = 'blue';
}
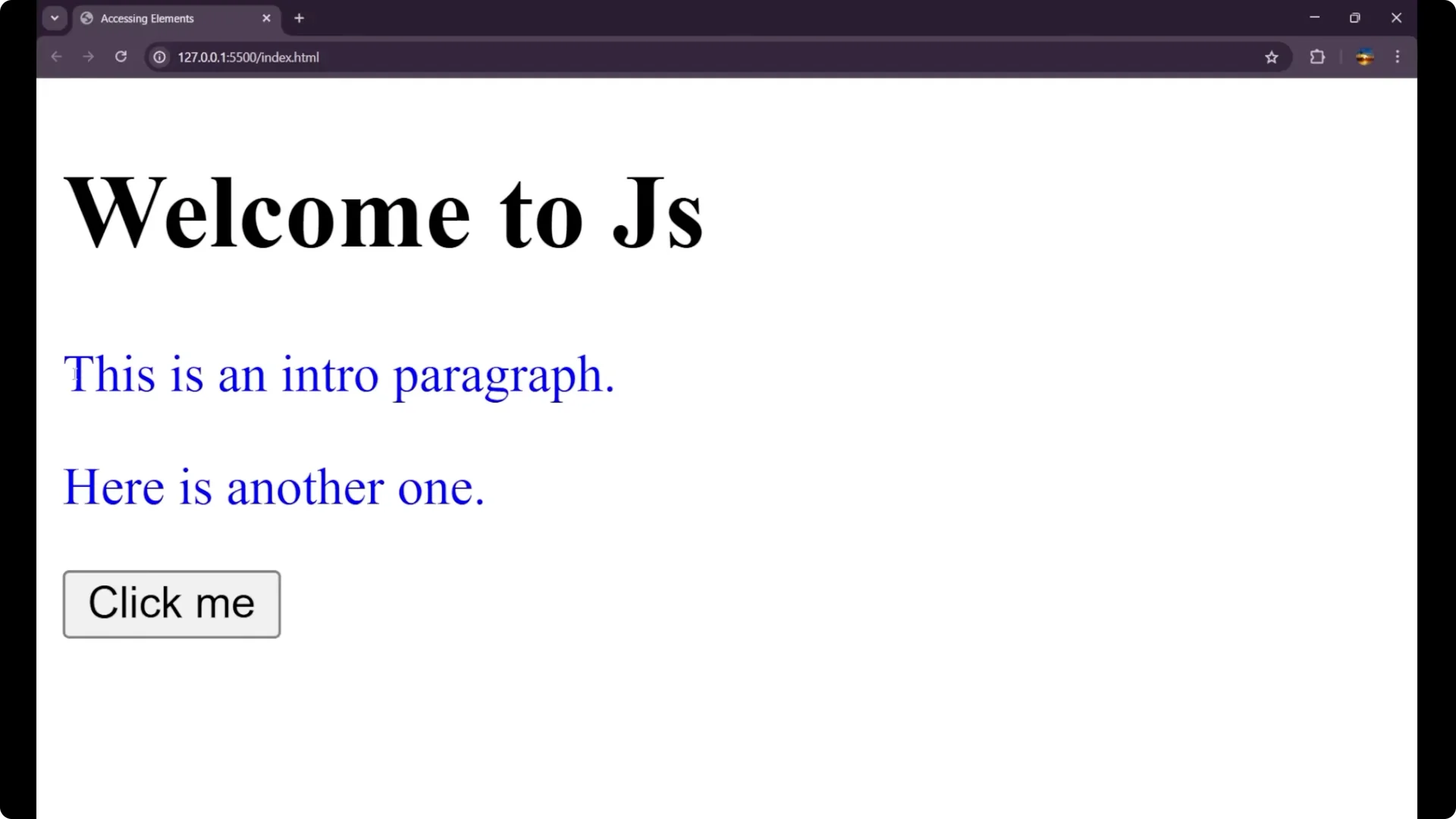
It will select both paragraphs, because both have the class intro. You can apply conditions too, like styling odd or even indexes differently.
JavaScript DOM Selection with querySelector
 querySelector
querySelector lets you select with CSS selectors. You can select by id or class using the same method.
Use a hash for an id.
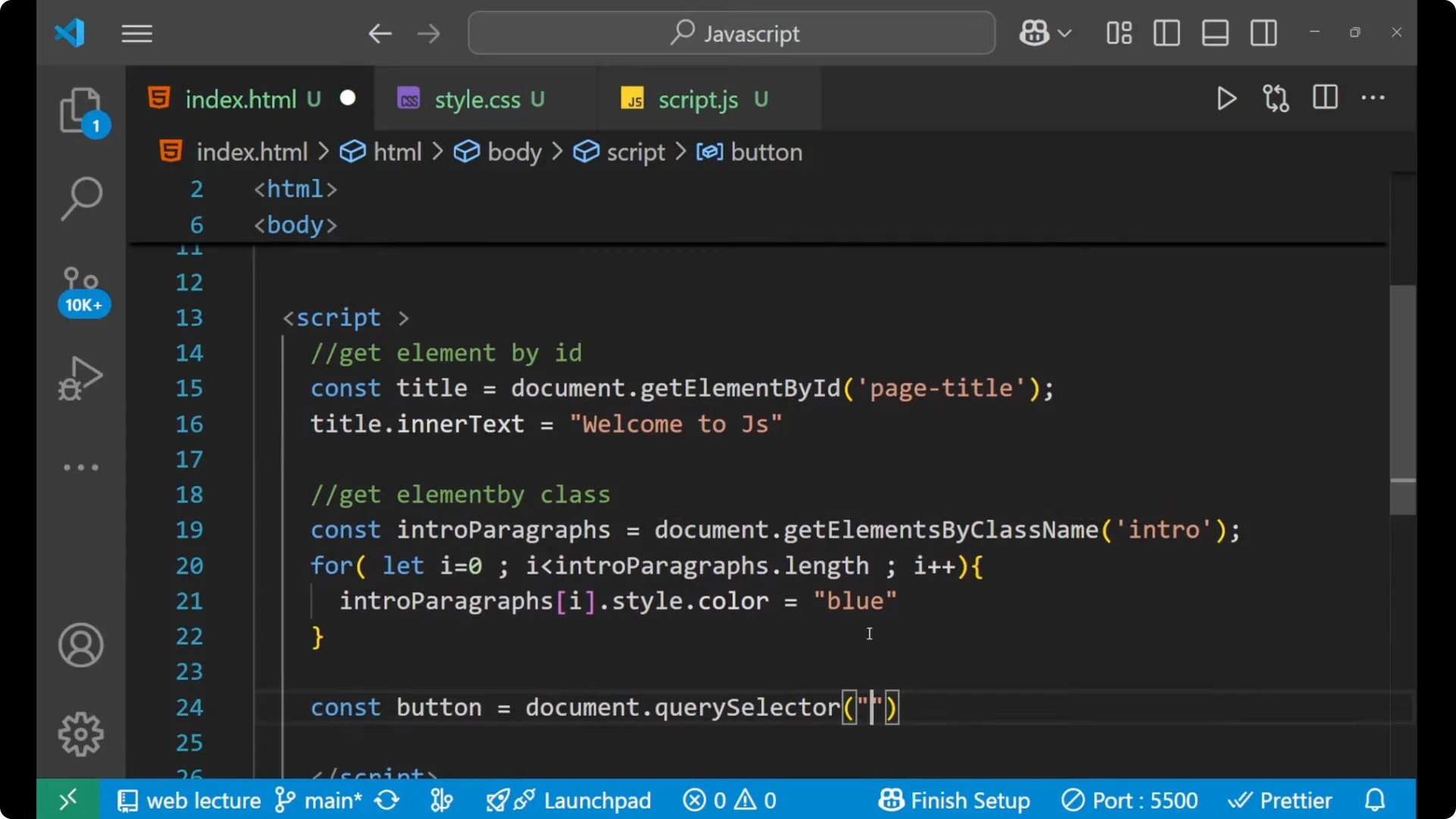
Use a dot for a class.
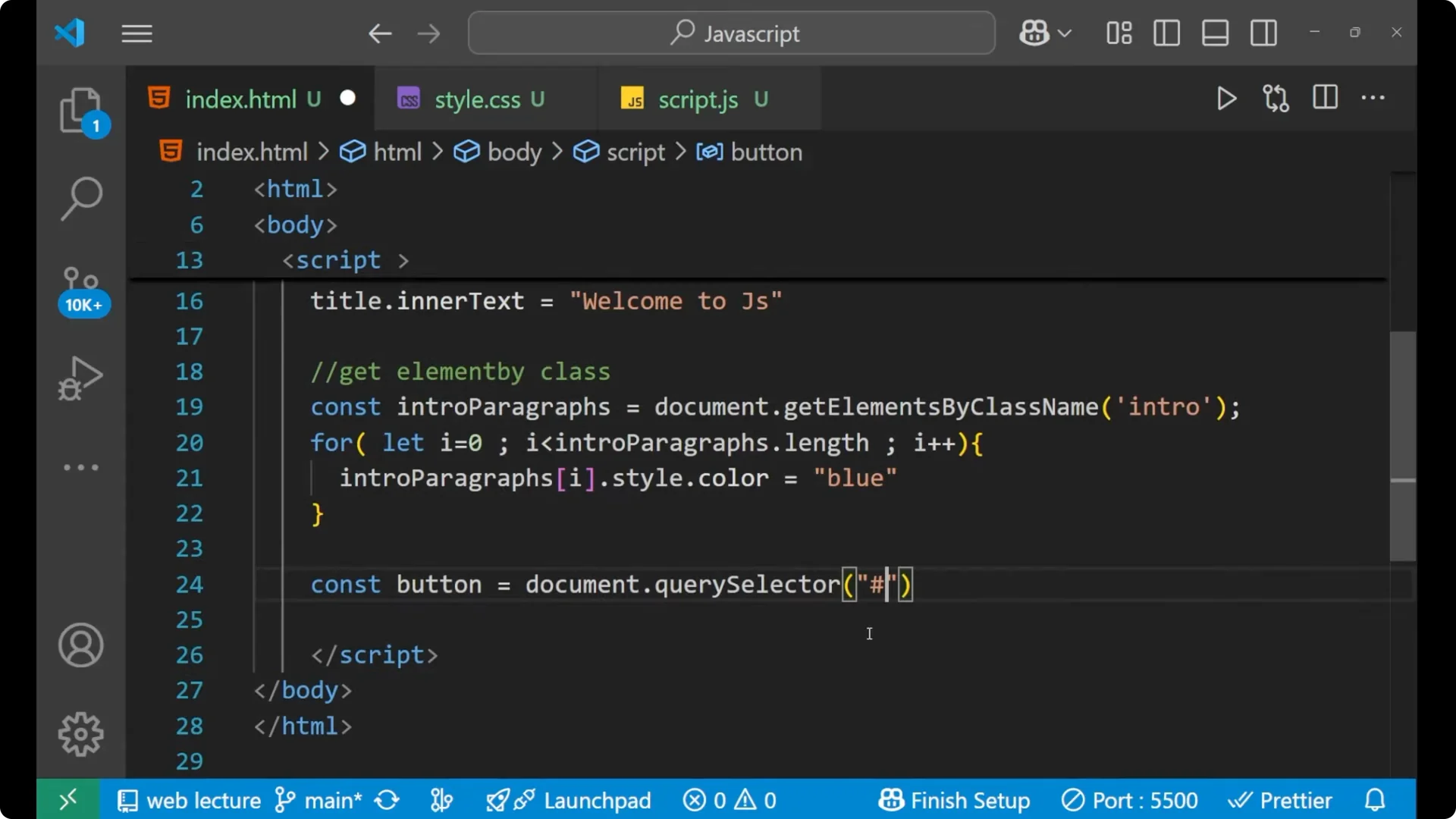
Since the button has an id of my-button, select it with #my-button.
const button = document.querySelector('#my-button');
// Successfully selected this particular button
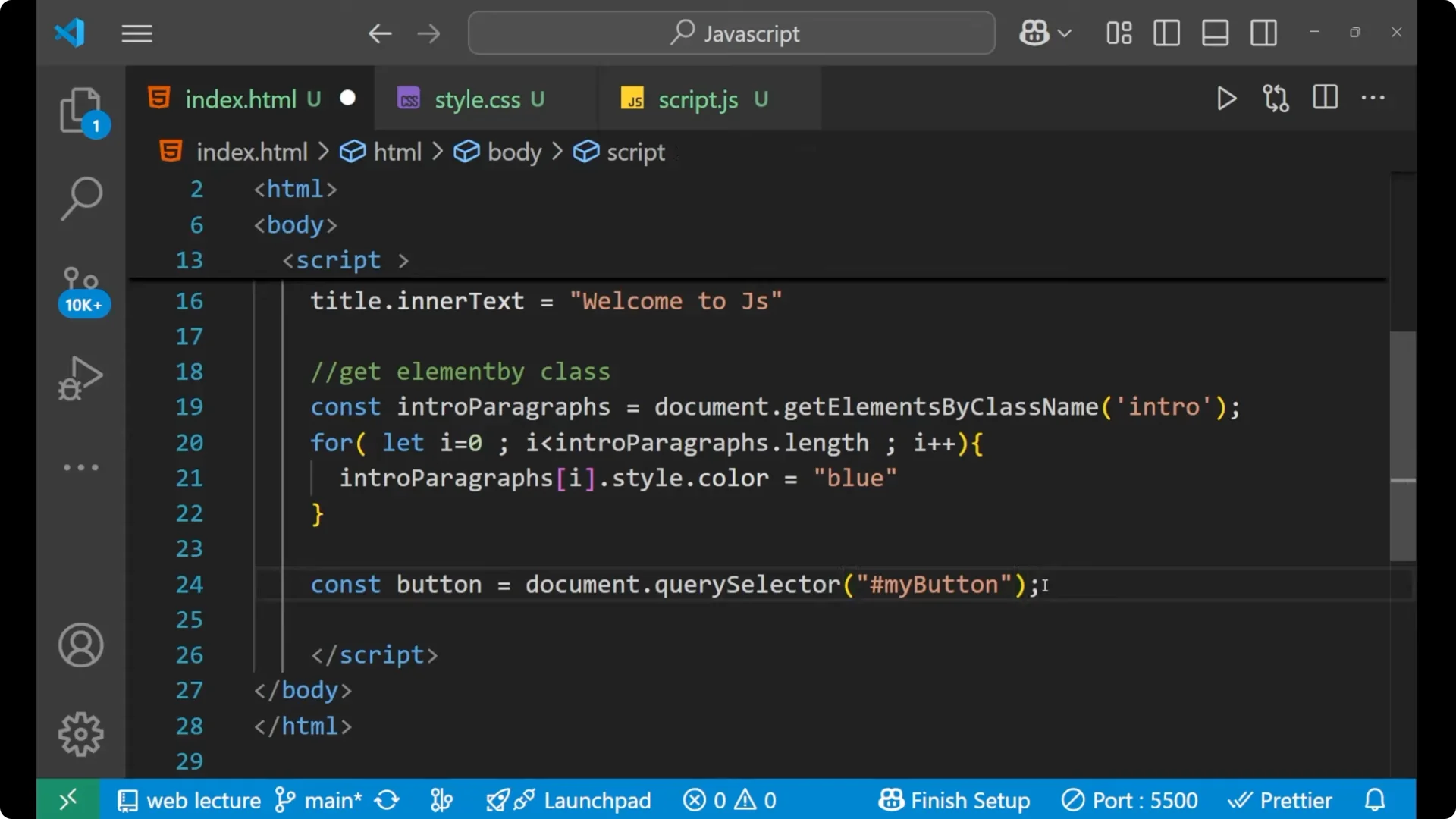
This gives you the first matching element for the selector you provide.
JavaScript DOM Selection with querySelectorAll
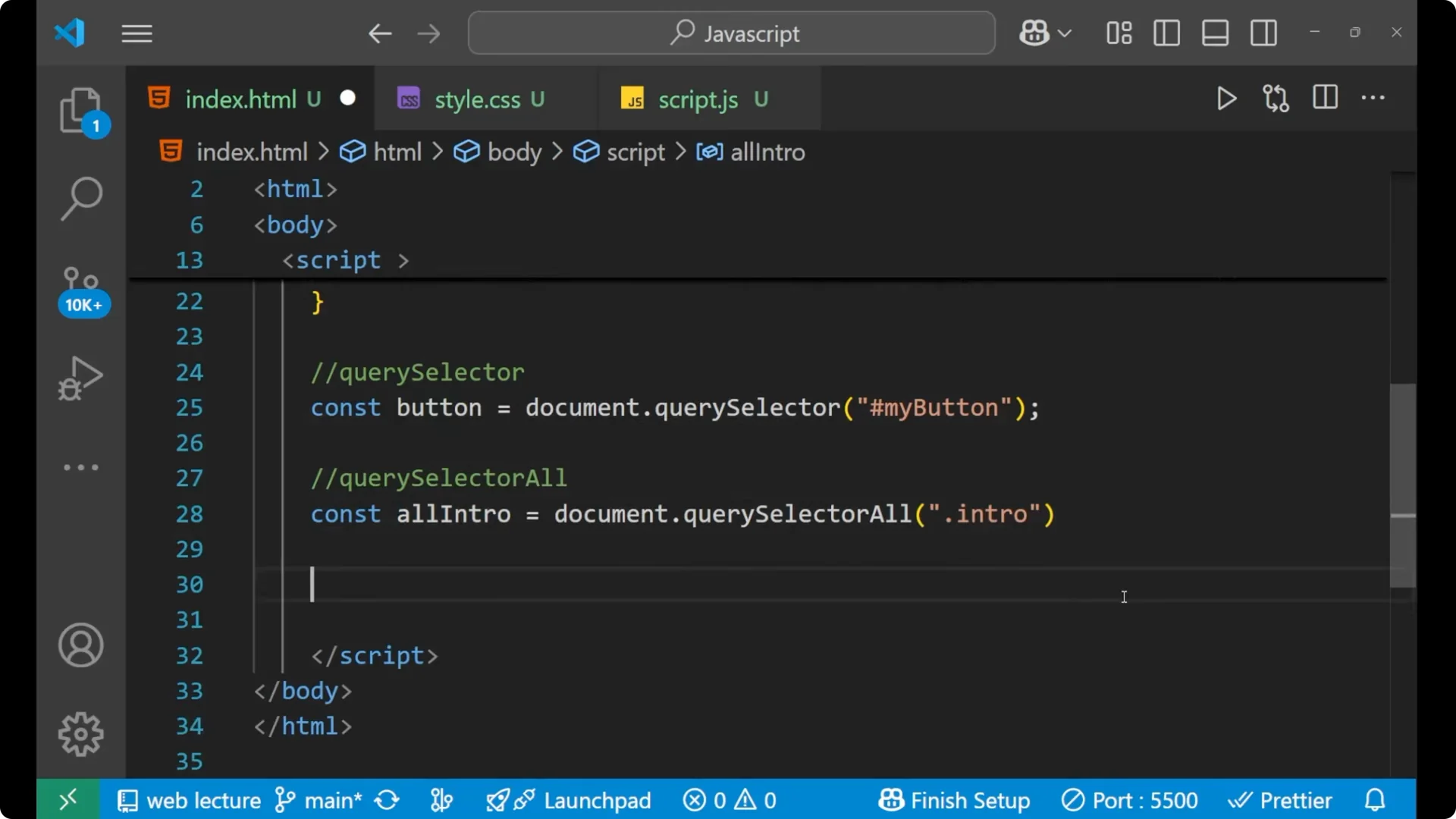
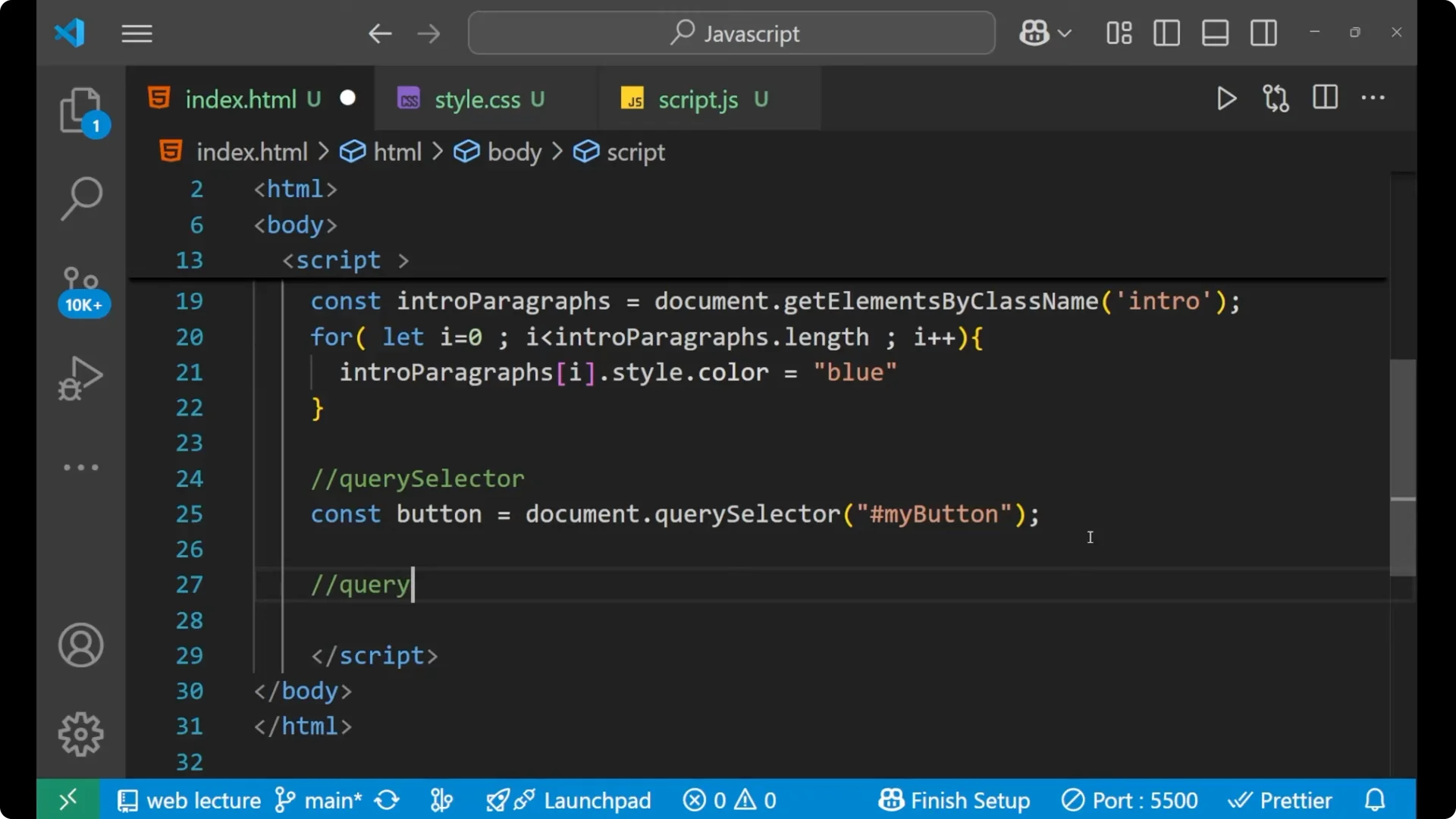 querySelectorAll
querySelectorAll selects all elements that match the CSS selector and returns a static NodeList, which supports
forEach.
Select all elements with the class intro.
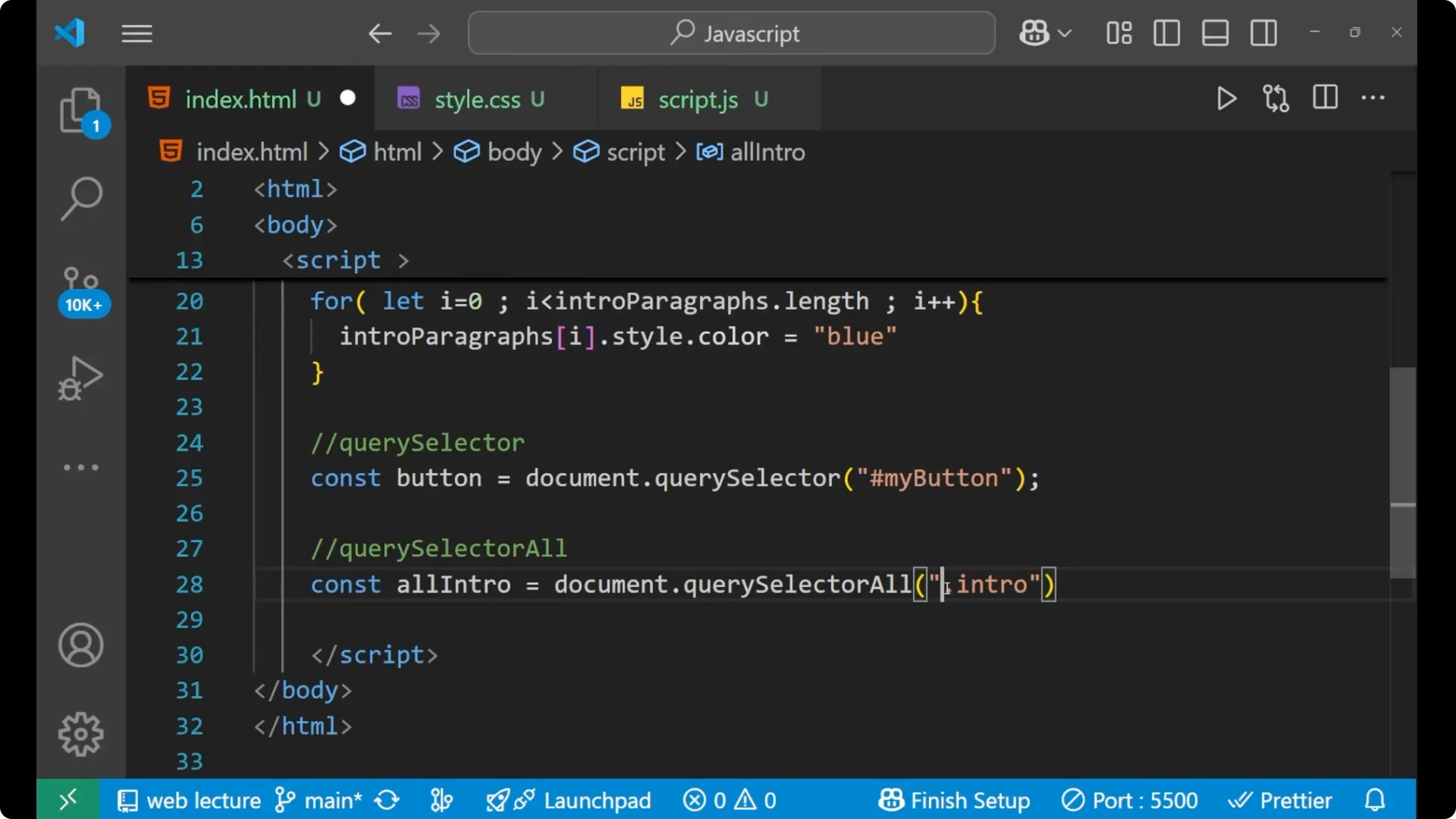
Loop each selected element.
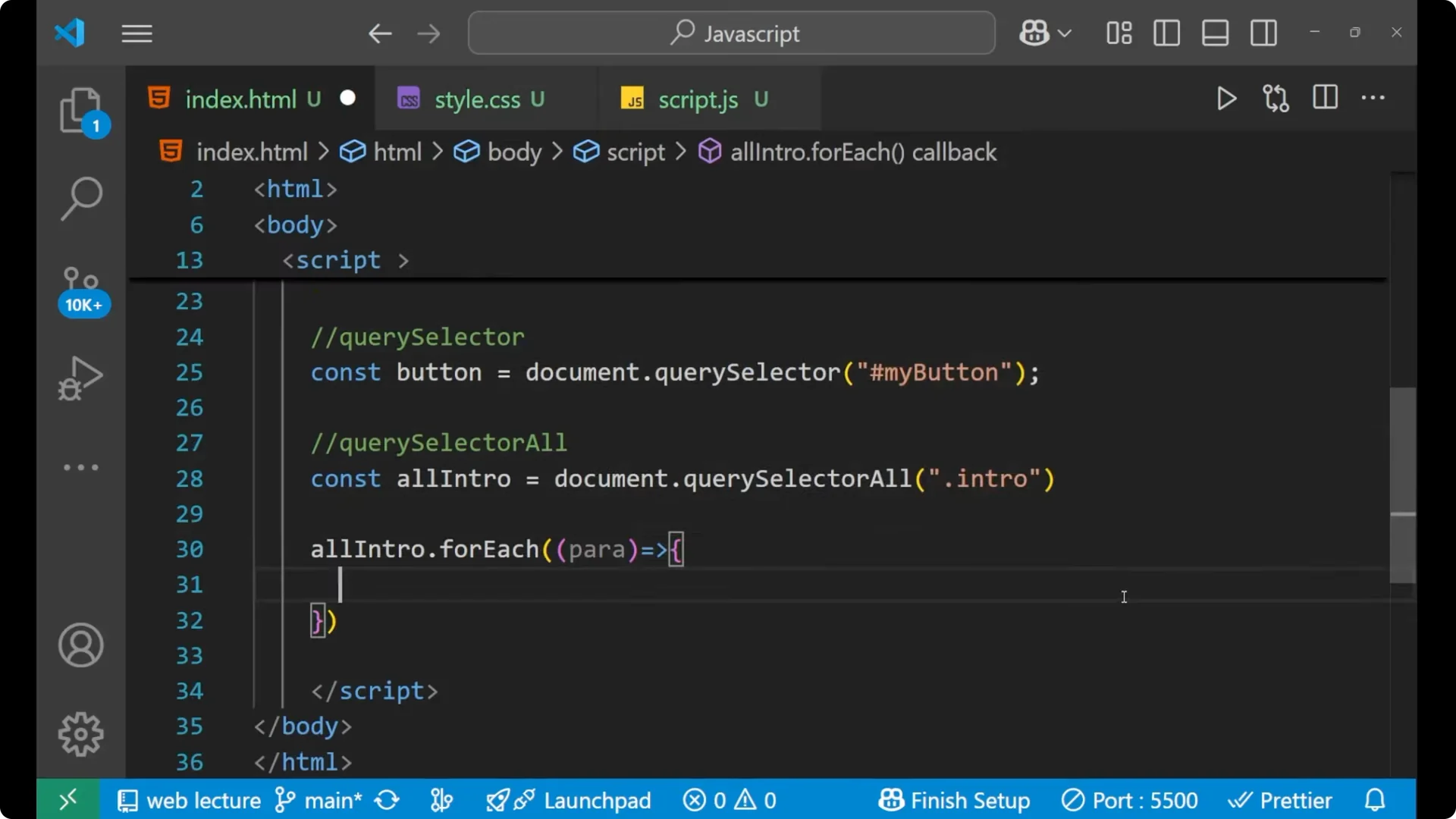
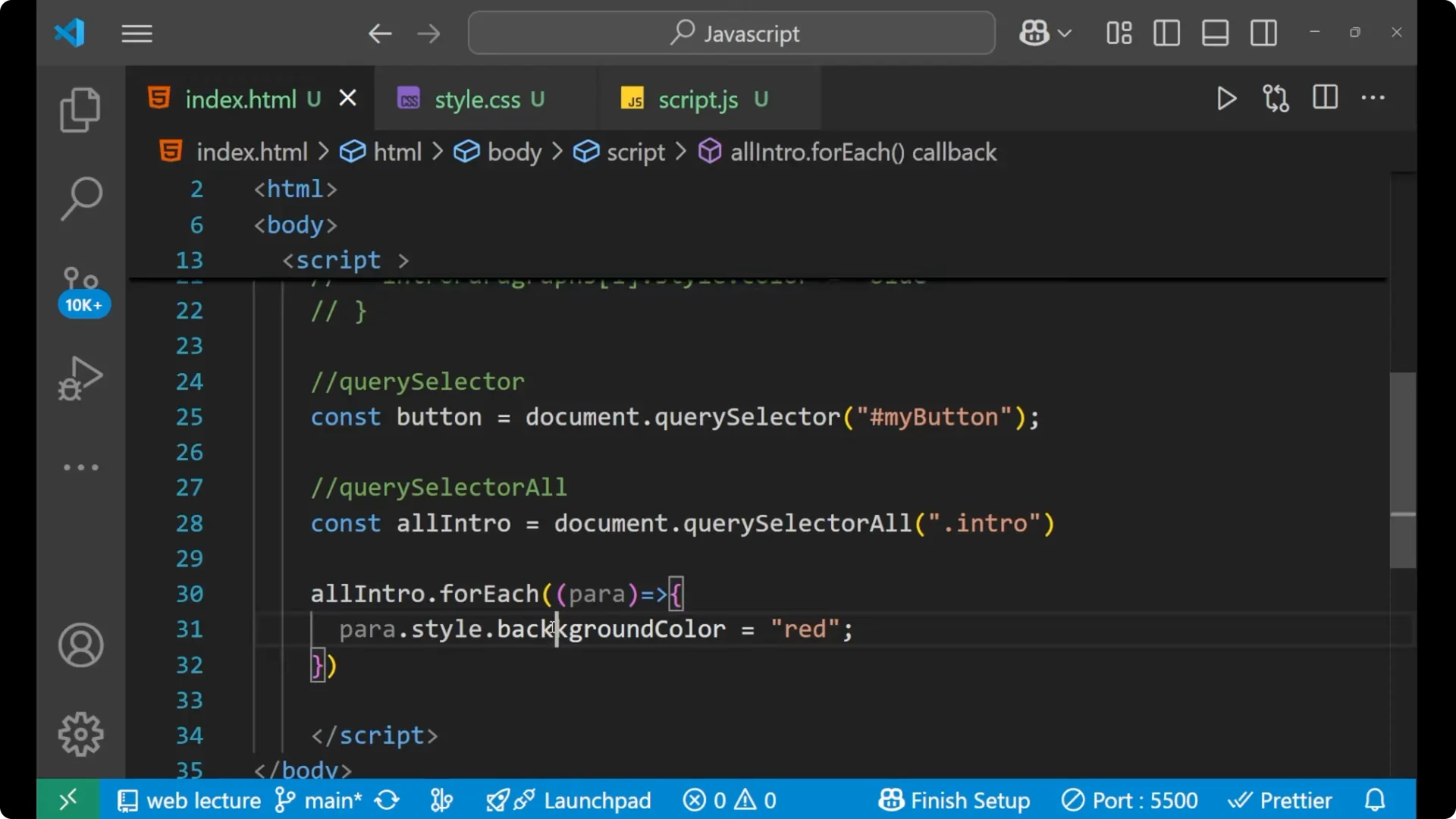
Change the background color. Use
backgroundColor, not background color.
const allIntro = document.querySelectorAll('.intro');
allIntro.forEach((para) => {
para.style.backgroundColor = 'red';
});
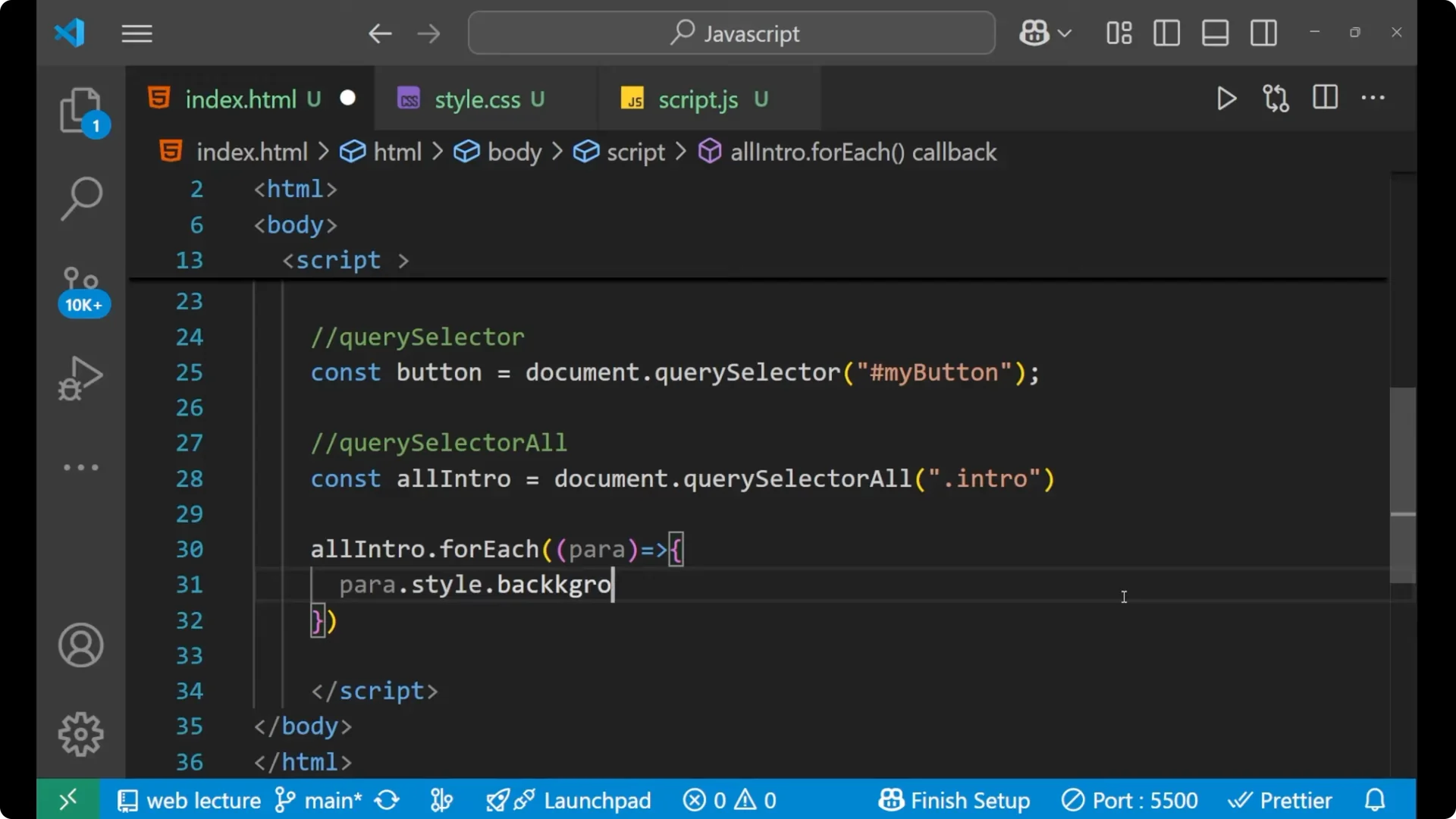
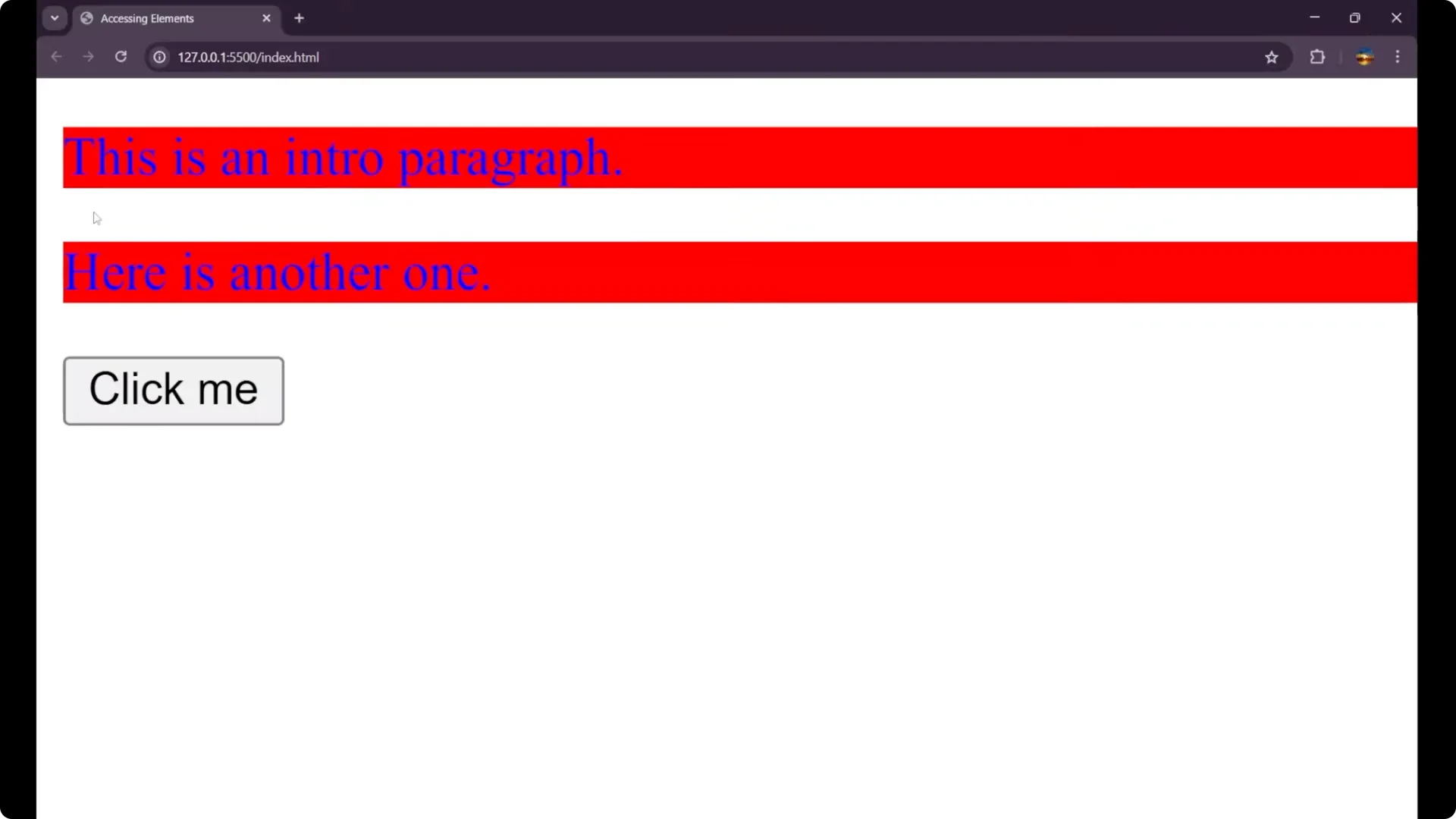
You can see both paragraphs now have blue text and a red background, showing how we changed the CSS with JavaScript and
DOM manipulation.
Complete Script Example
<h1 id="page-title">My Website</h1>
<p class="intro">This is the first intro paragraph.</p>
<p class="intro">This is the second intro paragraph.</p>
<button id="my-button">Press Me</button>
<script>
// By id
const title = document.getElementById('page-title');
title.innerText = 'Welcome to JS';
// By class name
const introParagraphs = document.getElementsByClassName('intro');
for (let i = 0; i < introParagraphs.length; i++) {
introParagraphs[i].style.color = 'blue';
}
// By CSS selector
const button = document.querySelector('#my-button');
// All by CSS selector
const allIntro = document.querySelectorAll('.intro');
allIntro.forEach((para) => {
para.style.backgroundColor = 'red';
});
</script>
Final Thoughts
We learned how to select HTML elements with JavaScript using
getElementById,
getElementsByClassName,
querySelector, and
querySelectorAll, and how to apply
DOM manipulation such as changing text and styles. These methods cover selecting by id, by class, and by flexible CSS selectors for single or multiple elements.

 The first method to access an element is by using the document object. The document represents the whole browser page. Then you use the getElementById method to get an element by its id.
The first method to access an element is by using the document object. The document represents the whole browser page. Then you use the getElementById method to get an element by its id.
 Select the element by id.
Select the element by id.
 Store it inside a variable.
Store it inside a variable.
 Change its inner text.
Change its inner text.

 Earlier it was My Website and now it is Welcome to JS. We can simply change the HTML part with the help of JavaScript by performing DOM manipulation and using document.getElementById.
Earlier it was My Website and now it is Welcome to JS. We can simply change the HTML part with the help of JavaScript by performing DOM manipulation and using document.getElementById.

 The second method is getting elements with the help of class using getElementsByClassName. For selecting elements with a class, this returns a live HTMLCollection, so we typically loop over it.
The second method is getting elements with the help of class using getElementsByClassName. For selecting elements with a class, this returns a live HTMLCollection, so we typically loop over it.
 Select all elements with the class intro.
Select all elements with the class intro.
 Store them in a variable.
Store them in a variable.
 Loop through the collection up to its length.
Loop through the collection up to its length.
 Change the style for each indexed element.
Change the style for each indexed element.

 It will select both paragraphs, because both have the class intro. You can apply conditions too, like styling odd or even indexes differently.
It will select both paragraphs, because both have the class intro. You can apply conditions too, like styling odd or even indexes differently.

 querySelector lets you select with CSS selectors. You can select by id or class using the same method.
querySelector lets you select with CSS selectors. You can select by id or class using the same method.
 Use a hash for an id.
Use a hash for an id.
 Use a dot for a class.
Use a dot for a class.
 Since the button has an id of my-button, select it with #my-button.
Since the button has an id of my-button, select it with #my-button.

 This gives you the first matching element for the selector you provide.
This gives you the first matching element for the selector you provide.

 querySelectorAll selects all elements that match the CSS selector and returns a static NodeList, which supports forEach.
querySelectorAll selects all elements that match the CSS selector and returns a static NodeList, which supports forEach.
 Select all elements with the class intro.
Select all elements with the class intro.
 Loop each selected element.
Loop each selected element.
 Change the background color. Use backgroundColor, not background color.
Change the background color. Use backgroundColor, not background color.

 You can see both paragraphs now have blue text and a red background, showing how we changed the CSS with JavaScript and DOM manipulation.
You can see both paragraphs now have blue text and a red background, showing how we changed the CSS with JavaScript and DOM manipulation.



