We are going to learn about methods that are available in JavaScript. These methods are used again and again in almost every kind of work that we do with JavaScript. I’m going to explain the data types and the methods associated with them.
Essential JavaScript Methods for Strings
Let’s say a string is “hello JavaScript”.
Inspecting and changing case
- length – used to get the length.
const str = "hello JavaScript";
console.log(str.length); // 16
- toUpperCase and toLowerCase – convert to upper or lower case.
console.log(str.toUpperCase()); // "HELLO JAVASCRIPT"
console.log(str.toLowerCase()); // "hello javascript"
Searching and positions
- includes – checks if the given text is present or not.
- indexOf – gets the index value of the text you are searching.
console.log(str.includes("Java")); // true
console.log(str.indexOf("Java")); // 6
console.log(str.slice(0, 5)); // "hello"
console.log(str.substring(6, 16)); // "JavaScript"
console.log(str.replace("JavaScript", "World")); // "hello World"
console.log(str.split(" ")); // ["hello", "JavaScript"]
console.log(str.split("a")); // ["hello J", "v", "Script"]
console.log(str.split("")); // ["h","e","l","l","o"," ",...]
const spaced = " hello JavaScript ";
console.log(spaced.trim()); // "hello JavaScript"
console.log(str.startsWith("hello")); // true
console.log(str.endsWith("Script")); // true
console.log(str.charAt(1)); // "e" (H is 0, E is 1)
console.log("hi".repeat(3)); // "hihihi"
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4];
arr.push(5); // [1,2,3,4,5]
arr.pop(); // [1,2,3,4]
arr.shift(); // [2,3,4]
arr.unshift(0); // [0,2,3,4]
const a = [0,1,2,3,4,5];
a.splice(2, 2); // removes two numbers from index 2 -> [0,1,4,5]
const b = [0,1,2,3,4,5];
console.log(b.slice(1, 3)); // [1,2]
const base = [1,2,3,4];
console.log(base.concat([5,6])); // [1,2,3,4,5,6]
console.log(base.join("-")); // "1-2-3-4"
Finding and checking
- indexOf – index value of an element.
- includes – boolean check if element is present.
const nums = [10, 20, 30];
console.log(nums.indexOf(20)); // 1
console.log(nums.includes(40)); // false
Map, filter, reduce
- map – performs iteration on all elements and returns another array based on your code.
- filter – filters out elements that meet a condition.
- reduce – takes all elements and gives a single value using accumulator and current value.
const data = [1,2,3,4];
const doubled = data.map(x => x * 2); // [2,4,6,8]
const evens = data.filter(x => x % 2 === 0); // [2,4]
const sum = data.reduce((acc, cur) => acc + cur, 0); // 10
find and findIndex
- find – find the particular element.
- findIndex – find the index of that element.
console.log(data.find(x => x > 2)); // 3
console.log(data.findIndex(x => x > 2)); // 2
every and some, reverse and sort
- every – boolean check that all elements satisfy a condition.
- some – boolean check that at least one element satisfies a condition.
- reverse – reverse the array.
- sort – sort based on a condition like b – a for descending order.
console.log(data.every(x => x > 0)); // true
console.log(data.some(x => x > 3)); // true
const r = [1,2,3];
r.reverse(); // [3,2,1]
const s = [3,1,4,2];
s.sort((a, b) => b - a); // [4,3,2,1]
flat and at
- flat – flatten the array.
- at – access element by index, supports negative index for last elements.
const nested = [1, [2, 3], [4, [5]]];
console.log(nested.flat()); // [1,2,3,4,[5]]
const last = [10, 20, 30].at(-1);
console.log(last); // 30
Essential JavaScript Methods for Objects
Keys, values, entries
- Object.keys – find keys.
- Object.values – find values.
- Object.entries – key-value pairs.
const obj = { name: "Alex", age: 25 };
console.log(Object.keys(obj)); // ["name","age"]
console.log(Object.values(obj)); // ["Alex",25]
console.log(Object.entries(obj)); // [["name","Alex"],["age",25]]
Assign, hasOwnProperty, delete
- Object.assign – assign properties from source objects to a target.
- hasOwnProperty – check if a key exists on the object.
- delete – remove a key.
const target = { a: 1 };
const source = { b: 2 };
Object.assign(target, source); // { a:1, b:2 }
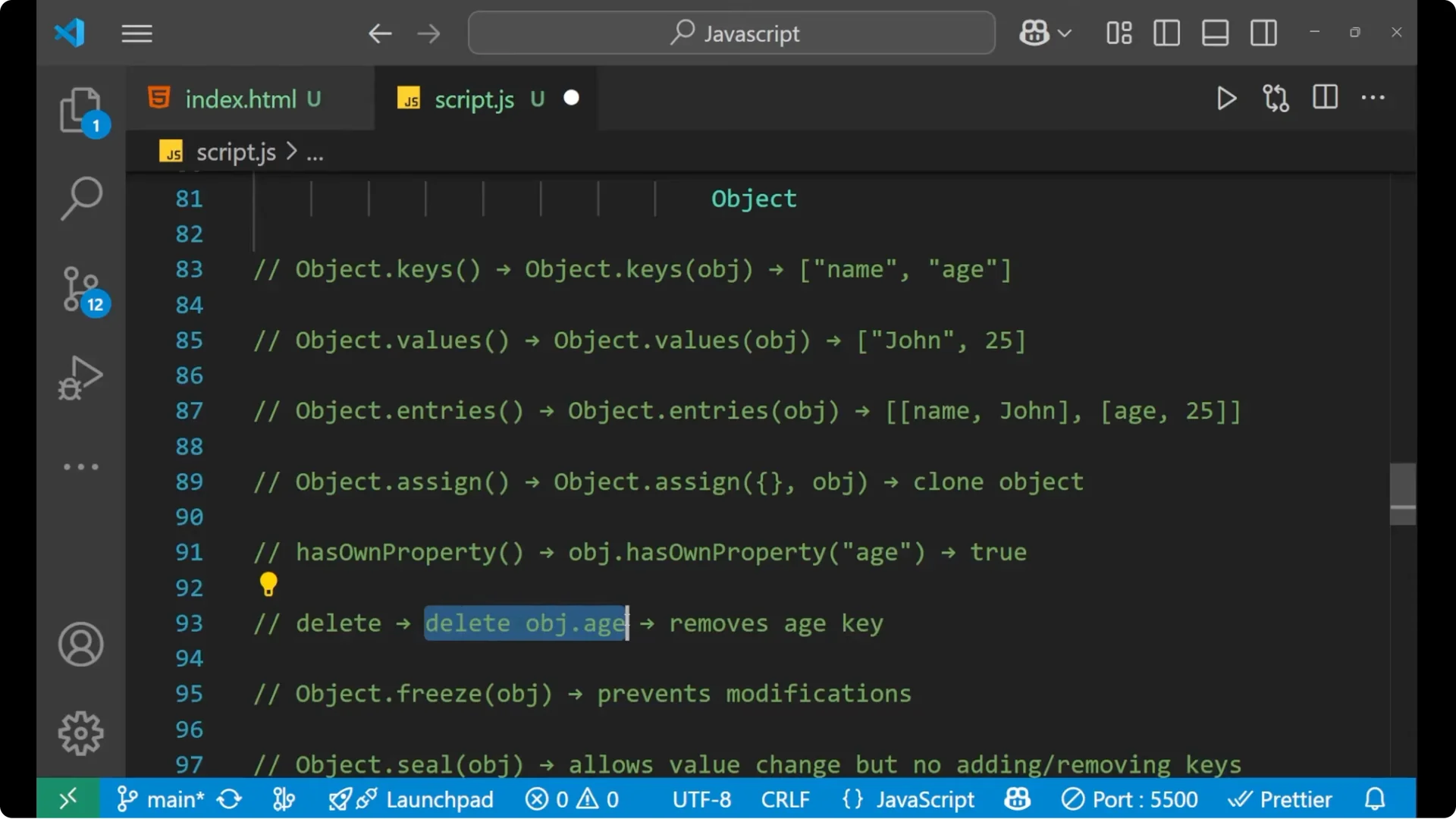
console.log(obj.hasOwnProperty("age")); // true
delete obj.age; // removes age key
Freeze and seal
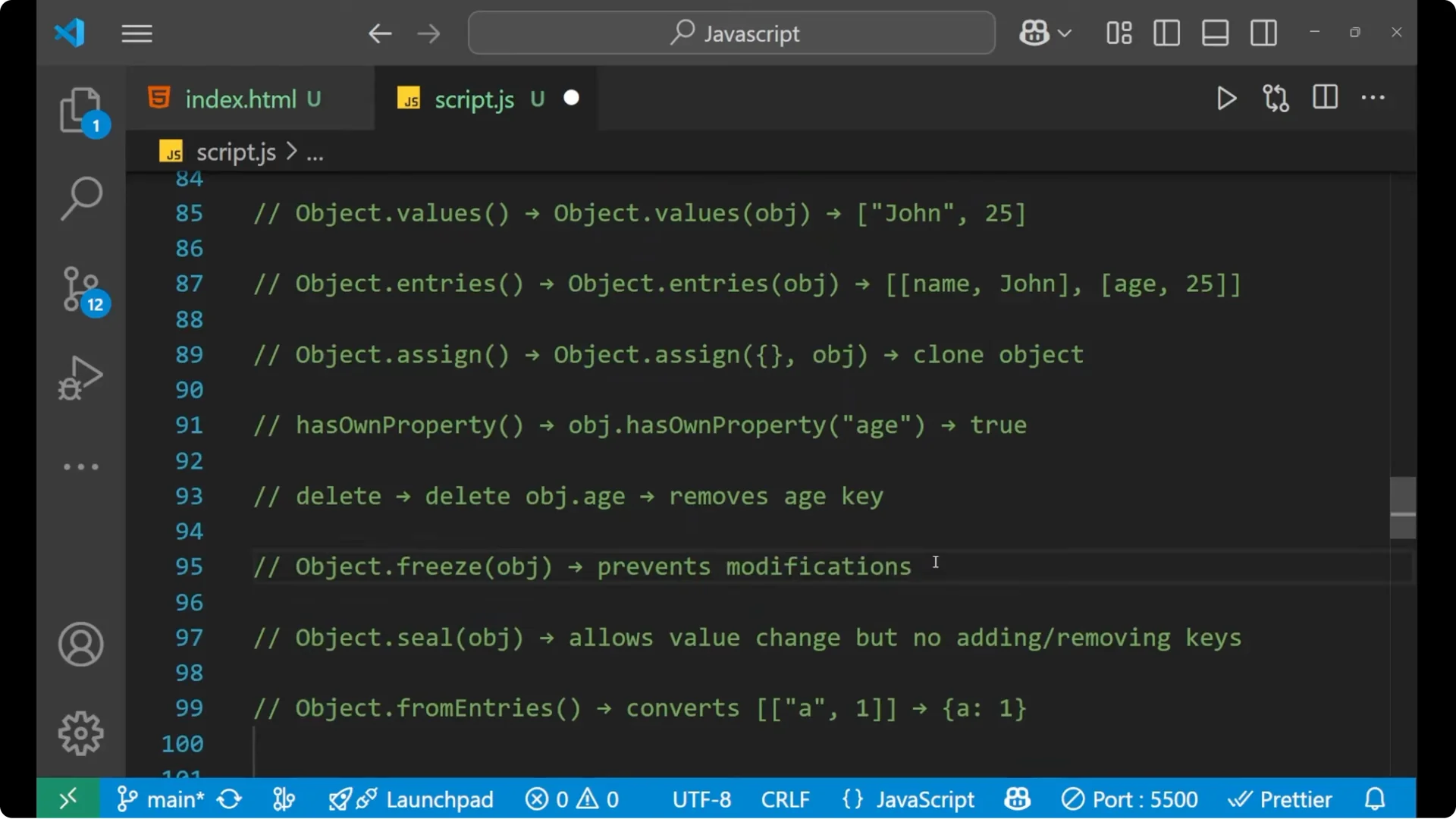
- Object.freeze – prevent modification. You cannot change, add, or remove keys.
- Object.seal – allow value change but not adding or removing keys.
const frozen = Object.freeze({ x: 1 });
// frozen.x = 2; // no effect
const sealed = Object.seal({ x: 1 });
sealed.x = 2; // OK
// sealed.y = 3; // not allowed
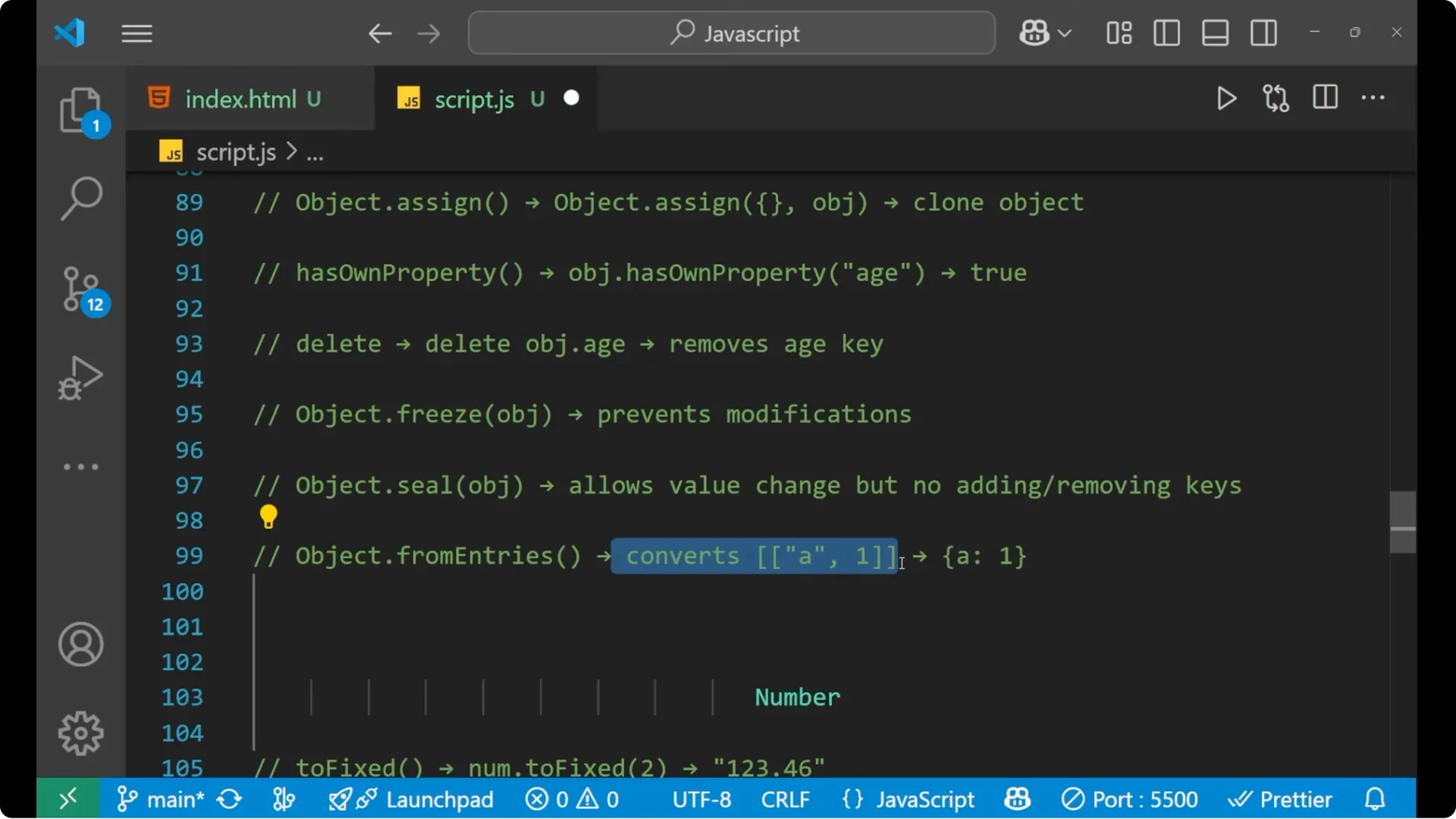
fromEntries
- Object.fromEntries – convert an array of pairs into an object.
const pairs = [["k", 1], ["v", 2]];
console.log(Object.fromEntries(pairs)); // { k:1, v:2 }
Essential JavaScript Methods for Numbers
Formatting and conversion
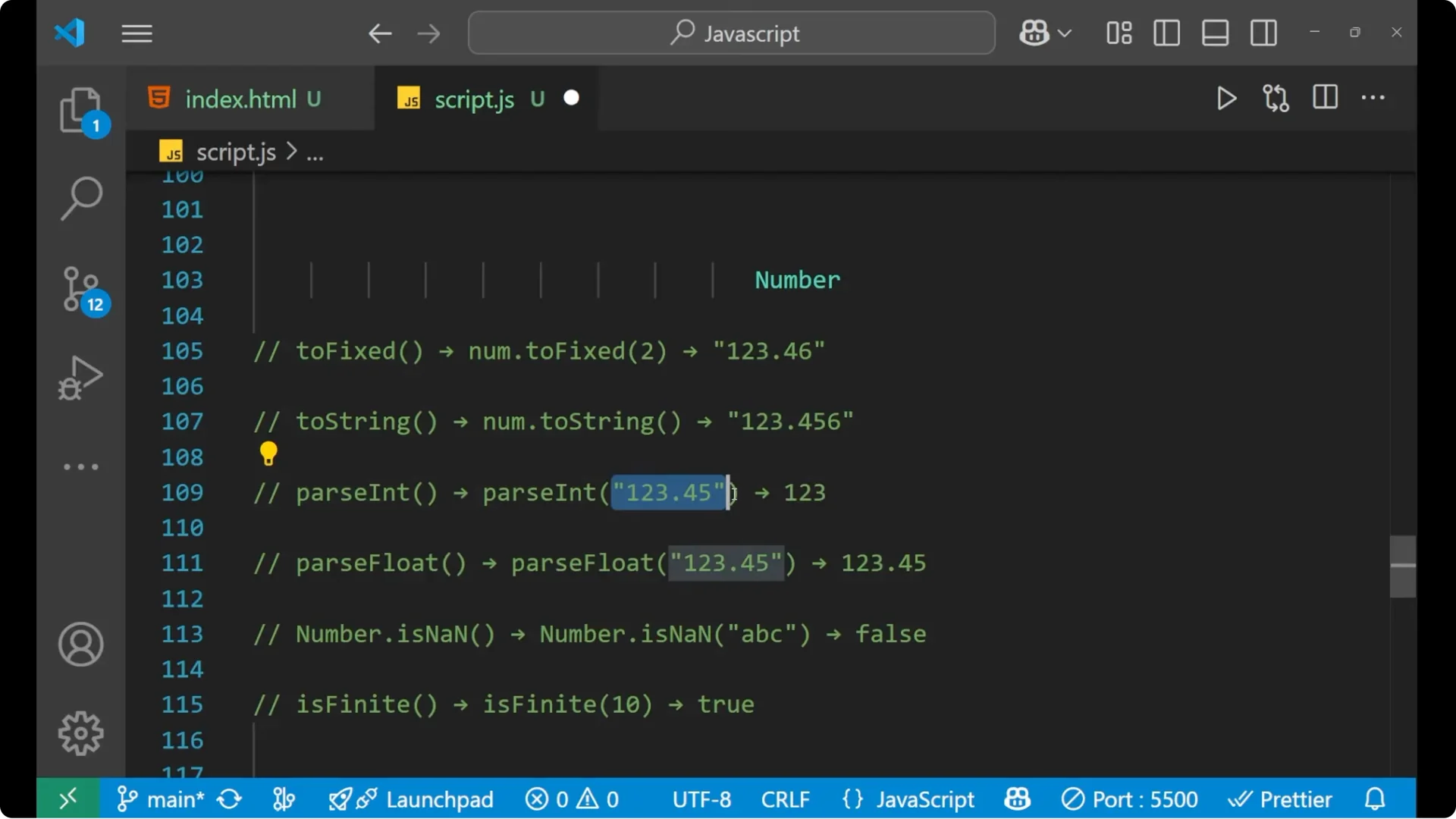
- toFixed – fix the decimal points.
- toString – convert number to string.
const n = 12.3456;
console.log(n.toFixed(2)); // "12.35"
console.log((123).toString()); // "123"
- parseInt – convert string to integer.
- parseFloat – convert string to floating number.
console.log(parseInt("12345", 10)); // 12345
console.log(parseFloat("123.045")); // 123.045
Validation
- isNaN – check if the value is Not-a-Number.
- isFinite – check if the number is finite.
console.log(isNaN("abc")); // true
console.log(isFinite(100 / 2)); // true
const d = new Date();
console.log(d.getFullYear()); // e.g., 2026
console.log(d.getMonth()); // 0-11
console.log(d.getDate()); // 1-31
console.log(d.getDay()); // 0-6 (Sun-Sat)
console.log(d.getHours()); // 0-23
console.log(d.getMinutes()); // 0-59
console.log(d.getSeconds()); // 0-59
console.log(d.toDateString()); // e.g., "Wed Feb 12 2026"
console.log(Math.max(1, 9, 3)); // 9
console.log(Math.min(1, 9, 3)); // 1
console.log(Math.floor(4.7)); // 4
console.log(Math.ceil(4.2)); // 5
console.log(Math.round(4.5)); // 5
console.log(Math.abs(-5)); // 5
console.log(Math.sqrt(9)); // 3
console.log(Math.random()); // 0 <= n < 1
console.log(Math.pow(2, 3)); // 8
console.log(2 ** 3); // 8
